Validación de una metodología analítica para determinar bifenilos policlorados en muestras de plasma sanguíneo
Resumen
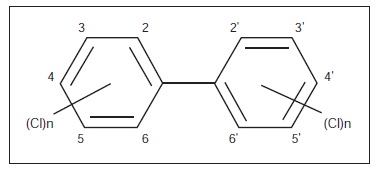
Introducción. Los bifenilos policlorados se encuentran entre los cinco contaminantes orgánicos persistentes más tóxicos para los organismos vivos, según la Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) de los Estados Unidos.
Objetivo. Estandarizar y validar un método analítico para la determinación y cuantificación de los bifenilos policlorados indicadores en muestras de plasma sanguíneo, mediante cromatografía de gases acoplada a espectrometría de masas.
Materiales y métodos. Se fortificó un pool de plasma para hacer los ensayos en la matriz. Además, se utilizó el material de referencia NIST SRM® 1958 (Organic Contaminants in Fortified Human Serum, Freeze-Dried) para los ensayos de veracidad y precisión intermedia.
Resultados. Los porcentajes de recuperación obtenidos con la metodología estuvieron entre 88,4 y 97,5 %, y el sesgo fue menor del 20 %. Los límites de detección y cuantificación de los bifenilos policlorados indicadores policlorados fueron de 0,04 μg/L y 0,10 μg/L, respectivamente. La linealidad representada por el coeficiente de determinación (R2) varió entre 0,9866 y 0,9886. La precisión expresada como desviación estándar relativa fue menor del 20 % en todo el rango lineal de trabajo (0,5-500 μg/L). Por último, se analizaron 115 muestras de población colombiana de diferentes zonas del país y se encontraron 65 muestras positivas, de las cuales dos estuvieron por encima de los valores de control biológico en humanos (Human Biomonitoring Values, HBM- II): 7,0 μg/L, 2XΣPCB 138, 153, 180, y otras dos, por encima del HBM-I: 3,5 μg/L, 2XΣPCB 138, 153, 180.
Conclusión. El método desarrollado resultó ser preciso para el análisis de los bifenilos policlorados en muestras de plasma sanguíneo y se puede utilizar para el control biológico de estos contaminantes en población colombiana.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Medio Ambiente (PNUMA). Transformadores y condensadores con PCB: desde la gestión hasta la reclasificación y eliminación. Primera edición. Ginebra: PNUMA; 2002. Fecha de consulta: 4 de marzo de 2014. Disponible en: http://www.inti.gob.ar/pcb/documentos/informesReportesDocumentos/Interes/PCBtranscap_s.pdf
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. ToxFAQs™ Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB). Fecha de consulta: 5 de mayo de 2016. Disponible en: http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/es/toxfaqs/es_tfacts17.html
McGovern V. PCBs are endocrine disruptors: Mixture affects reproductive development in female mice. Environ Health Perspect. 2006;114:A368-9.
Facts on Health and Environment, Green Facts. PCB bifenilos policlorados. Fecha de consulta: 5 de mayo de 2016. Disponible en: http://www.greenfacts.org/es/pcb/l-2/6-effects-human.htm#1
European Food Safety Authority. Results of the monitoring of non-dioxin-like PCBs in food and feed. EFSA Journal. 2010;8:1701. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1701
Schettgen T, Alt A, Esser A, Kraus T. Current data on the background burden to the persistent organochlorine pollutants HCB, p, p-DDE as well as PCB 138, PCB 153 and PCB 180 in plasma of the general population in Germany. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2015;218:380-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2015.02.006
Human Biomonitoring Commission (HBM Commission). Human biomonitoring (HBM) is an important tool in environmental medicine to assess and evaluate the level of internal exposure of the general population, population groups and individuals to environmental toxins. Fecha de consulta: 12 de junio de 2015. Disponible en: http://www.umweltbundesamt.de/en/topics/health/commissions-working-groups/humanbiomonitoring-commission-hbm-commission
Agence nationale de sécurité sanitaire de l’alimentation, de l’environnement et du travail - Anses. Opinion of the French Food Safety Agency on interpreting the health impact of PCB concentration levels in the French population. AFSSA– Request N° 2008-SA-0053. 2010. Fecha de consulta: 12 de junio de 2015. Disponible en: https://www.anses.fr/fr/system/files/RCCP2008sa0053EN.pdf
Ayotte P, Dewailly E, Ryan J, Bruneau S, Lebel G. PCBs and dioxin-like compounds in plasma of adult Inuit living in Nunavik (Arctic Quebec). Chemosphere. 1997;34:1459-68.
Covaci A, Koppen G, Cleuvenbergen RV, Schepens P, Winneke G, van Larebeke N, et al. Persistent organochlorine pollutants in human serum of 50-65 years old women in the flanders environmental and health study (FLEHS). Part 2: Correlations among PCBs, PCDD/PCDFs and the use of predictive markers. Chemosphere. 2002;48:827-32. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00112-1
Anthony P. Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) exposure assessment by multivariate statistical analysis of serum congener profiles in an adult Native American population. Environ Res. 2005;98:284-302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2004.09.004
Albrecht M, Appel M, Hilger B, Völkel W, Liebl B, Roscher E. PCBs, PCDD/Fs and PBDEs in blood samples of a rural population in South Germany. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2015;218:41-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2014.07.004
Gabrio T, Piechotowski I, Wallenhorst T, Klett M, Cott L, Friebel P, et al. PCB-blood levels in teachers, working in PCB-contaminated schools. Chemosphere. 2000;40:1055-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00353-7
Koppen G, Covaci A, van Cleuvenbergen R, Schepens P, Winneke G, Nelen V, et al. Persistent organochlorine pollutants in human serum of 50 – 65 years old women in the Flanders Environmental and Health Study (FLEHS). Part 1: Concentrations and regional differences. Chemosphere.2002;48:811-25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00111-X
Schettgen T, Gube M, Esser A, Alt A, Kraus T. Plasma polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) levels of workers in a transformer recycling company, their family members, and employees of surrounding companies. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2012;75:414-22. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2012.674905
Tanabe S, Senthilkumar K, Kannan K, Subramanian N. Monitoring of PCBs in human blood plasma: Methodological developments and influence of age, lactation, and fish consumption. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1997;32:329-36.
Wittsiepe J, Fobil J, Till H, Burchard G, Wilhelm M, Feldt T. Levels of polychlorinated dibenzo-P-dioxins, dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) and biphenyls (PCBs) in blood of informal e-waste recycling workers from Agbogbloshie, Ghana, and controls. Environ Int. 2015;79:65-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2015.03.008
Atuma S, Aune M. Method for the determination of PCB congeners and chlorinated pesticides in human blood serum. Bull Environ ContamToxicol. 1999;62:8-15.
Udai S, Harold M, Wheatley S, Wheatley B. Congener specific analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in serum using GC/MSD. Chemosphere. 1995;30:1969-77.
https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(95)00078-M
López R, Goñi F, Etxandia A, Millán E. Determination of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in human serum using headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-electron capture detection. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007;846:298-305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.09.009
Moreno F, Torres M, Garrido A, Martínez J, Olea-Serrano F, Olea N. Determination of organochlorine compounds in human biological samples by GC-MS/MS. Biomed Chromatogr. 2004;18:102-11. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.300
Turci R, Franco B, Minoia C. Determination of coplanar and non-coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls in human serum by gas chromatography with mass spectrometric detection: Electron impact or electron-capture negative ionization? Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2003;17:1881-8. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.1129
Vizcaíno E, Arellano L, Fernández P. Analysis of whole congener mixtures of polybromodiphenyl ethers by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in both environmental and biological samples at femtogram levels. J Chromatogr A. 2009;1216:5045-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.04.049
Corley J. Best practices in establishing detection and quantification limits for pesticide residue in foods. Handbook of Residue Analytical Methods for Agrochemicals. West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.; 2003.
EURACHEM/CITAC Guide CG 4. Cuantificación de la incertidumbre en medidas analíticas. Fecha de consulta: 4 de febrero de 2016. Disponible en: http://www.citac.cc/QUAM2012_P1_ES.pdf
European Commission. Safety of the food chain pesticides and biocides, SANTE/11945/2015. Fecha de consulta: 4 de febrero de 2016. Disponible en: http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/docs/plant_pesticides_mrl_guidelines_wrkdoc_11945_en.pdf
López R, Goñi F, Etxandia A, Milan E. Determination of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in human serum using headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-electron capture detection. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007;846:298-305. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.09.009
Turci R, Balducci C, Brambilla G, Colosio C, Imbriani M, Mantovani A, et al. A Simple and fast method for the determination of selected organohalogenated compounds in serum samples from the general population. Toxicol Lett. 2010; 192: 66-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.04.011
Lopez R, Goñi F, Etxandia A, Milan E. Determination of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in human serum using headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-electron capture detection. J Chromatogr B. 2007;846:298-305. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.09.009
Arrebola J.P, Cuellar M, Quevedo M, Claure E, Antelo S.R, Mutch E, et al. Concentration of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in human serum and adipose tissue from Bolivia. Environ Res. 2012;112:40-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2011.10.006
Gill U, Schwartz H, Wheatley B. Congener Specific Analysis of Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in serum using GC/MSD. Chemosphere. 1995;30:1969-77. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(95)00078-M
Lopez R, Goñi F, Etxandia A, Milan E, Amiano P. High throughput method for the determination of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in human serum. J Chromatogry B. 2007; 852:15-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.12.049
Algunos artículos similares:
- Itali M. Linero, Adriana Doncel, Orlando Chaparro, Proliferación y diferenciación osteogénica de células madre mesenquimales en hidrogeles de plasma sanguíneo humano , Biomédica: Vol. 34 Núm. 1 (2014)
| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |

























