Artificial intelligence model for early detection of diabetes
Abstract
Introduction. Diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by a high blood glucose level. It can lead to complications that affect the quality of life and increase the costs of healthcare. In recent years, prevalence and mortality rates have increased worldwide. The development of models with high predictive performance can help in the early identification of the disease.
Objective. To develope a model based on artificial intelligence to support clinical decisionmaking in the early detection of diabetes.
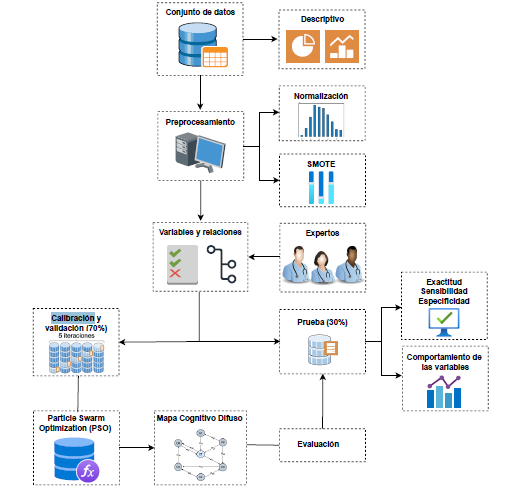
Materials and methods. We conducted a cross-sectional study, using a dataset that contained age, signs, and symptoms of patients with diabetes and of healthy individuals. Pre-processing techniques were applied to the data. Subsequently, we built the model based on fuzzy cognitive maps. Performance was evaluated with three metrics: accuracy, specificity, and sensitivity.
Results. The developed model obtained an excellent predictive performance with an accuracy of 95%. In addition, it allowed to identify the behavior of the variables involved using simulated iterations, which provided valuable information about the dynamics of the risk factors associated with diabetes.
Conclusions. Fuzzy cognitive maps demonstrated a high value for the early identification of the disease and in clinical decision-making. The results suggest the potential of these approaches in clinical applications related to diabetes and support their usefulness in medical practice to improve patient outcomes.
Downloads
References
O’Connell JM, Manson SM. Understanding the economic costs of diabetes and prediabetes and what we may learn about reducing the health and economic burden of these conditions. Diabetes Care. 2019;42:1609-11. https://doi.org/10.2337/dci19-0017
Sutton RT, Pincock D, Baumgart DC, Sadowski DC, Fedorak RN, Kroeker KI. An overview of clinical decision support systems: Benefits, risks, and strategies for success. NPJ Digit Med. 2020;3:1-10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-020-0221-y
Xue J, Min F, Ma F. Research on diabetes prediction method based on machine learning. J Phys Conf Ser. 2020;1684:1-6. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1684/1/012062
Chang V, Ganatra MA, Hall K, Golightly L, Xu QA. An assessment of machine learning models and algorithms for early prediction and diagnosis of diabetes using health indicators. Healthcare Analytics. 2022;2:1-14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.health.2022.100118
Khanam JJ, Foo SY. A comparison of machine learning algorithms for diabetes prediction. ICT Express. 2021;7:432-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icte.2021.02.004
Dinh A, Miertschin S, Young A, Mohanty SD. A data-driven approach to predicting diabetes and cardiovascular disease with machine learning. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019;19:1-15. https://doi.org/s12911-019-0918-5
Chaves L, Marques G. Data mining techniques for early diagnosis of diabetes: A comparative study. Appl Sci. 2021;11:1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052218
Giles BG, Findlay CS, Haas G, LaFrance B, Laughing W, Pembleton S. Integrating conventional science and aboriginal perspectives on diabetes using fuzzy cognitive maps. Soc Sci Med. 2007;64:562-76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2006.09.007
Alam A. Fuzzy cognitive maps approach to identify risk factors of diabetes. J Phys Sci. 2017;22:13-21.
Bhatia N, Kumar S. Prediction of severity of diabetes mellitus using fuzzy cognitive maps. Adv Life Sci Technol. 2015;29:71-8.
Hoyos W, Aguilar J, Toro M. PRV-FCM: An extension of fuzzy cognitive maps for prescriptive modeling. Expert Syst Appl. 2023;231:1-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120729
Islam M, Ferdousi R, Rahman S, Bushra HY. Likelihood prediction of diabetes at early stage using data mining techniques. Computer vision and machine intelligence in medical image analysis. 2020:113-25. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8798-2_12
Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique. J Artif Intell Res. 2002;16:321-57. https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.953
Amirkhani A, Papageorgiou EI, Mohseni A, Mosavi MR. A review of fuzzy cognitive maps in medicine: Taxonomy, methods, and applications. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2017;142:129-45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.02.021
Kosko B. Fuzzy cognitive maps. Int J Man-Machine Studies. 1986;24:65-75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7373(86)80040-2
Aguilar J. A fuzzy cognitive map based on the random neural model. Engineering of intelligent systems. 2001;333-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45517-5_37
Hoyos W, Aguilar J, Toro M. A clinical decision-support system for dengue based on fuzzy cognitive maps. Health Care Manag Sci. 2022;25:666-81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10729-022-09611-6
Battineni G, Sagaro GG, Nalini C, Amenta F, Tayebati SK. Comparative machine-learning approach: A follow-up study on type 2 diabetes predictions by cross-validation methods. Machines. 2019;7:1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines7040074
Kennedy J, Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. Proceedings of ICNN’95 - International Conference on Neural Networks. 1995;4:1942-48. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
Ministerio de Salud, Colombia. Resolución Número 8430 de 1993. Por la cual se establecen las normas científicas, técnicas y administrativas para la investigación en salud. Fecha de consulta: 9 de mayo de 2023. Disponible en: https://www.minsalud.gov.co/sites/rid/Lists/BibliotecaDigital/RIDE/DE/DIJ/RESOLUCION-8430-DE-1993.PDF
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th edition. Brussels, Belgium: Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice; 2021. Fecha de consulta: 5 de mayo de 2023. Disponible en: https://www.diabetesatlas.org
Elreedy D, Atiya AF. A comprehensive analysis of Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) for handling class imbalance. Inf Sci. 2019;505:32-64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.07.070
Shu CJ, Benoist C, Mathis D. The immune system’s involvement in obesity-driven type 2 diabetes. Semin Immunol. 2012;24:436-42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2012.12.001
Njomnang Soh P, Vidal F, Huyghe E, Gourdy P, Halimi JM, Bouhanick B. Urinary and genital infections in patients with diabetes: How to diagnose and how to treat. Diabetes Metab. 2016;42:16-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2015.07.002
Hussain A, Ashique S, Afzal O, Altamimi MA, Malik A, Kumar S, et al. A correlation between oxidative stress and diabetic retinopathy: An updated review. Exp Eye Res. 2023;236:1-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2023.109650
Rhou YJJ, Henshaw FR, McGill MJ, Twigg SM. Congestive heart failure presence predicts delayed healing of foot ulcers in diabetes: An audit from a multidisciplinary high-risk foot clinic. J Diabetes Complications. 2015;29:556-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.02.009
Shiraki T, Iida O, Takahara M, Soga Y, Yamauchi Y, Hirano K, et al. Predictors of delayed wound healing after endovascular therapy of isolated infrapopliteal lesions underlying critical limb ischemia in patients with high prevalence of diabetes mellitus and hemodialysis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2015;49:565-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2015.01.017
Froelich W, Wakulicz-Deja A. Mining temporal medical data using adaptive fuzzy cognitive maps. Proceedings of ICNN’95 - International Conference on Neural Networks. 2009;16-23. https://doi.org/10.1109/HSI.2009.5090946
Copyright (c) 2023 Biomedica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























