Eficacia de los niveles séricos de S100B, TRAIL y adropina para predecir el resultado clínico, el núcleo del infarto final y los subtipos de ataque cerebrovascular de los pacientes con accidente cerebrovascular isquémico agudo
Resumen
Introducción. Más de la mitad de todas las muertes y discapacidades en todo el mundo fueron causadas por accidentes cerebrovasculares. La aterosclerosis de las grandes arterias se identifica como un factor de alto riesgo etiológico debido a que representa el 20 % de los accidentes cerebrovasculares isquémicos.
Objetivo. Determinar la importancia de la liberación de TRAIL y adropina y los cambios relativos relacionados con los niveles de S100B, así como la relación entre
estos biomarcadores y el núcleo final del infarto, el resultado clínico y la presencia de aterosclerosis de arterias grandes en pacientes con accidente cerebrovascular agudo.
Materiales y métodos. Durante un año, se evaluaron los hallazgos demográficos, clínicos y de neuroimágenes de 90 pacientes con accidente cerebrovascular isquémico agudo.
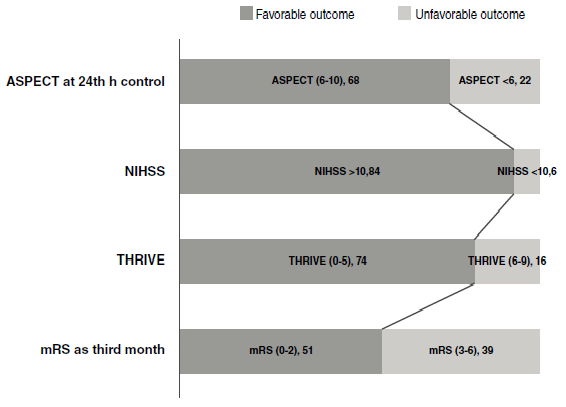
Resultados. La edad media de los pacientes fue de 69,28 ± 10 y 39 eran mujeres. El aumento del nivel de S100B y la disminución de los niveles de sTRAIL y adropina se asociaron significativamente con una presentación neurológica moderada a grave en los pacientes (p=0,0001, p=0,002 y p=0,002, respectivamente). En la TC de control, un gran núcleo de infarto se asoció significativamente con una disminución del nivel sérico de sTRAIL y adropina (p=0,001 y p=0,000, respectivamente); sin embargo, los niveles de S100B no se asociaron significativamente con una buena puntuación en el ASPECT (p=0,684). La discapacidad y el resultado desfavorable se relacionaron significativamente con la disminución de los niveles de sTRAIL y adropina (p=0,001 y p=0,000 para una puntuación >5 en el THRIVE, respectivamente). La disminución de los niveles de sTRAIL y adropina y el aumento del nivel de S100B, se correlacionaron con la presencia de un factor etiológico aterosclerótico de arterias grandes entre la población de estudio (p=0,000, p=0,000 y p=0,036, respectivamente).
Conclusiones. Los niveles séricos de TRAIL y adropina se asociaron con un resultado clínico deficiente y una mayor área infartada en pacientes con ataque cerebrovascular isquémico agudo.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Goldstein LB, Bushnell CD, Adams RJ, Appel LJ, Braun LT, Chaturvedi S, et al. Guidelines for the primary prevention of stroke: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014;42:517-84. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000046
Powers WJ, Derdeyn CP, Biller J, Coffey CS, Hoh BL, Jauch EC, et al. 2015 American Heart Association/American Stroke association focused update of the 2013 guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ıschemic stroke regarding endovascular treatment. Stroke. 2015;46:3020-35. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000074
Campbell BCV, De Silva DA, Macleod MR, Coutts SB, Schwamm LH, Davis SM, et al. Ischaemic stroke. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:70. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0118-8
Hewitt J, Castilla-Guerra L, Fernández-Moreno M del C, Sierra C. Diabetes and stroke prevention: A review. Stroke Res Treat. 2012;673187. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/673187
Prakash R, Li W, Qu Z, Johnson MA, Fagan SC, Ergul A. Vascularization pattern after ischemic stroke is different in control versus diabetic rats: Relevance to stroke recovery. Stroke. 2013;44:2875-82. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.001660
Verma S, Buchanan MR, Anderson TJ. Endothelial function testing as a biomarker of vascular disease. Circulation. 2003;108:2054-9. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000089191.72957.ED
Tisato V, Gonelli A, Voltan R, Secchiero P, Zauli G. Clinical perspectives of TRAIL: Insights into central nervous system disorders. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73:2017-27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2164-7
Secchiero P, Zauli G. TRAIL, a new weapon against neointimal hyperplasia. Cardiology. 2012;123:94-6. https://doi.org/10.1159/000342983
Marczuk N, Cecerska-Heryć E, Jesionowska A, Dołęgowska B. Adropin - physiological and pathophysiological role. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2016;70:981-8. https://doi.org/10.5604/17322693.1220082
Wu L, Fang J, Chen L, Zhao Z, Luo Y, Lin C, et al. Low serum adropin is associated with coronary atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013;52:751-8. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2013-0844
Weglewski A, Ryglewicz D, Mular A, Juryńczyk J. Changes of protein S100B serum concentration during ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in relation to the volume of stroke lesion. Neurologia i Neurochirurgia Polska. 2005;39:310-7.
Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Zhang J, Buchan AM. Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. Lancet. 2000;355:1670-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(00)02237-6
Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1019-30. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1414905
Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993;24:35-41. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.24.1.35
Flint AC, Cullen SP, Rao VA, Faigeles BS, Pereira VM, Levy EI, et al. The THRIVE score strongly predicts outcomes in patients treated with the Solitaire device in the SWIFT and STAR trials. Int J Stroke. 2014;9:698-704. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijs.12292
Aydin S. Three new players in energy regulation: Preptin, adropin and irisin. Peptides. 2014;56:94-110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2014.03.021
Dassan P, Keir G, Brown M. Criteria for a clinically informative serum biomarker in acute ischaemic stroke: A review of S100B. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009;27:295-302. https://doi.org/ 10.1159/000199468
Wunderlich MT, Wallesch CW, Goertler M. Release of neurobiochemical markers of brain damage is related to the neurovascular status on admission and the site of arterial occlusion in acute ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci. 2004;227:49-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2004.08.005
Park SY, Kim MH, Kim OJ, Ahn HJ, Song JY, Jeong, JY, et al. Plasma heart-type fatty acid binding protein level in acute ischemic stroke: Comparative analysis with plasma S100B level for diagnosis of stroke and prediction of long-term clinical outcome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013;115:405-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.06.004
Watt V, Chamberlain J, Steiner T, Francis S, Crossman D. TRAIL attenuates the development of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E deficient mice. Atherosclerosis. 2011;215:348-54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.01.010
Tufekci KU, Vurgun U, Yigitaslan O, Keskinoglu P, Yaka E, Kutluk K, et al. Follow-up analysis of serum TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand protein and mRNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. 2018;9:102. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00102
Kang YH, Park MG, Noh KH, Park HR, Lee HW, Son SM, et al. Low serum TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) levels are associated with acute ischemic stroke severity. Atherosclerosis. 2015;240:228-33. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.03.028
Wu L, Fang J, Chen L, Zhao Z, Luo Y, Lin C, et al. Low serum adropin is associated with coronary atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2014;52:751-8. https://doi.org/ 10.1515/cclm-2013-0844
Sato K, Yamashita T, Shirai R, Shibata K, Okano T, Yamaguchi M, et al. Adropin contributes to anti-atherosclerosis by suppressing monocyte-endothelial cell adhesion and smooth muscle cell proliferation. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051293
Li L, Xie W, Zheng XL, Yin WD, Tang CK. A novel peptide adropin in cardiovascular diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 2016;453:107-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2015.12.010
Celik A, Balin M, Kobat K, Erdem MA, Baydas A, Bulut M, et al. Deficiency of a new protein associated with cardiac syndrome X, called adropin. Cardiovasc Ther. 2013;31:174-8. https://doi.org/ 10.1111/1755-5922.12025
Altamimi TR, Gao S, Karwi QG, Fukushima A, Rawat S, Wagg CS, et al. Adropin regulates cardiac energy metabolism and improves cardiac function and efficiency. Metabolism. 2019;98:37-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2019.06.005
Secchiero P, Corallini F, Ceconi C, Parrinello G, Volpato S, Ferrari R, et al. Potential prognostic significance of decreased serum levels of TRAIL after acute myocardial infarction. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e4442. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004442
Cartland SP, Genner SW, Martínez GJ, Robertson S, Kockx M, Lin RC, et al. TRAILexpressing monocyte/macrophages are critical for reducing inflammation and atherosclerosis. iScience. 2019;12:41-52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2018.12.037
Butler AA, St-Onge MP, Siebert EA, Medici V, Stanhope KL, Havel PJ. Differential responses of plasma adropin concentrations to dietary glucose or fructose consumption in humans. Sci Rep. 2015;5:14691. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14691
Datos de los fondos
-
Bezmialem Vakıf Üniversitesi
Números de la subvención Decision No: 06.2015/19
| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |

























