Sialometry and concentration of phosphate and calcium in stimulated whole saliva and gingival crevicular fluid and its association with dental caries in schoolchildren
Abstract
Introduction: The remineralizing properties of saliva contribute to maintain the physical and chemical integrity of the mineral structure of teeth, which protects it from the installation and evolution of dental caries.
Objective: To relate sialometry, buffering capacity, calcium and phosphate concentration in whole stimulated saliva, and in gingival crevicular fluid with school children caries severity and activity.
Materials and methods: We selected 36 schoolchildren aged 6 years: 18 with caries (International Caries Detection and Assessment System, ICDAS>1 group) and 18 without caries (ICDAS=0 group). The severity and activity of dental caries were diagnosed in the primary dentition: in the occlusal surface of molars and in the vestibular of the anterior teeth by ICDAS-II.
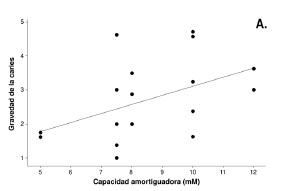
Results: Caries in occlusal surface were more severe than in vestibular surface. The concentration of calcium in saliva and phosphate in healthy teeth gingival crevicular fluid were higher in the ICDAS>1 group. The concentration of calcium in gingival crevicular fluid was higher in the ICDAS=0 group than in the decayed teeth of the ICDAS>1 group. We found a statistically significant association between the frequency of active caries andthe concentration of phosphate in gingival crevicular fluid of teeth with caries, as well as between the severity of caries with buffering capacity and the concentration of phosphate in the gingival crevicular fluid of teeth with caries.
Conclusion: We found an association between dental caries with buffering capacity and buccal calcium and phosphate.
Downloads
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























