Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as an early predictor of delayed graft function
Abstract
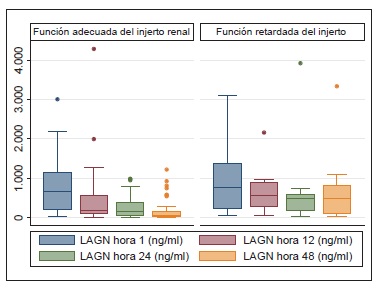
Introduction: Delayed graft function occurs in about 20 to 50 percent of kidney transplants. Objective: To describe the behavior of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGALu) in deceased-donor renal transplant recipients and to compare this indicator with the percentage of creatinine decrease (PdC) for the early detection of delayed graft function. Materials and methods: NGALu levels were evaluated in a prospective cohort in the first, 12th, 24th and 48th hours after kidney transplant, and compared with the daily PdC until day 5. Results: We included 79 patients in the study. Delayed graft function occurred in 13 patients (16.5%), and five patients (6.3%) required dialysis in the first week. NGALu levels at all cut-off points were higher in patients with delayed graft function (p=0.526, p=0.049, p=0.032, and p=0.001). NGALu levels above 120 ng/ml at 48 hours predicted delayed graft function with a sensitivity of 75% and a specificity of 71%. A PdC of 59.5% best discriminated the delayed graft function, with a sensitivity of 92% and a specificity of 83% at 48 hours. Using logistic regression for the adjusted delayed graft function, the only significant values to predict it were those of PdC. Conclusions: NGALu levels measured at 48 hours after renal transplantation predicted delayed graft function, including the need for dialysis; however, this marker was not superior to the PdC for early detection.
Downloads
References
Cohen DJ, Vella JV. Transplantation. NephSAP. 2013;12: 309-99.
Rostami Z, Nikpoor M, Einollahi B. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) for early diagnosis of acute kidney injury in renal transplant recipients. Nephrourol Mon. 2013;5:745-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.5812/numonthly.9385
Siedlecki A, Irish W, Brennan DC. Delayed graft function in the kidney transplant. Am J Transplant. 2011;11:2279-96. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03754.x
Cohen DJ, Vella JoV. NephSAP (Nephrology Self-Assessment Program). Transplantation. 2011;10:531-61.
Hall IE, Yarlagadda SG, Coca SG, Wang Z, Doshi M, Devarajan P, et al . IL-18 and urinary NGAL predict dialysis and graft recovery after kidney transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21:189-97. http://dx.doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2009030264
Hollmen ME, Kyllönen LE, Inkinen KA, Lalla ML, Salmela KT. Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is a marker of graft recovery after kidney transplantation. Kidney Int. 2011;79:89-98. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ki.2010.351
Lin M, Li L, Li L, Pokhrel G, Qi G, Rong R, et al . The protective effect of baicalin against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014;14:19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-14-19
Choi HM, Park KT, Lee JW, Cho E, Jo SK, Cho WY, et al . Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predicts graft outcome up to 1 year after kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2013;45:122-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2012.05.080
Yarlagadda SG, Coca SG, Formica RN, Poggio ED, Parikh CR. Association between delayed graft function and allograft and patient survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:1039-47. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfn667
Rahimzadeh N, Otukesh H, Hoseini R, Sorkhi H, Otukesh M, Hoseini S, et al . Are serum and urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predictive of renal graft function in short term? Pediatr Transplant. 2012;16:796-802. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3046.2012.01770.x
Yarlagadda SG, Coca SG, Garg AX, Doshi M, Poggio E, Marcus RJ, et al . Marked variation in the definition and diagnosis of delayed graft function: A systematic review. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:2995-3003. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfn158
Parikh CR, Jani A, Mishra J, Ma Q, Kelly C, Barasch J, et al . Urine NGAL and IL-18 are predictive biomarkers for delayed graft function following kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2006;6:1639-45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2006.01352.x
Devarajan P. NGAL in acute kidney injury: From serendipity to utility. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;52:395-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.07.008
Bataille A, Abbas S, Semoun O, Bonnet F, Rescherigon M, Abboud I, et al . Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in kidney transplantation and early renal function. Transplantation. 2011;92:1024-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e318230c079
. Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Schlattmann P, Haase-Fielitz A. Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;54:1012-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.07.020
Kim SC, Page EK, Knechtle SJ. Urine proteomics in kidney transplantation. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2014;28:15-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.trre.2013.10.004
Heyne N, Kemmner S, Schneider C, Nadalin S, Königsrainer A, Häring HU. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin accurately detects acute allograft rejection among other causes of acute kidney injury in renal allograft recipients. Transplantation. 2012;93:1252-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e31824fd892
Helmersson-Karlqvist J, Ärnlöv J, Larsson A. Day-to-day variation of urinary NGAL and rational for creatinine correction. Clin Biochem. 2013;46:70-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.09.022
Bolignano D, Donato V, Coppolino G, Campo S, Buemi A, Lacquaniti A, et al . Neutrophil gelatinase�associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a marker of kidney damage. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;52:595-605. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.01.020
Fonseca I, Oliveira JC, Almeida M, Cruz M, Malho A, Martins LS, et al . Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in kidney transplantation is an early marker of graft dysfunction and is associated with one-year renal function. J Transplant. 2013;2013:650123. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/650123
Kaufeld JK, Gwinner W, Scheffner I, Haller HG, Schiffer M. Urinary NGAL ratio is not a sensitive biomarker for monitoring acute tubular injury in kidney transplant patients: NGAL and ATI in renal transplant patients. J Transplant. 2012;2012:563404. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/563404.
Vanmassenhove J, Vanholder R, Nagler E, Biesen W Van. Urinary and serum biomarkers for the diagnosis of acute kidney injury: An in-depth review of the literature. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2013;28:254-73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfs380
Singer E, Marko L, Paragas N, Barasch J, Dragun D, Muller N, et al . Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: Pathophysiology and clinical applications. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2013;207:663-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/apha.12054
Glassford NJ, Schneider AG, Xu S, Eastwood GM, Young H, Peck L, et al . The nature and discriminatory value of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in critically ill patients at risk of acute kidney injury. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39:1714-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00134-013-3040-7
Adiyanti SS, Loho T. Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) biomarker. Acta Med Indones. 2012;44:246-55.
Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M, Zahedi K, Yang J, et al . Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:2534-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.ASN.0000088027.54400.C6
Magnusson NE, Hornum M, Jørgensen KA, Hansen JM, Bistrup C, Feldt-Rasmussen B, et al . Plasma neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) is associated with kidney function in uraemic patients before and after kidney transplantation. BMC Nephrol. 2012;13:1-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2369-13-8.
Mishra J, Ma Q, Kelly C, Mitsnefes M, Mori K, Barasch J, et al . Kidney NGAL is a novel early marker of acute injury following transplantation. Pediatr Nephrol. 2006;21:856-63. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00467-006-0055-0
Lee EY, Kim MS, Park Y, Kim HS. Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and interleukin-18 as predictive biomarkers for delayed graft function after kidney transplantation. J Clin Lab Anal. 2012;26:295-301. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcla.21520
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























