Regulación del calcio por SERC-A antes de la enfermedad de Alzheimer y durante la misma
Resumen
Hay muchos factores implicados en la incidencia de la enfermedad de Alzheimer que, en combinación, terminan por impedir o dificultar las funciones neuronales normales.
Actualmente, poco se conoce sobre la regulación del calcio, antes de la enfermedad y durante la misma. La inestabilidad interna de los niveles de calcio se asocia a un mayor riesgo vascular, condición prevalente en un gran número de individuos ya comprometidos por la enfermedad de Alzheimer.
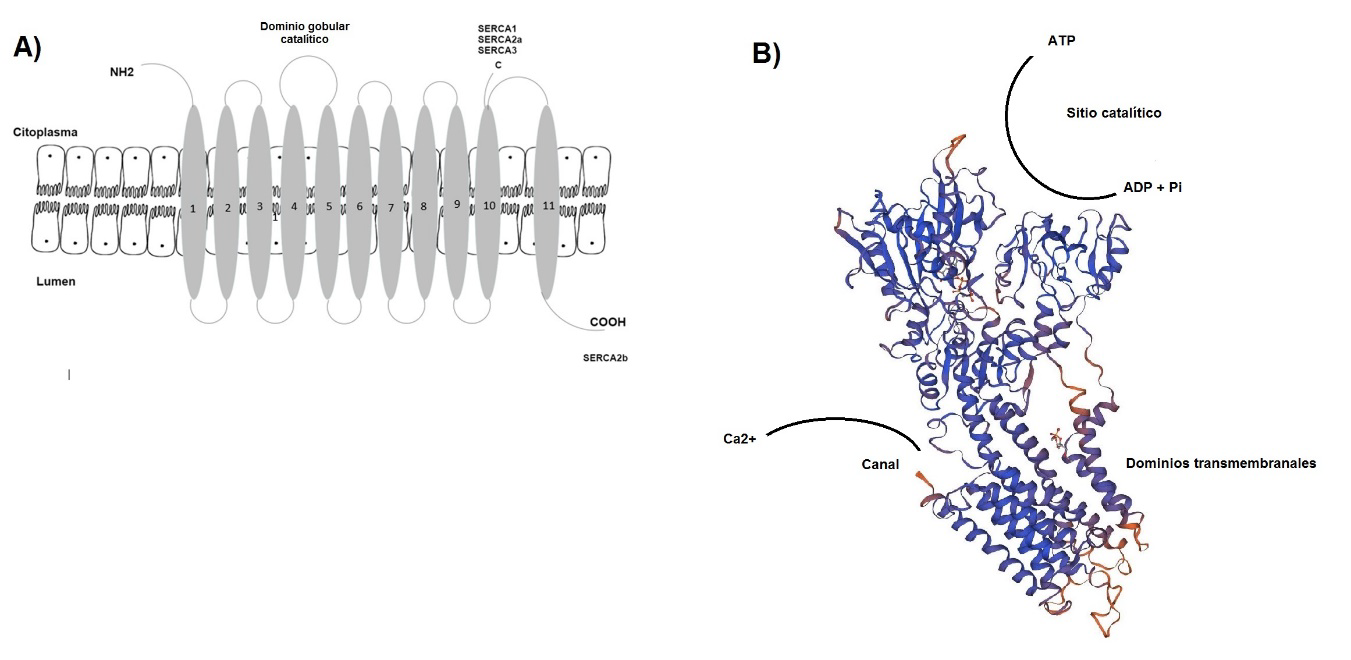
Esta revisión proporciona una reevaluación de los mecanismos moleculares de la ATPasa dependiente de Ca2+ del retículo sarcoendoplásmico (SERC-A) en la enfermedad y analiza los aspectos más destacados de la función de los canales de calcio dependientes de voltaje; de esta manera, se podrán abrir nuevas alternativas de tratamiento. Estos mecanismos de regulación son clínicamente relevantes, ya que se ha implicado la función irregular de SERC-A en diversas alteraciones de la función cerebral.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Prince M, Comas-Herrera A, Knapp M, Karagiannidou M. World Alzheimer report 2016: Improving healthcare for people living with dementia. London: Alzheimer’s Disease International; 2016.
Bermejo-Pareja F, Gómez de la CA, del Ser T, Contador I, Llamas-Velasco S, López-Arrieta JM, et al. The health status: The ignored risk factor in dementia incidences. NEDICES cohort. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022;34:1275-83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-021-02045-0
Delacourte A, Buee L. Tau pathology: A marker of neurodegenerative disorders. Curr Opin Neurol. 2000;13:371-6. https://doi.org/10.1097/00019052-200008000-00002
Bondi MW, Edmonds EC, Salmon DP. Alzheimer’s disease: Past, present, and future. J Int Neuropsy Soc. 2017;23:818-31. https://doi.org/10.1017/S135561771700100X
Cholerton B, Gleason CE, Baker LD, Asthana S. Estrogens and Alzheimer’s disease: The story so far. Drugs Aging. 2002;19:405-27. https://doi.org/ 10.2165/00002512-200219060-00002
Villarroya-Pastor MT. Alzheimer’s disease: The women´s profile. Rev Neuro. 2001;32:1178-81.
Xu Z, Dong Y, Wang H, Culley DJ, Marcantonio ER, Crosby G, et al. Age-dependent postperative cognitive impairment an Alzheimer-related neuropathology in mice. Sci Rep. 2014;4:3766. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03766
Creese B, Ismail Z. Mild behavioral impairment: Measurement and clinical correlates of a novel marker of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2022;14:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-021-00949-7
Ugbaja SC, Lawal MM, Kumalo HM. An overview of beta-amyloid cleaving enzyme (BACE1) in Alzheimer’s disease therapy: Elucidating its exosite-binding antibody and allosteric inhibitor. Curr Med Chem. 2022;29:114-35. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867328666210608145357
Kim H, Fraser S. Neural correlates of dual-task walking in people with central neurological disorders: A systematic review. J Neurol. 2022;269:2378-402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10944-5
Firoz CK, Jabir NR, Khan MS, Mahmoud M, Shakil S, Damanhouri GA, et al. An overview on the correlation of neurological disorders with cardiovascular disease. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2015;22:19-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2014.09.003
Akata T. Cellular and molecular mechanism regulating vascular tone. Part 1: basic mechanisms controlling cytosolic Ca2+ concentration and the Ca2+- dependent regulation of vascular tone. J Anesth. 2007;21:220-31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-006-0487-5
Brandenburg VM, Krammann R, Gottsch C, Kaesler N. Update on cardiovascular calcificacion. Nephrologe. 2017;12:168-72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11560-017-0141-2
Severi S, Bolasco P, Badiali F, Concas G, Mancini E, Summa A, et al. Calcium profiling in hemodiafiltration: A new way to reduce the calcium overload risk without compromising cardiovascular stability. Int J Artif Organs. 2014;37:206-14. https://doi.org/10.5301/ijao.5000320
Haas JS. A new measure for the strength of electrical synapses. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:378. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00378
Michaelis ML. Ion transport systems and Ca2+ regulation in aging neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994;747:407-18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb44425.x
Chami M, Checler F. Alterations of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) calcium signaling molecular components in Alzheimer’s disease. Cells. 2020;1:2577. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122577
Berridge MJ. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993;361:315-25.
Squier TC, Bigelow DJ. Protein oxidation and age-dependent alterations in calcium homeostasis. Front Biosci. 2000;5:D504-26. https://doi.org/10.2741/squier
Mattson MP, LaFerla FM, Chan SL, Leissring MA, Shepel PN, Geiger JD. Calcium signaling in the ER: Its role in neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:222-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-2236(00)01548-4
Pittman JK. Vacuolar Ca2+ uptake. Cell Calcium. 2011;7:1-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2011.01.004
Inesi G. Sequential mechanism of calcium binding and translocation in sarcoplasmic reticulum adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:16338-42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)49260-5
Hasselbach W. Relaxation and the sarcotubular calcium pump. Fed Proc. 1964;23:909-12.
MacLennan DH. Purification and properties of an adenosine triphosphatase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1970;245:4508-18. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)63820-2
Manjarres IM, Rodríguez-García A, Alonso MT, García-Sancho J. The Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERC-A) is the third element in capacitative calcium entry. Cell Calcium. 2010;47:412-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2010.03.001
Sweadner KJ, Donnet C. Structural similarities of Na, k-ATPase and SERC-A, the Ca2+ ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 2001;356:685-704. https://doi.org/10.1042/0264-6021:3560685
Wuytack F, Raeymaekers L, Missiaen L. Molecular physiology of the SERC-A and SPCA pumps. Cell Calcium. 2002;32:279-305. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143416002001847
Periasamy M, Kalyanasundaram A. SERC-A pump isoforms: Their role in calcium transport and disease. Muscle Nerve. 2007;35:430-42. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.2074515
Callen DF, Baker E, Lane S, Nancarrow J, Thompson A, Whitmore S, et al. Regional mapping of the Batten disease locus (CLN3) to human chromosome 16p12. Am J Hum Genet. 1991;49:1372-7.
Odermatt A, Taschner PE, Khanna VK, Busch HF, Karpati G, Jablecki CK, et al. Mutations in the gene-encoding SERC-A1, the fast twitch skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase, are associated with Brody disease. Nat Genet. 1996;14:191-4. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1096-191
Salvador JM, Berengena M, Sepúlveda MR, Mata AM. Distribution of the intracellular Ca2+- ATPase isoform 2b in pig brain subcellular fractions and cross-reaction with a monoclonal antibody raised against the enzyme isoform. J Biochem. 2001;129:621-6. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a002899
Sakuntabhai A, Ruiz-Pérez V, Carter S, Jacobsen N, Burge S, Monk S, et al. Mutations in ATP2A2, encoding a Ca2+ pump, cause Darier disease. Nat Genet. 1999;21:271-7. https://doi.org/10.1038/6784
Jones I, Jacobsen N, Green EK, Elvidge GP, Owen MJ, Craddock N. Evidence for familial cosegregation of major affective disorder and genetic markers flanking the gene for Darier’s disease. Mol Psychiatry. 2002;7:424-7. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000989
Misquitta CM, Ghosh P, Mwanjewe J, Grover AK. Role of cis-acting elements in the control of SERC-A2b Ca2+ pump mRNA decay by nuclear proteins. Biochem J. 2005;388:291-7. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20041568
Li SH, Zhao F, Tang QL, Xi CC, He J, Wang YJ, et al. Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERC-A2b) mediates oxidation-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress to regulate neuropathic pain. Br J Pharmacol. 2022;179:2016-36. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.15744
Gallego-Sandín S, Alonso MT, García-Sancho J. Calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALhM1) reduces the calcium content of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and triggers ER stress. Biochem J. 2011;437:469-75. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20110479
Taipa R, Pinho J, Melo-Pires M. Clinico-pathological correlations of the most common neurodegenerative dementias. Front Neurol. 2012;3:1-13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2012.00068
West MJ, Coleman PD, Flood DG, Troncoso JC. Differences in the pattern of hippocampal neuronal loss in normal ageing and Alzheimer´s disease. Lancet. 1994;344:769-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(94)92338-8
Dahl R. A new target for Parkinson´s disease: Samll molecule SERCA activator CDN1163 ameliorates dyskinesia in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017;25:53-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2016.10.008
Krajnak K, Dahl R. A new target for Alzheimer’s disease: A small molecule SERC-A activator is neuroprotective in vitro and improves memory and cognition in APP/PS1 mice. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018;28:1591-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.03.052
López OL. The growing burden of Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Manag Care. 2011;17(Suppl.13):S339-45.
Park SW, Zhou Y, Lee J, Ozcan U. Sarco(endo)plasmic reticulim Ca2+-ATPase 2b is a major regulator of endoplasmic reticulum stress and glucose homeostasis in obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:19320-5. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1012044107
Lin JH, Walter P, Yen TSB. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in disease pathogenesis. Ann Rev Pathol. 2008;3:399-425. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pathmechdis.3.121806.151434
Ron D, Walter P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:519-29. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2199
Kim I, Xu W, Reed JC. Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: Disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:1013-30. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2755
Zhang K, Kaufman RJ. From endoplasmic-reticulum stress to the inflammatory response. Nature. 2008;454:455-62. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07203
Thastrup O, Cullen PJ, Drobak BK, Hanley MR, Dawson AP. Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:2466-70. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.87.7.2466
Aulestia FJ, Redondo PC, Rodríguez-García A, Rosado JA, Salido GM, Alonso MT, et al. Two distinct calcium pools in the endoplasmic reticulum of HEK-293T cells. Biochem J. 2011;435:227-35. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20101427
Sordi G, Goti A, Young HS, Palchetti I, Tadini-Buninsegni F. Stimulation of Ca2+-ATPase transport activity by a small-molecule drug. Chem Med Chem. 2021;16:3293-99. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202100350
Zhang W, Ye F, Pang N, Kessi M, Xiong J, Chen S, et al. Restoration of Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase activity functions as a pivotal therapeutic target of anti-glutamateinduced excitotoxicity to attenuate endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ depletion. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:877175. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.877175
Algunos artículos similares:
- Andrés Villegas, Mónica M. Castañeda, Luis Fernando Arias, Beatriz Vieco, Francisco Lopera, Gabriel Bedoya, Evaluación de la producción de b-amiloide por la mutación E280A en el gen de la presenilina 1 , Biomédica: Vol. 27 Núm. 3 (2007)
- Lucero Rengifo, Duverney Gaviria, Herman Serrano, Polimorfismos del gen ApoE en individuos con síndrome de Down y sus progenitores en una población colombiana , Biomédica: Vol. 32 Núm. 2 (2012)
- Luz E. Botero, Andrés E. Toro, Alber J. Patiño, Guillermo Salazar, Juan C. Rodríguez, Juan C. Suárez-Escudero, Gustavo A. Alarcón, Ana Corcimaru, Cristina Osorio, Joseph S. Y. Jeong, Oscar Alzate, Diabetes mellitus en pacientes con enfermedad de Alzheimer: descripción clínica y correlación con el genotipo APOE en una muestra de población del departamento de Antioquia, Colombia , Biomédica: Vol. 32 Núm. 2 (2012)
- Angélica María Muñoz, Gloria María Agudelo, Francisco Javier Lopera, Diagnóstico del estado nutricional de los pacientes con demencia tipo Alzheimer registrados en el Grupo de Neurociencias, Medellín, 2004. , Biomédica: Vol. 26 Núm. 1 (2006)
- Felipe Vargas-Restrepo, Angélica María Sabogal-Guáqueta, Gloria Patricia Cardona-Gómez, La quercetina disminuye la inflamación en la región CA1 del hipocampo en un modelo de ratón triple transgénico para la enfermedad de Alzheimer. , Biomédica: Vol. 38 Núm. Sup.1 (2018): Suplemento 1, Enfermedades crónicas
- Silvia Martínez , Bárbara Ochoa , María Rafaela Pérez , Fátima Torrico , Ildemaro García , Carmen Cristina Garcia, Polimorfismos del gen de la apolipoproteína E en adultos mayores de 60 años con disminución de la memoria cognitiva y enfermedad de Alzheimer en diferentes poblaciones venezolanas , Biomédica: Vol. 42 Núm. Sp. 1 (2022): Mayo, Enfermedades crónicas en el trópico
- Astrid Torres, Loida Camargo , Norman López , Aducanumab: una mirada dos años después de su aprobación , Biomédica: Vol. 44 Núm. Sp. 1 (2024): Enfermedades crónicas no transmisibles
Derechos de autor 2023 Biomédica

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |

























