Relationship between death and admission of pediatric patients to intensive care due to Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia acquired in the community, 2014-2017
Abstract
Introduction: The bacteremia caused by Staphylococcus aureus acquired in the community (SA-AC) is a frequent pathology in pediatrics and it is considered a public health problem generating high rates of morbidity, mortality, and bacterial resistance.
Objectives: To analyze the factors related to death and admission to intensive care units of patients under 18 years of age with AC-SA bacteremia admitted to the Hospital Infantil Los Ángeles, Pasto, Colombia, from 2014 to 2017.
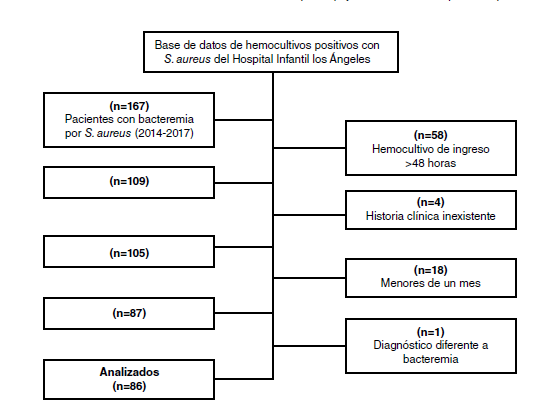
Material and methods: We conducted a descriptive, transversal, cross-sectional observational study. We analyzed 86 patients with bacteremia due to AC-SA that met the inclusion criteria for the study using a multivariate logistic regression model.
Results: Of the 86 cases, 25.6% died and 40.7% entered the intensive care unit. The resistance to methicillin was 52.3%. The main foci of infection were the soft tissues and the osteoarticular and respiratory systems; 32.6% of patients came from the Pacific area of Nariño. The predominant ethnic groups were the mestizo and the indigenous. Indigenous patients had higher mortality compared to the mestizo and Afro-Colombian ethnic groups. The multivariate analysis showed significance in terms of death for endocarditis (adjusted OR=20; CI: 1.5-254; p=0.02) while no statistical significance was registered for the admission to the intensive care unit.
Conclusions: The AC-SA led to high mortality and admission to the intensive care unit; 52.3% of strains were resistant and resistance to methicillin showed higher mortality, although the mortality with sensitive strains was considerable. Endocarditis showed fairly high mortality. The empirical therapy should be adjusted when bacteremia due to AC-SA is suspected.
Downloads
References
Pérez G, Martiren S, Reijtman V, Romero R, Mastroianni A, Casimir L, et al. Communityacquired Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in children: A cohort study for 2010-2014. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2016;114:508-13. https://doi.org/10.5546/aap.2016.eng.508
Moreno G, Cortés L, Pabón S. Factores de riesgo para infección por Staphylococcus aureus meticilino resistente comunitario en la Fundación Hospital de La Misericordia entre 2011 a 2013. Rev Médica Sanitas. 2014;17:110-8.
Park D, Lee S, Peck K, Joo E, Oh E. Impact of methicillin-resistance on mortality in children and neonates with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: A meta-analysis. Infect Chemother. 2013;45:202-10. https://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2013.45.2.202
Ligon J, Kaplan S, Hulten K, Mason E, McNeil J. Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia without a localizing source in pediatric patients. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014;33:132-4. https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.0000000000000195
van Hal S, Jensen S, Vaska V, Espedido B, Paterson D, Gosbell I. Predictors of mortality in Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012;25:362-86. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.05022-11
Le J, Dam Q, Tran T, Nguyen A, Adler F, Kim S, et al. Epidemiology and hospital readmission associated with complications of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in pediatrics over a 25-year period. Epidemiol Infect. 2017;145:2631-9. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268817001571
Cobos E, Soler P, Larrosa M, Bartolomé R, Martín A, Antoinette M, et al. Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in children. Changes during eighteen years. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015;34:1329-34. https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.0000000000000907
Khokhlova O, Hung W, Wan T, Iwao Y, Takano T, Higuchi W, et al. Healthcare- and community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and fatal pneumonia with pediatric deaths in Krasnoyarsk, Siberian Russia: Unique MRSA’s multiple virulence factors, genome, and stepwise evolution. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:1-30. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128017
Kumarachandran G, Johnson J, Shirley D, Graffunder E, Heil E. Predictors of adverse outcomes in children with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2017;22:218-26. https://doi.org/10.5863/1551-6776-22.3.218
McMullan B, Bowen A, Blyth C, van Hal S, Korman T, Buttery J, et al. Epidemiology and mortality of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in Australian and New Zealand children. JAMA Pediatr. 2016;170:979-86. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2016.1477
Cervantes E, García R, Salazar P. Características generales del Staphylococcus aureus. Rev Latinoam Patol Clin Med Lab. 2014;1:28-40.
Asgeirsson H, Gudlaugsson O, Kristinsson K, Vilbergsson G, Heiddal S, Haraldsson A, et al. Low mortality of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in Icelandic children nationwide study on incidence and outcome. J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2015;34:140-4. https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.0000000000000485
Geng W, Dong F, Weng J, Dong S, Jin F, Shen X, et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of invasive community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in Chinese neonates. Chinese J Microbiol Immunol. 2017;37:552-6
Gentile A, Bakira J, Ensinckb G, Cancellarac A, Casanuevad E, Carusof M, et al. Infecciones por Staphylococcus aureus meticilino resistente adquirido en la comunidad: hospitalización y riesgo de letalidad en 10 centros pediátricos de Argentina. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2018;116:47-53.
Abu N, Nor F, Mohamad M, Abidin A, Adnan A, Nor N, et al. Community-acquired bacteremia in paediatrics: Epidemiology, aetiology and patterns of antimicrobial resistance in a tertiary care centre, Malaysia. Med J Malaysia. 2016;71:117-21.
Guillén R, Carpinelli L, Rodríguez F, Castro H, Quiñónez B, Campuzano A, et al. Staphylococcus aureus adquiridos en la comunidad: caracterización clínica, fenotípica y genotípica de aislados en niños paraguayos. Rev Chil Infectol. 2016;33:609-18. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0716-10182016000600002
Gupta S, Sakhuja A, McGrath E, Asmar B. Trends, microbiology, and outcomes of infective endocarditis in children during 2000-–2010 in the United States. Congenit Heart Dis. 2017;12:196-201. https://doi.org/10.1111/chd.12425
Jomaa W, Ben Ali I, Abid D, Hajri Ernez S, Abid L, Triki F, et al. Clinical features and prognosis of infective endocarditis in children: Insights from a Tunisian multicentre registry. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2017;110:676-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acvd.2016.12.018
Some similar items:
- Óscar García , Tatiana Álvarez, Santiago Granados, Vanessa Garzón, Santiago González, Comparison of quick SOFA and SIRS scales at the bedside of patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia , Biomedica: Vol. 40 No. Supl. 1 (2020): Mayo, Infecciones en el trópico
- Martine Bonnaure-Mallet, Paula Juliana Pérez-Chaparro, Patrice Gracieux, Vincent Meuric, Zohreh Tamanai-Shacoori, Jaime Eduardo Castellanos, Distribution of Porphyromonas gingivalis fimA genotypes in isolates from subgingival plaque and blood sample during bacteremia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 2 (2009)
- César A. Arias, Marylin Hidalgo, Jinnethe Reyes, Ana María Cárdenas, Lorena Díaz, Sandra Ríncon, Natasha Vanegas, Paula Lucía Díaz, Elizabeth Castañeda, Resistance profiles to fluoroquinolones in clinical isolates of Gram positive cocci , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 2 (2008)
- Gloria Heresi, Germán A. Contreras, Norma Pérez, James R. Murphy, Thomas G. Cleary, Empyema necessitans and acute osteomyelitis associated with community acquired methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an infant , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 4 (2009)
- Ana María Perilla, Camilo González, Sandra Liliana Valderrama, Natasha Vanegas, Bibiana Chavarro, Luis Carlos Triana, José Roberto Támara, Carlos Arturo Álvarez, Necrotizing pneumonia by community-acquired, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 4 (2009)
- Germán González, Marta Lía Valencia, Nelson Armando Agudelo, Liliana Acevedo, Isabel Cristina Vallejo, Perceived urgency of medical condition and use of health care services in Medellín, Colombia, 2005-2006 , Biomedica: Vol. 27 No. 2 (2007)
- Jairo Lizarazo, Melva Linares, Catalina de Bedout, Ángela Restrepo, Clara Inés Agudelo, Elizabeth Castañeda, Grupo Colombiano para el Estudio de la Criptococosis, Results of nine years of the clinical and epidemiological survey on cryptococcosis in Colombia, 1997-2005 , Biomedica: Vol. 27 No. 1 (2007)
- Berta Nelly Restrepo, María Teresa Restrepo, Juan Camilo Beltrán, Mónica Rodríguez, Ruth Emilia Ramírez, Nutritional status of indigenous children aged up to six years in the Embera-Katio Indian , Biomedica: Vol. 26 No. 4 (2006)
- Andrés F. Henao-Martínez, Guido R. González-Fontal, Steven Johnson, A case of community-acquired Acinetobacter junii-johnsonii cellulitis , Biomedica: Vol. 32 No. 2 (2012)
- Ángela M. Pedraza, Carlos E. Rodríguez-Martínez, Ranniery Acuña, Initial validation of a scale to measure the burden for parents/caregivers of children with asthma and factors associated with this burden in a population of asthmatic children , Biomedica: Vol. 33 No. 3 (2013)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























