Seroprevalence of human T-lymphotropic virus in blood bank donors at Fundación Valle del Lili, Cali, Colombia, 2008-2014
Abstract
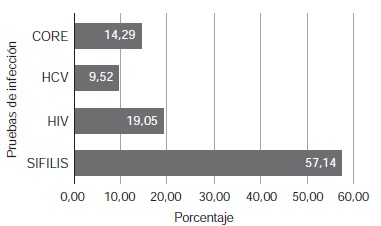
Introduction: Human lymphotropic virus (HTLV I/II) is a retrovirus that is prevalent across the Colombian Pacific coast, and is potentially transmissible by transfusion. Blood bank screening has been regulated since 2004, in order to reduce transmission of HTLV I/II through donation. Information on the seroprevalence of the virus in southwestern Colombia is limited. Objective: To determine the seroprevalence and the behavior of reactivity to HTLV I/II before and after the introduction of Western blot, and the comorbidity of HTLV and other infectious markers in donors from a blood bank in Cali, Colombia. Materials and methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study of 77,117 blood bank donors from the Fundación Valle del Lili by analyzing records of donors who had been tested with the reactive test for anti-HTLV I-II antibodies (IgG) between January, 2008, and December, 2014. Results: The cumulative seroprevalence during the study period was 0.24% (186/77,119). Reactivity was more common in women (61%), and the median age was 37 years (IQR: 24-48). The seroprevalence in the years before the introduction of Western blot was 0.13%, 0.19%, 0.31%, 0.32% and 0.18% (2008-2012), and thereafter it was 0.08% and 0.07% (2012-2014). Concomitant reactivity with other infectious markers was 11%: syphilis (57%), followed by HIV (19%), hepatitis B (14%) and hepatitis C (9%). The highest seroprevalence (0.38%) was reported in 2012. Conclusion: We found a high prevalence of reactivity to HTLV I-II compared to that reported in other studies. The results of this study are a starting point for the development of population studies.
Downloads
References
García-Vallejo F. Caracterización molecular y genómica del proceso de integración de provirus del virus linfotrópico humano (HTLV) tipo I. Rev Acad Colomb Cienc. 2006;30: 155-70.
Poiesz BJ, Ruscetti FW, Gazdar AF, Bunn PA, Minna JD, Gallo RC. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1980;77:7415-9.
Kalyanaraman VS, Narayanan R, Feorino P, Ramsey RB, Palmer EL, Chorba T, et al. Isolation and characterization of a human T cell leukemia virus type II from a hemophilia-A patient with pancytopenia. EMBO J. 1985;4:1455-60.
Mahieux R, Gessain A. The human HTLV-3 and HTLV-4 retroviruses: New members of the HTLV family. Pathol Biol. 2009;57:161-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.patbio.2008. 02.015
Gotuzzo-Herencia E, González-Lagos E, Verdonck-Bosteels K, Mayer-Arispe E, Ita-Nagy F, Clark-Leza D. Veinte años de investigación sobre HTLV-1 y sus compli-caciones médicas en el Perú: perspectivas generales. Acta Médica Peru. 2010;27:196-203.
Proietti FA, Carneiro-Proietti AB, Catalan-Soares BC, Murphy EL. Global epidemiology of HTLV-I infection and associated diseases. Oncogene. 2005;24:6058-68. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208968
Gonçalves DU, Proietti FA, Ribas JG, Araújo MG, Pinheiro SR, Guedes AC, et al. Epidemiology, treatment, and prevention of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-associated diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010;23:577-89. http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00063-09.
Matsuura E, Umehara F, Nose H, Higuchi I, Matsuoka E, Izumi K, et al. Inclusion body myositis associated with human T-lymphotropic virus-type I infection: Eleven patients from an endemic area in Japan. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008;67:41-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/nen. 0b013e31815f38b7
Tsukasaki K, Hermine O, Bazarbachi A, Ratner L, Ramos JC, Harrington W, et al. Definition, prognostic factors, treatment, and response criteria of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: A proposal from an international consensus meeting. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:453-9. http://dx. doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2008.18.2428
Blank A, Rosso F. Hiperinfección por Strongyloides stercolaris en portadores del virus linfotrófico humano tipo I (HTLV-I). Acta Méd Colomb. 1996;21:122-6.
Fujino T, Nagata Y. HTLV-I transmission from mother to child. J Reprod Immunol. 2000;47:197-206.
Osame M, Janssen R, Kubota H, Nishitani H, Igata A, Nagataki S, et al. Nationwide survey of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy in Japan: Association with blood transfusion. Ann Neurol. 1990;28:50-6.
León G, Quirós AM, López JL, Hung M, Díaz AM, Goncalves J, et al. Seropositividad al virus linfotrópico de células T humanas tipos I y II en donantes del Banco Municipal de Sangre de Caracas y factores de riesgo asociados. Rev Panam Salud Pública. 2003;13:117-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1020-49892003000200012
Chang YB, Kaidarova Z, Hindes D, Bravo M, Kiely N, Kamel H, et al. Seroprevalence and demographic determinants of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 and 2 infections among first-time blood donors--United States, 2000-2009. J Infect Dis. 2013;209:523-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jit497
Alarcón-Villaverde J, Romaní-Romaní F, Montaño-Torres S, Zunt JR. Vertical transmission of HTLV-1 in Perú. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Pública. 2011;28:101-8. http://dx. doi.org/10.1590/S1726-46342011000100016
Gessain A, Cassar O. Epidemiological aspects and world distribution of HTLV-1 infection. Front Microbiol. 2012;3:388. http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2012.00388
Trujillo JM, Concha M, Muñoz A, Bergonzoli G, Mora C, Borrero I, et al. Seroprevalence and cofactors of HTLV-I infection in Tumaco, Colombia. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992;8:651-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/aid.1992.8.651
Zaninovic V, Moreno D, Payán C, Rodríguez A. A propósito de 5 casos de paraparesia espástica tropical en Puerto Tejada (Cauca). Colombia Médica. 1997;28:67-70.
Bermúdez HC, Enrique J, Collazos M, Sierra MR, Fonseca AA. Seroprevalencia de tamizaje frente a virus linfotrópico de células T (HTLV) y factores asociados a coinfección en donantes voluntarios de sangre de Colombia. Salud Uninorte. 2014;30:95-103.
Martínez-Nieto O, Isaza-Ruget M, Rangel-Espinosa N, Morales-Reyes OL. Seroprevalencia de anticuerpos para virus linfotrópicos humanos (HTLV I/II) en donantes de sangre de una clínica de Bogotá, Colombia. 1999-2004. Rev Salud Pública. 2007;9:253-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0124-00642007000200009
Buelvas AC, Beltrán M, Gallego GA, Isaza LM. Estudio prospectivo seroepidemiológico de infección por el virus linfotrópico humano I y II (HTLV-I/II) en donantes de sangre de áreas colombianas endémicas y no endémicas. Colombia Médica. 1999:30:19-25.
Red Nacional de Bancos de Sangre. Informe Nacional de Indicadores. 1 de enero a 31 de diciembre de 2013. Fecha de consulta: 21 de abril de 2015. Disponible en: http://www.ins.gov.co/lineas-de-accion/Red-Nacional-Laboratorios/reas%20Estratgicas/Informe%20Anual%20Red%20Sangre%202013.pdf
Ministerio de Salud y Protección Social. Resolución número 000437. Fecha de consulta: 21 de abril de 2015. Disponible en: https://www.minsalud.gov.co/Normatividad_Nuevo/Resoluci%C3%B3n%200437%20de%202014.pdf
Gonçalves DU, Proietti FA, Ribas JG, Araújo MG, Pinheiro SR, Guedes AC, et al. Epidemiology, treatment, and prevention of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-associated diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010;23:577-89. http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00063-09
de Thé G, Bomford R. An HTLV-I vaccine: Why, how, for whom? AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993;9:381-6.
Zaaijer HL, Cuypers HT, Dudok de Wit C, Lelie PN. Results of 1-year screening of donors in The Netherlands for human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV) type I: Significance of Western blot patterns for confirmation of HTLV infection. Transfusion. 1994;34:877-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j. 1537-2995.1994.341095026973.x
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Current trends human T-lymphotropic virus type I screening in volunteer blood donors, United States, 1989. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1990;39:921-4.
Viana GM, Nascimento MdoD, de Oliveira RA, Dos Santos AC, Galvão CdeS, da Silva MA. Seroprevalence of HTLV-1/2 among blood donors in the state of Maranhão, Brazil. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter. 2014;36:50-3. http://dx. doi.org/10.5581/1516-8484.20140013
Galvão-Castro B, Loures L, Rodriques LG, Sereno A, Ferreira-Júnior OC, Franco LG, et al. Distribution of human T-lymphotropic virus type I among blood donors: A nationwide Brazilian study. Transfusion. 1997;37:242-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1537-2995.1997.37297203532.x
Mota A, Nunes C, Melo A, Romeo M, Boasorte N, Dourado I, et al. A case-control study of HTLV-infection among blood donors in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil - associated risk factors and trend towards declining prevalence. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter. 2006;28:120-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-84842006000200011
Monteiro-de-Castro MS, Assunção RM, Proietti FA. Spatial distribution of the human T-lymphotropic virus types I and II (HTLV-I/II) infection among blood donors of Hemominas Foundation, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais State, Brazil, 1994-1996. Cad Saúde Pública. 2001;17:1219-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0102-311X2001000500014
Navas MC, Iglesias A, Martínez BM, Caraballo L. Preva-lencia de anticuerpos contra HTLV-1 en una población negra de Colombia. Biomédica. 1995;15:34-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.v15i1.855
Some similar items:
- Marcel Marín, Yudy Alexandra Aguilar, José Robinson Ramírez, Omar Triana, Carlos Enrique Muskus, Molecular and immunological analyses suggest the absence of hydrophilic surface proteins in Leishmania (Viannia) panamensis , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 3 (2008)
- Liliana Morales, Myriam L. Velandia, María Angélica Calderon, Jaime E. Castellanos, Jacqueline Chaparro-Olaya, Polyclonal antibodies against recombinant dengue virus NS3 protein , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. 1 (2017)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























