Production and evaluation of the recombinant antigen TES-30 of Toxocara canis for the immunodiagnosis of toxocariasis
Abstract
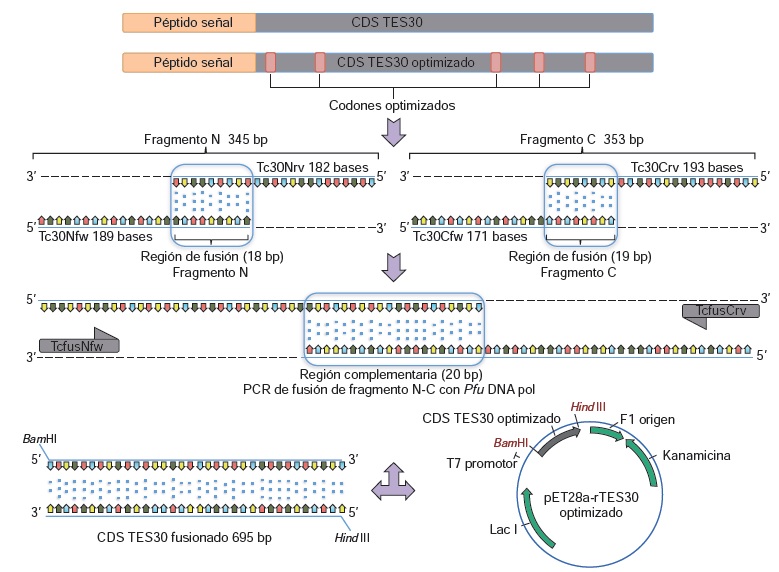
Introduction: Toxocara canis is a pathogenic nematode of canines which can be accidentally transmitted to humans. Although serology is the most important diagnostic tool for this zoonosis, diagnostic kits use crude excretion/secretion antigens, most of them being glycoproteins which are not species-specific and may cross-react with antibodies generated against other parasites. Objectives: To produce the rTES-30 recombinant antigen of Toxocara canis and evaluate it in the immunodiagnosis of toxocariasis. Materials and methods: The gene that codes for TES-30 was cloned in the expression vector pET28a (+) using single-stranded oligonucleotides united by PCR. The protein rTES-30 was purified by Ni2+ affinity chromotography. Seroreactivity of rTES-30 was evaluated by immunoblot. Given that there is no gold standard test, the behaviour of the antigen was compared with the method that is routinely used to immunodiagnose toxocariasis, i.e., the conventional ELISA technique using excretion/secretion antigens. Results: The rTES-30 was produced from an Escherichia coli LB culture which yielded 2.25 mg/L of the antigen with a purity of 95%. The results obtained showed 73% (46/63) concordance of reactivity between the rTES-30 immunoblot and the conventional ELISA, and 100% concordance with the nonreactive sera (21). Nineteen of the 21 sera positive for other parasitoses reacted with ELISA, while only seven of these were positive with the rTES-30 immunoblot. Concordance between the ELISA and the immunoblot was moderate (kappa coefficient: 0.575; 95% CI: 0.41- 0.74). Conclusions: The data presented show the potential of the rTES-30 inmunoblot for confirmation of possible ELISA positives, not only in epidemiological studies, but also as a candidate for the development of diagnostic tests for ocular toxocariasis in Colombia.
Downloads
References
Schantz PM, Glickman LT. Ascarids of cats and dogs: A public health and veterinary medicine problem. Bol Of Sanit Panam. 1983;94:571-86.
Botero JHM, Cañas L, Bravo JD, Lopera MON. Frecuencia de toxocarosis ocular en menores de edad remitidos al servicio de parasitología intestinal - Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Antioquia; 2000-2001. Estudio piloto. Acta Médica Colomb. 2001;26:11-20.
Despommier D. Toxocariasis: Clinical aspects, epidemiology, medical ecology, and molecular aspects. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2003;16:265-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/CMR.16.2.265-272.2003
Doligalska M, Donskow K. Environmental contamination with helminth infective stages implicated in water and foodborne diseases. Acta Microbiol Pol. 2003;52 (Suppl.): 45- 56.
Schwartzbrod J, Banas S. Parasite contamination of liquid sludge from urban wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci Technol. 2003;47:163-6.
Sprent JF. Observations on the development of Toxocara canis (Werner, 1782) in the dog. Parasitology. 1958;48: 184- 209.
Sprent JF. On the migratory behavior of the larvae of various Ascaris species in white mice. I. Distribution of larvae in tissues. J Infect Dis. 1952;90:165-76.
Nichols RL. The etiology of visceral larva migrans. I. Diagnostic morphology of infective second-stage Toxocara larvae. J Parasitol. 1956;42:349-62.
Magnaval JF, Glickman LT, Dorchies P, Morassin B. Highlights of human toxocariasis. Korean J Parasitol. 2001;39:1-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2001.39.1.1
Pawlowski Z. Toxocariasis in humans: Clinical expression and treatment dilemma. J Helminthol. 2001;75:299-305. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X01000464
Schantz PM, Glickman LT. Toxocaral visceral larva migrans. N Engl J Med. 1978;298:436-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM197802232980806
Minvielle MC, Niedfeld G, Ciarmela ML, Basualdo JA. Toxocariasis caused by Toxocara canis: Clinico-epidemiological aspects. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 1999;17:300-6.
Barriga OO. A critical look at the importance, prevalence and control of toxocariasis and the possibilities of immunological control. Vet Parasitol. 1988;29:195-234. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0304-4017(88)90126-4
Macpherson CN. The epidemiology and public health importance of toxocariasis: A zoonosis of global importance. Int J Parasitol. 2013;43:999-1008. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2013.07.004
Berrocal J. Prevalence of Toxocara canis in babies and in adults as determined by the ELISA test. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1980;78:376-413.
Cancrini G, Bartoloni A, Zaffaroni E, Guglielmetti P, Gamboa H, Nicoletti A, et al. Seroprevalence of Toxocara canis -IgG antibodies in two rural Bolivian communities. Parassitologia. 1998;40:473-5.
Alonso JM, Bojanich M V, Chamorro M, Gorodner JO. Toxocara seroprevalence in children from a subtropical city in Argentina. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2000;42:235-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0036-46652000000400010
García-Pedrique ME, Díaz-Suárez O, Estévez J, Cheng NR, Araújo- Fernández M, Castellano J, et al . Prevalencia de infección por Toxocara en pre-escolares de una comu- nidad educativa de El Moján, estado Zulia, Venezuela. Resultados preliminares. Invest Clin. 2004;45:347-54.
Fillaux J, Santillán G, Magnaval JF, Jensen O, Larrieu E, Sobrino-Becaria CD. Epidemiology of toxocariasis in a steppe environment: The Patagonia study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007;76:1144-7.
Espinoza YA, Huapaya PE, Roldán WH, Jiménez S, Abanto EP, Rojas CA, et al . Seroprevalence of human toxocariasis in Andean communities from the Northeast of Lima, Perú. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2010;52:31-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0036-46652010000100005
Correa M, González M, D´Alessandro A. Primer caso colombiano de toxocariasis. Breve actualización del síndrome de la larva migrans visceral. Antioquia Méd. 1966;16:489-97.
Agudelo C, Villareal E, Cáceres E, López C, Eljach J, Ramírez N, et al . Human and dogs Toxocara canis infection in a poor neighborhood in Bogotá. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1990;85:75-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0074-02761990000100012
Acero M, Muñoz M, Flórez A, Nicholls R. Seroprevalencia de anticuerpos contra Toxocara canis y factores de riesgo en niños. Ciudad Bolívar, Bogotá, DC, 2001. Biomédica. 2001;21:256-63. http://dx.doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.v21i3.1116
Flórez A, Correa M. Situación de la toxocariasis en Colombia, enero de 1996, enero de 2002. Inf Quinc Epidemiol Nac. 2002;7:375-84. Fecha de consulta: 10 de julio de 2015. Disponible en: http://www.ins.gov.co/iqen/IQUEN/IQEN%20vol%2007%202002%20num%2020.pdf.
Fillaux J, Magnaval JF. Laboratory diagnosis of human toxocariasis. Vet Parasitol. 2013;193:327-36. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.12.028
Roldán WH, Espinoza YA, Huapaya PE, Jiménez S. Diagnóstico de la toxocarosis humana. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Pública. 2010;27:613-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1726-46342010000400019
Moreira GMSG, Telmo P de L, Mendonça M, Moreira ÂN, McBride AJA, Scaini CJ, et al . Human toxocariasis: Current advances in diagnostics, treatment, and inter-ventions. Trends Parasitol. 2014;30:456-64. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2014.07.003
Lee S-U, Yu J-R, Huh S. Ultrastructural localization of Toxocara canis larval antigen reacted with a seropositive human serum. Korean J Parasitol. 2009;47:65–8. http://dx.doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2009.47.1.65
Yamasaki H, Araki K, Lim PK, Zasmy N, Mak JW, Taib R, et al. Development of a highly specific recombinant Toxocara canis second-stage larva excretory-secretory antigen for immunodiagnosis of human toxocariasis. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:1409-13.
Mohamad S, Azmi NC, Noordin R. Development and evaluation of a sensitive and specific assay for diagnosis of human toxocariasis by use of three recombinant antigens (TES-26, TES-30USM, and TES-120). J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:1712-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00001-09
Noordin R, Smith HV, Mohamad S, Maizels RM, Fong MY. Comparison of IgG-ELISA and IgG4-ELISA for Toxocara serodiagnosis. Acta Trop. 2005;93:57-62. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2004.09.009
Sambrook J, W Russell D. Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harb Lab Press; 2001. p. 999.
Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970;227:680-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Maizels RM, de Savigny D, Ogilvie BM. Characterization of surface and excretory-secretory antigens of Toxocara canis infective larvae. Parasite Immunol. 1984;6:23-37.
Badley JE, Grieve RB, Bowman DD, Glickman LT, Rockey JH. Analysis of Toxocara canis larval excretory-secretory antigens: Physicochemical characterization and antibody recognition. J Parasitol. 1987;73:593-600. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3282142
Tetteh KK, Loukas A, Tripp C, Maizels RM. Identification of abundantly expressed novel and conserved genes from the infective larval stage of Toxocara canis by an expressed sequence tag strategy. Infect Immun. 1999;67:4771-9.
Wickramasinghe S, Yatawara L, Nagataki M, Takamoto M, Watanabe Y, Rajapakse RP, et al . Development of a highly sensitive IgG-ELISA based on recombinant arginine kinase of Toxocara canis for serodiagnosis of visceral larva migrans in the murine model. Parasitol Res. 2008;103:853-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1067-4
Norhaida A, Suharni M, Liza AT, Tuda J, Rahmah N. rTES-30USM: Cloning via assembly PCR, expression, and evaluation of usefulness in the detection of toxocariasis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2008;102:151-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1179/136485908X252250
Maizels RM, Kennedy MW, Meghji M, Robertson BD, Smith HV. Shared carbohydrate epitopes on distinct surface and secreted antigens of the parasitic nematode Toxocara canis . J Immunol. 1987;139:207-14.
Meghji M, Maizels RM. Biochemical properties of larval excretory-secretory glycoproteins of the parasitic nematode Toxocara canis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986;18:155-70. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0166-6851(86)90035-6
Some similar items:
- María Isabel Giraldo, Nora Lizeth García, Jhon Carlos Castaño, Prevalence of intestinal helminths in dogs from Quindío Province. , Biomedica: Vol. 25 No. 3 (2005)
- Iman Fathy Abou-El-Naga, Developmental stages and viability of Toxocara canis eggs outside the host , Biomedica: Vol. 38 No. 2 (2018)
- Elizabeth Lara-Reyes, Israel A. Quijano-Hernández , Roger I. Rodríguez-Vivas, Javier Del Ángel-Caraza, José Simón Martínez-Castañeda, Factors associated with endoparasites and ectoparasites in domiciled dogs in the metropolitan area of Toluca, México , Biomedica: Vol. 41 No. 4 (2021)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























