Sincronización entre la videodeglución y la electromiografía de superficie en pacientes con afectación neurológica y síntomas de disfagia
Resumen
Introducción. La disfagia se define como la dificultad para movilizar la comida desde la boca hasta el estómago. La prueba diagnóstica para esta condición es la videofluoroscopia, la cual no es totalmente inocua pues utiliza radiación ionizante. La electromiografía de superficie registra la actividad eléctrica de los músculos de manera no invasiva, por lo que puede considerarse como una alternativa para evaluar la deglución y estudiar la disfagia.
Objetivo. Evaluar la relación entre los tiempos relativos de activación de los músculos implicados en la fase oral y faríngea de la deglución, con los movimientos registrados durante la videofluoroscopia.
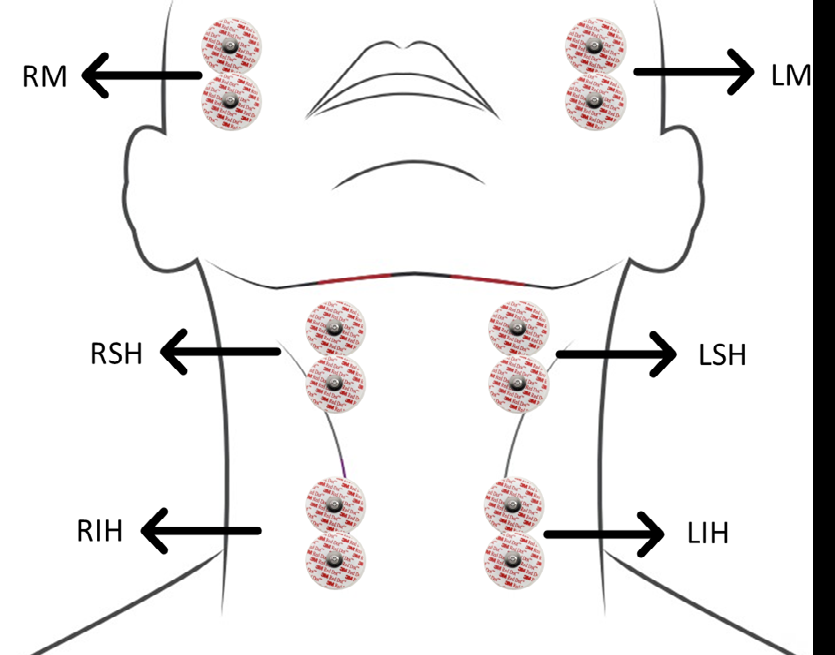
Materiales y métodos. Se analizaron las señales de la electromiografía de superficie de 10 pacientes neurológicos con síntomas de disfagia, captadas en forma simultánea con la videofluoroscopia. Se suministraron 5 ml de yogur y 10 ml de agua, y 3 g de galleta. Se estudiaron bilateralmente los grupos musculares maseteros, suprahioideos e infrahioideos. Se analizó el paso del bolo por la línea mandibular, las valleculas y el músculo cricofaríngeo, correlacionándolo con el tiempo inicial y el final de la activación de cada uno de los grupos musculares.
Resultados. El tiempo promedio de la fase faríngea fue de 0,89 ± 0,12 s. En la mayoría de los casos, hubo activación muscular antes del paso por la línea mandibular y las valleculas. La terminación de la actividad muscular parece corresponder al momento en que se completa el paso del bolo alimenticio por el músculo cricofaríngeo.
Conclusión. Se determinaron los tiempos de actividad muscular, la duración de la fase faríngea y la secuencia de la activación de los grupos musculares involucrados en la deglución, mediante electromiografía de superficie, validada con la videofluoroscopia.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Baijens LWJ, Clavé P, Cras P, Ekberg O, Forster A, Kolb GF, et al. European society for swallowing disorders - European union geriatric medicine society white paper: Oropharyngeal dysphagia as a geriatric syndrome. Clin Interv Aging. 2016;11:1403-28. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S107750
Cámpora HL, Falduti AL. Evaluación y tratamiento de las alteraciones de la deglución. Rev Am Med Respir Rev Am Med Resp. 2012;12:98-107.
Matsuo K, Palmer JB. Anatomy and physiology of feeding and swallowing: Normal and abnormal. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2008;19:691-707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmr.2008.06.001
Wirth R, Dziewas R, Beck AM, Clavé P, Hamdy S, Heppner HJ, et al. Oropharyngeal dysphagia in older persons – from pathophysiology to adequate intervention: A review and summary of an international expert meeting. Clin Interv Aging. 2016;11:189-208. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S97481
Hey C, Pluschinski P, Pajunk R, Almahameed A, Girth L, Sader R, et al. Penetration–aspiration: Is their detection in FEES® reliable without video recording? Dysphagia. 2015;30:418-22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-015-9616-3
Roy N, Stemple J, Merrill RM, Thomas L. Dysphagia in the elderly: Preliminary evidence of prevalence, risk factors, and socioemotional effects. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2007;116:858-65. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348940711601112
Kawashima K, Motohashi Y, Fujishima I. Prevalence of dysphagia among communitydwelling elderly individuals as estimated using a questionnaire for dysphagia screening. Dysphagia. 2004;19:266-71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-004-0013-6
Suárez-Escudero JC, Rueda-Vallejo ZV, Orozco-Duque AF. Disfagia y neurología: ¿una unión indefectible? Acta Neurológica Colomb. 2018;34:92-100.
Dudik JM, Coyle JL, Sejdic E. Dysphagia screening: Contributions of cervical auscultation signals and modern signal-processing techniques. IEEE Trans Human-Machine Syst. 2015;45:465-77. https://doi.org/10.1109/THMS.2015.2408615
Rommel N, Hamdy S. Oropharyngeal dysphagia: Manifestations and diagnosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13:49-59. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2015.199
Azola A, Greene L, Taylor-kamora I, Macrae P, Anderson C, Humbert IA. The relationship between submental surface electromyography and Hyo-Laryngeal kinematic measures of Mendelsohn maneuver duration. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2015;24:1-14. Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13:49-59. https://doi.org/10.1044/2015_JSLHR-S-14-0203
Chen DF. Dysphagia in the hospitalized patient. Hosp Med Clin. 2017;6:38-52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ehmc.2016.07.004
Fattori B, Giusti P, Mancini V, Grosso M, Barillari MR, Bastiani L, et al. Comparison between videofluoroscopy, fiberoptic endoscopy and scintigraphy for diagnosis of oro-pharyngeal dysphagia. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2016;36:395-402. https://doi.org/10.14639/0392-100X-829
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I. Neurophysiology of swallowing. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003;114:2226-44. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1388-2457(03)00237-2
Archer SK, Smith CH, Newham DJ. Surface electromyographic biofeedback and the effortful swallow exercise for stroke-related dysphagia and in healthy ageing. Dysphagia. 2021;36:281-92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-020-10129-8
Nazmi N, Rahman MAA, Yamamoto SI, Ahmad SA, Zamzuri H, Mazlan SA. A review of classification techniques of EMG signals during isotonic and isometric contractions. Sensors (Basel). 2016;16:1-28. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081304
Restrepo-Agudelo S. Methodology of sequential classification of non-invasive multichannel biosignals, oriented to automatic diagnosis of dysphagia (tesis). Medellín: Instituto Tecnológico Metropolitano; 2019.
Poorjavad M, Talebian S, Nakhostin Ansari N, Soleymani Z. Surface electromyographic assessment of swallowing function. Iran J Med Sci. 2017;42:194-200.
Sakai K, Nakayama E, Rogus-Pulia N, Takehisa T, Takehisa Y, Urayama KY, et al. Submental muscle activity and its role in diagnosing sarcopenic dysphagia. Clin Interv Aging. 2020;15:1991-9. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S278793
Wang CM, Chen JY, Chuang CC, Tseng WC, Wong AM, Pei YC. Aging-related changes in swallowing, and in the coordination of swallowing and respiration determined by novel noninvasive measurement techniques. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2015;15:736-44. https://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.12343
Suzuki M, Sasaki M, Kamata K, Nakayama A, Shibamoto I, Tamada Y. Swallowing pattern classification method using multichannel surface EMG signals of suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles. Adv Biomed Eng. 2020;9:10-20. https://doi.org/10.14326/abe.9.10
Shieh WY, Wang CM, Chang CS. Development of a portable non-invasive swallowing and respiration assessment device. Sensors (Basel). 2015;15:12428-53. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150612428
Shieh W-Y, Wang C-M, Cheng H-YK, Wang C-H. Using wearable and non-invasive sensors to verification, and clinical application. Sensors (Basel). 2019;19:2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112624
Sejdic E, Malandraki GA, Coyle JL. Computational deglutition: Using signal- and imageprocessing methods to understand swallowing and associated disorders. IEEE Signal Process Mag. 2019;36:138-46. https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2018.2875863
Giraldo-Cadavid LF, Gutiérrez-Achury AM, Ruales-Suárez K, Rengifo-Varona ML, Barros C, Posada A, et al. Validation of the Spanish version of the Eating Assessment Tool-10 (EAT-10spa) in Colombia. A blinded prospective cohort study. Dysphagia. 2016;31:398-406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9690-1
Belafsky PC, Mouadeb DA, Rees CJ, Pryor JC, Postma GN, Allen J, et al. Validity and reliability of the Eating Assessment Tool (EAT-10). Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2008;117:919-24. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348940811701210
Newman R, Vilardell N, Clavé P, Speyer R. Effect of bolus viscosity on the safety and efficacy of swallowing and the kinematics of the swallow response in patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia: White Paper by the European Society for Swallowing Disorders (ESSD). Dysphagia. 2016:31;232-49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-016-9696-8
Barrett KE, Barman SM, Boitano S, Brooks HL, editors. Gastrointestinal motility. En: Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology. Twenty-fifth ed. New York, NY: McGraw Hill; 2018. https://accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=1587§ionid=97165321
Restrepo-Agudelo S, Roldán-Vasco S, Ramírez-Arbeláez L, Cadavid-Arboleda S, Pérez-Giraldo E, Orozco-Duque AF. Improving surface EMG burst detection in infrahyoid muscles during swallowing using digital filters and discrete wavelet analysis. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2017;35:1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2017.05.001
Prosiegel M, Schelling A, Wagner-Sonntag E. Dysphagia and multiple sclerosis. Int MS J. 2004;11:22-31.
Daroff R, Jankovic J, Mazziotta J, Pomeroy S. Bradley’s neurology in clinical practice. 7th edition. Elsevier Inc.; 2015.
Pfeiffer RF. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2003;2:107-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(03)00307-7
Clavé P, Kraa M, Arreola V, Girvent M, Farré R, Palomera E, et al. The effect of bolus viscosity on swallowing function in neurogenic dysphagia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24:1385-94. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.03118.x
Guzmán MJ, Dulbecco M. Abordaje del paciente con disfagia. ACTA Gastroenterológica Latinoam. 2020;50:42-50.
Lee JT, Park E, Hwang JM, Jung T Du, Park D. Machine learning analysis to automatically measure response time of pharyngeal swallowing reflex in videofluoroscopic swallowing study. Sci Rep. 2020;10:1-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71713-4
Park D, Lee HH, Lee ST, Oh Y, Lee JC, Nam KW, et al. Normal contractile algorithm of swallowing related muscles revealed by needle EMG and its comparison to videofluoroscopic swallowing study and high resolution manometry studies: A preliminary study. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2017;36:81-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2017.07.007
Koyama Y, Ohmori N, Momose H, Kondo E, Yamada S, Kurita H. Detection of swallowing disorders using a multiple channel surface electromyography sheet: A preliminary study. J Dent Sci. 2021;16:160-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jds.2020.06.009
Ko JY, Kim H, Jang J, Lee JC, Ryu JS. Electromyographic activation patterns during swallowing in older adults. Sci Rep. 2021;11:1-10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-84972-6
Poorjavad M, Talebian S, Ansari NN, Soleymani Z. Surface electromyographic assessment of swallowing function. Iran J Med Sci. 2017;42:194-200.
Ertekin C. Electrophysiological evaluation of oropharyngeal dysphagia in ALS. Handb Clin Neurophysiol. 2004;4:487-512.
Algunos artículos similares:
- Jaime E. Castellanos, José I. Neissa, Sigrid J. Camacho, La infección con el virus del dengue induce apoptosis en células del neuroblastoma humano SH-SY5Y , Biomédica: Vol. 36 (2016): Suplemento 2, Enfermedades virales
- Jorge Enrique Machado-Alba, Luis Felipe Calvo-Torres, Andrés Gaviria-Mendoza, Juan Daniel Castrillón-Spitia, Patrones de prescripción de fármacos antiparkinsonianos en un grupo de pacientes de Colombia, 2015 , Biomédica: Vol. 38 Núm. 3 (2018)
- María del Pilar Olaya, Nadezdha Esperanza Vergel, José Luis López, María Dolores Viña, Mario Francisco Guerrero, El análogo de cumarina 3-metil-7H-furo[3,2-g]cromen-7-ona, un posible agente antiparkinsoniano , Biomédica: Vol. 39 Núm. 3 (2019)
Derechos de autor 2022 Biomédica

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |

























