Hemolytic disease in fetuses and newborns due to antibodies against the M-antigen
Abstract
There are few case reports of hemolytic disease in fetuses and newborns (HDFN) caused by alloantibodies against the MNS blood group system. The reason for this dearth is that antibodies toward these antigens are usually IgM, which not only cannot cross the placental circulation but also react at temperatures below 37°C. They are, therefore, of minimal clinical importance. Nevertheless, cases have been reported in which the presence of anti-M IgG antibodies caused severe HDFN and even intrauterine death in the presence of maternal-fetal MNS incompatibility indicating that they could have a high clinical impact. The hemolytic pattern observed in these cases is similar to that caused by anti-Kell antibodies.
Progressive anemia is mediated and developed through hematopoietic suppression inducing the destruction of bone marrow precursor cells with the resulting absence of reticulocytes in peripheral blood.
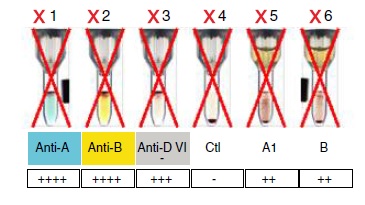
This occurred in the case of a woman at 38.5 weeks of gestation who showed a discrepancy between direct and reverse blood type determination. A direct Coombs test was performed on the newborn’s blood, which was positive in the absence of maternal-fetal ABO incompatibility. Further tests were performed and anti-M antibodies were found in the maternal serum screening. Our final diagnosis was largely due to discrepancy issues in maternal blood. Although anti-M antibodies do not usually play a significant role in HDFN, this case stresses the importance of identifying the presence of antibodies that can be crucial in preventing HDFN and lead to new recommendations for the screening and prompt treatment of hemolysis in newborns.
Downloads
References
Philip J, Kushwaha N, Jain N. Report of two cases of anti-M antibody in antenatal patients. Asian J Transfus Sci. 2015;9:89-91. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-6247.150963
Heathcote DJ, Carroll TE, Flower RL. Sixty years of antibodies to MNS system hybrid glycophorins: What have we learned? Transfus Med Rev. 2011;25:111-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmrv.2010.11.003
Gandhi MJ, Strong DM, Whitaker BI, Petrisli E. A brief overview of clinical significance of blood group antibodies. Immunohematology. 2019;34:4-6.
Wolff E, Jonsson B. Studien uber die untergruppen A1 and A2 mitesonderer berucksichtigung der paternitatsuntersuchungen. Dtsch Ztschr Gerichtl Med. 1933;22:65-85.
Khalid S, Dantes R, Varghese S, Al Hakawati I. Naturally occurring anti M complicating ABO grouping. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2011;54:170-2. https://doi.org/110.4103/0377-4929.77394
Ugarte-Rubio L, Cestafe M, Lete I, Lapuente-Ocamica O, González-Calviño J. Enfermedad hemolítica perinatal causada por anticuerpos anti-M y tratada con inmunoglobulinas intravenosas fetales. Prog Obstet Ginecol. 2015;58:327-29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pog.2015.02.012
Suresh B, Sreedhar KV, Reji A, Jothibai DS. Prevalence of “unexpected antibodies” in the antenatal women attending the Government Maternity Hospital, Tirupati. J Clin Sci Res. 2015;4:22-30. https://doi.org/10.15380/2277-5706.JCSR.14.041
Yasuda H, Ohto H, Nollet KE, Kawabata K, Saito S, Yagi Y, et al. Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn with late-onset anemia due to anti-M: A case report and review of the Japanese literature. Transfus Med Rev. 2014;28:1-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmrv.2013.10.002
Tondon R, Kataria R, Chaudhry R. Anti-M: Report of two cases and review of literature. Asian J Transfus Sci. 2008;2:81-3. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-6247.42695
Kaur G, Basu S, Kaur P, Kaur R. Clinically significant anti M antibodies --a report of two cases. Transfus Apher Sci. 2012;47:259-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transci.2012.07.023
Duro EA, Desalvo L, Kuret S. Severe hemolytic disease of the newborn caused by anti-M antibodies. Iran J Pediatr. 2013;23:607-8.
Ishida A, Ohto H, Yasuda H, Negishi Y, Tsuiki H, Arakawa T, et al. Anti-M antibody induced prolonged anemia following hemolytic disease of the newborn due to erythropoietic suppression in 2 siblings. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2015;37:e375-7. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPH.0000000000000341
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























