Análisis de supervivencia y factores asociados de pacientes con glioma de alto grado
Resumen
Introducción. Los gliomas de alto grado son los tumores cerebrales primarios más comunes en adultos y, por lo general, tienen un curso mortal rápido. La supervivencia media es de 18 meses, principalmente, como consecuencia de la resistencia del tumor al protocolo Stupp.
Objetivo. Determinar la supervivencia de los pacientes con glioma de alto grado y el efecto de las variables de persuasión en la supervivencia.
Materiales y métodos. Se llevó a cabo un estudio descriptivo longitudinal en el que participaron 80 pacientes con diagnóstico reciente de glioma de alto grado no tratados. Se hizo una encuesta sobre su exposición a algunos factores de riesgo, grado de inestabilidad genética en sangre periférica mediante cuantificación de micronúcleos en linfocitos binucleares, micronúcleos en reticulocitos e intercambios de cromátidas hermanas en linfocitos. En el análisis estadístico, se construyeron tablas de vida, se utilizó Kaplan-Meier y la prueba de rangos logarítmicos, y en el análisis multivariado, se construyó un modelo de riesgos proporcionales de Cox.
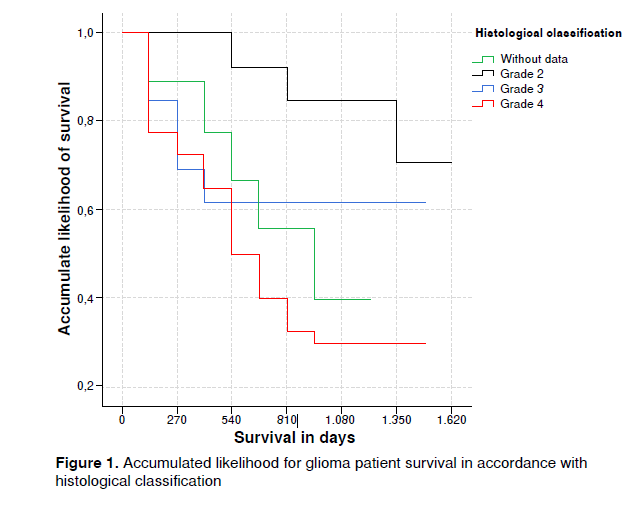
Resultados. Se analizaron las características clínicas, demográficas y de estilo de vida de 80 pacientes, así como sus tasas de supervivencia y el tiempo medio de supervivencia fue de 784 días (rango intercuartílico: 928). Factores como la edad, la exposición laboral a hidrocarburos policíclicos y el número de intercambios de cromátidas hermanas en linfocitos en el primer muestreo se relacionaron significativamente con la supervivencia en el análisis multivariante.
Conclusión. Según los resultados, el estudio determinó que solo tres de las variables analizadas tienen un efecto importante en el tiempo de supervivencia cuando se trata de pacientes con glioma de alto grado.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, et al. La clasificación de la OMS de 2007 de tumores del sistema nervioso central. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;114:97-109. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4
WHO. Media Centre. The top 10 causes of death. 2012. Consulted: June 1th, 2017. Available: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/
Piñeros M, Sierra MS, Izarzugaza MI, Forman D. Epidemiología descriptiva de los cánceres de cerebro y del sistema nervioso central en Centro y Sudamérica. Cáncer Epidemiol. 2016;44:S141–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canep.2016.04.007
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, et al. Clasificación de tumores del sistema nervioso central de 2016 de la organización mundial de la salud: resumen. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:803-20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Global Cancer Observatory. Accessed: July 18, 2014. Available at: https://gco.iarc.fr/en
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29210
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–96. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa043330
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJB, Janzer RC, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTCNCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459-66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7
Bleeker FE, Molenaar RJ, Leenstra S. Recent advances in the molecular understanding of glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 2012;108:11–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0793-0
Baldi I, Gruber A, Alioum A, Berteaud E, Lebailly P, Huchet A, et al. Descriptive epidemiology of CNS tumors in France: results from the Gironde Registry for the period 2000-2007. Neuro Oncol. 2011;13:1370–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nor120
Grossman SA, Ye X, Piantadosi S, Desideri S, Nabors LB, Rosenfeld M, et al. Survival of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma treated with radiation and temozolomide in Research studies in the United States. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:2443-9. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3106
Dolecek TA, Propp JM, Stroup NE, Kruchko C. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005-2009. Neuro Oncol. 2012;14(Suppl.5):1-49. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nos218
Alentorn A, Duran-Peña A, Pingle SC, Piccioni DE, Idbaih A, Kesari S. Molecular profiling of gliomas: potential therapeutic implications. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2015;15:955-62. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737140.2015.1062368
Coble JB, Dosemeci M, Stewart PA, Blair A, Bowman J, Fine HA, et al. Occupational exposure to magnetic fields and the risk of brain tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2009;11:242-9. https://doi.org/10.1215/15228517-2009-002
Michaud DS, Gallo V, Schlehofer B, Tjønneland A, Olsen A, Overvad K, et al. Coffee and tea intake and risk of brain tumors in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;92:1145-50. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2010.29876
Wigertz A, Lonn S, Hall P, Feychting M. Non-participant characteristics and the association between socioeconomic factors and brain tumour risk. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2010;64:736-43. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.2008.085845
Baglietto L, Giles GG, English DR, Karahalios A, Hopper JL, Severi G. Alcohol consumption and risk of glioblastoma; evidence from the Melbourne collaborative cohort study. Int J Cancer. 2011;128:1929-34. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25770
Cardis E, Armstrong BK, Bowman JD, Giles GG, Hours M, Krewski D, et al. Risk of brain tumours in relation to estimated RF dose from mobile phones: Results from five Interphone countries. Occup Environ Med. 2011;68:631-40. https://doi.org/10.1136/oemed-2011-100155
Claus EB, Calvocoressi L, Bondy ML, Schildkraut JM, Wiemels JL, Wrensch M. Family and personal medical history and risk of meningioma. J Neurosurg. 2011;115:1072–7. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.6.JNS11129
Claus EB, Calvocoressi L, Bondy ML, Schildkraut JM, Wiemels JL, Wrensch M. Dental x-rays and risk of meningioma. Cancer. 2012;118:4530–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.26625
Scheurer ME, Amirian ES, Davlin SL, Rice T, Wrensch M, Bondy ML. Effects of antihistamine and anti-inflammatory medication use on risk of specific glioma histologies. Int J Cancer. 2011;129:2290-6. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25883
Yiin JH, Brain Cancer Collaborative Study Group, Ruder AM, Stewart PA, Waters MA, Carreón T, et al. The upper midwest health study: A case–control study of pesticide applicators and risk of glioma. Environ Health. 2012;11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069x-11-39
Dertinger SD, Camphausen K, MacGregor JT, Bishop ME, Torous DK, Avlasevich S, et al. Three-color labeling method for flow cytometric measurement of cytogenetic damage in rodent and human blood. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2004;44:427-35. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.20075
Dertinger SD, Miller RK, Brewer K, Smudzin T, Torous DK, Roberts DJ, et al. Automated human blood micronucleated reticulocyte measurements for rapid assessment of chromosomal damage. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2007;626:111-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2006.09.003
Dertinger SD, Torous DK, Hayashi M, MacGregor JT. Flow cytometric scoring of micronucleated erythrocytes: An efficient platform for assessing in vivo cytogenetic damage. Mutagenesis. 2011;26:139-45. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/geq055
Fenech M, Chang WP, Kirsch-Volders M, Holland N, Bonassi S, Zeiger E. HUMN project: Detailed description of the scoring criteria for the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay using isolated human lymphocyte cultures. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2003;534:65-75. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1383-5718(02)00249-8
Fenech M. Cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:1084-104. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.77
Perry P, Wolff S. New Giemsa method for the differential staining of sister chromatids. Nature. 1974;251:156-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/251156a0
Collett D. Modelling survival data in medical research. 3rd ed. Boca Raton, London, New York: CRC Press; 2015. https://doi.org/10.1201/b18041
Kleinbaum, D, Kupper L, Nizam A, Rosenberg, E. Applied regression analysis and other multivariable methods. 5th. ed. Canada: Nelson Education; 2013.
Burbine A, Fryer D, Sturtevant J. Akaike information criterion to select well-fit resist models. In: Sturtevant JL, Capodieci L, editors. SPIE Proceedings; San José, California; 2015. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2085770
WHO. Población (OMS). 2015. Accessed. July 17, 2017. Available at: http://www.who.int/ageing/publications/world-report-2015/es/
Louis D, Ohgaki H, Wiestler O, Cavenee W, Burger P, Jouvet A, et al. The 2007 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;114:97-109.
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, et al. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:803-20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1
Marumoto T, Saya H. Molecular biology of glioma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;746:2-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3146-6_1
WHO. Obesidad y sobrepeso. 2004. Accesssed: Febrary 18, 2024. Available at: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
Fisher JL, Schwartzbaum JA, Wrensch M, Wiemels JL. Epidemiology of brain tumors. Neurol Clin. 2007;25:867-90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2007.07.002
Crocetti E, Trama A, Stiller C, Caldarella A, Soffietti R, Jaal J, et al. Epidemiology of glial and non-glial brain tumours in Europe. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:1532-42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2011.12.013
Yang P, Wang Y, Peng X, You G, Zhang W, Yan W, et al. Management and survival rates in patients with glioma in China (2004-2010): A retrospective study from a single-institution. J Neurooncol. 2013;113:259-66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1103-9
Instituto Nacional de Cancerología. Anuario Estadístico 2008. Accessed: February 6, 2017. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov.co/conozca-sobre-cancer-1/publicaciones/anuarioestadistico-2008
Casartelli G, Dorcaratto A, Ravetti JL, Sola S, Vitali A, Merlo DF, et al. Survival of high grade glioma patients depends on their age at diagnosis. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009;8:1719–21. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.8.18.9209
Cabaniols C, Giorgi R, Chinot O, Ferahta N, Spinelli V, Alla P, et al. Links between private habits, psychological stress and brain cancer: a case–control pilot study in France. J Neurooncol. 2011;103:307-16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0388-1
Plascak JJ, Fisher JL. Area-based socioeconomic position and adult glioma: A hierarchical analysis of surveillance epidemiology and end results data. PLoS One. 2013;8:e60910. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060910
Mukerji N, Rodrigues D, Hendry G, Dunlop PRC, Warburton F, Kane PJ. Treating high grade gliomas in the elderly: the end of ageism? J Neurooncol. 2008;86:329-36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-007-9476-2
View of neuropsychological characteristics of patients with glioma treated in the Institute of cancer of Medellín, Colombia. Incompleto ¿Año, volume, páginas? Actaneurologica.com. Consulted: February 18, 2024. Avalaible: https://www.actaneurologica.com/index.php/anc/article/view/1619/1359
Hardell L, Carlberg M, Hansson Mild K. Use of mobile phones and cordless phones is associated with increased risk for glioma and acoustic neuroma. Pathophysiology. 2013;20:85-110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pathophys.2012.11.001
Olar A, Sulman EP. Molecular markers in low-grade glioma-toward tumor reclassification. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2015;25:155-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semradonc.2015.02.006
Lu J, Cowperthwaite MC, Burnett MG, Shpak M. Molecular predictors of long-term survival in glioblastoma multiforme patients. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0154313. http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0154313
Chang P, Li Y, Li D. Micronuclei levels in peripheral blood lymphocytes as a potential biomarker for pancreatic cancer risk. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32:210-5. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgq247
Minniti G, Enrici RM. Radiation therapy for older adults with glioblastoma: Radical treatment, palliative treatment, or no treatment at all? J Neurooncol. 2014;120:225-33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1566-3
Neta G, Stewart PA, Rajaraman P, Hein MJ, Waters MA, Purdue MP, et al. Occupational exposure to chlorinated solvents and risks of glioma and meningioma in adults. Occup Environ Med. 2012;69:793-801. https://doi.org/10.1136/oemed-2012-100742
Lim YC, Roberts TL, Day BW, Harding A, Kozlov S, Kijas AW, et al. A role for homologous recombination and abnormal cell-cycle progression in radioresistance of glioma-initiating cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11:1863-72. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-1044
Algunos artículos similares:
- Lina Marcela Barrera, León Darío Ortiz, Hugo Grisales, Mauricio Rojas, Mauricio Camargo, Citometría de flujo en reticulocitos de sangre periférica como indicador de inestabilidad cromosómica en pacientes con gliomas de alto grado , Biomédica: Vol. 38 Núm. 3 (2018)
- Orlando Ricaurte, Karina Neita, Danyela Valero, Jenny Ortega-Rojas, Carlos E. Arboleda-Bustos, Camilo Zubieta, José Penagos, Gonzalo Arboleda, Estudio de mutaciones en los genes IDH1 e IDH2 en una muestra de gliomas de población colombiana , Biomédica: Vol. 38 Núm. Sup.1 (2018): Suplemento 1, Enfermedades crónicas
Derechos de autor 2024 Biomédica

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |

























