Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Report of a fatal case and analysis of predictive factors of a poor prognosis
Abstract
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome is an illness with multiple causes and distinctive clinicalradiological characteristics that should be known by intensivists and emergency room physicians for a timely diagnosis and treatment. A fatal case of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome is presented, and the risk factors related to the outcome are identified.
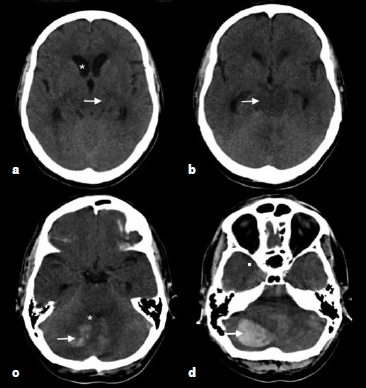
A 60-year-old man without a relevant medical history arrived at the emergency room presenting with depressed consciousness, seizures, and high blood pressure. Tomographic images revealed a posterior cerebellar hematoma. Resonance images showed ischemic zones, vasogenic edema from the thalamus to the brain stem, middle cerebellar peduncles, deep white matter of the cerebral hemispheres, and zones of hemorrhagic transformation. Despite medical-surgical management, the patient died. The risk factors described as the cause of the fatal outcome were identified. This case demonstrates that posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome can occur without triggering risk factors and highlights the need for early recognition to establish an appropriate intervention to avoid injury or a fatal outcome. Cases of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome provide opportunities to investigate the susceptibility for the development of this condition and to establish appropriate preventive measures.
Downloads
References
Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, Breen J, Pao L, Wang A, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:494-500. http://dx.doi.
org/10.1056/NEJM199602223340803
Yoshida K, Kamamoto T, Mori K, Maeda M. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome in a patient with hypertensive encephalopathy--case report. Neurol Med Chir. 2001;41:364-9. http://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.41.364
Bartynski WS. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, part 1: Fundamental imaging and clinical features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29:1036-42. http://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0928
Servillo G, Bifulco F, De Robertis E, Piazza O, Striano P, Tortora F, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in intensive care medicine. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33:230-6. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-006-0459-0
Casey SO, Sampaio RC, Michel E, Truwit CL. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Utility of fluidattenuated inversion recovery MR imaging in the detection
of cortical and subcortical lesions. Am J Neuroradiol. 2000;21:1199-206.
Rykken JB, McKinney AM. Distinct imaging patterns and lesion distribution in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28:1320-7. http://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0549
Rykken JB, McKinney AM. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Semin Ultrasound CT MRI. 2014;35:118-35. http://doi.org/10.1053/j.sult.2013.09.007
Bartynski WS. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, Part 2: Controversies surrounding patho-physiology of vasogenic edema. Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29:1043-9.
http://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0929
Rodríguez-Boto G, Rivero-Garvía M, Gutiérrez-González R, Márquez-Rivas J. Basic concepts about brain pathophysiology and intracranial pressure monitoring. Neurologia. 2015;30:16-22. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.nrl.2012.09.002
Hefzy HM, Bartynski WS, Boardman JF, Lacomis D. Hemorrhage in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Imaging and clinical features. Am J Neuroradiol.
;30:1371-9. http://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1588
McKinney AM, Short J, Truwit CL, McKinney ZJ, Kozak OS, SantaCruz KS, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Incidence of atypical regions of involvement and imaging findings. Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189:904-12. http://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.07.2024
Martins WA, Marrone LC. Malignant posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: A case of posterior irreversible encephalopathy syndrome. J Clin Neurol. 2016;12:236-7.http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2016.12.2.236
Alhilali LM, Reynolds AR, Fakhran S. A multi-disciplinary model of risk factors for fatal outcome in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 2014;347:59–65. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2014.09.019
Legriel S, Schraub O, Azoulay E, Hantson P, Magalhaes E, Coquet I, et al. Determinants of recovery from severe posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. PLoS
One. 2012;7:e44535. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0044534
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























