Racemose neurocysticercosis: Neuroimaging guides the diagnosis
Abstract
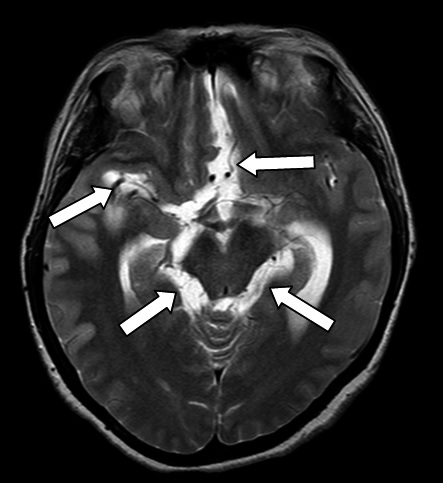
Neurocysticercosis is the leading cause of parasitosis of the central nervous system and acquired epilepsy in developing countries. The clinical manifestations of neurocysticercosis, especially its racemose variant, are pleomorphic and unspecific, characteristics that hinder the diagnosis and make it a challenge for the clinician.
The objective of this report was to describe two cases of racemose neurocysticercosis in which neuroimaging led to the definitive diagnosis. The first case involved a patient with persistent headache and focal neurological signs. She required multiple paraclinical tests that led to the definitive diagnosis of racemose neurocysticercosis with secondary cerebral vasculitis. Despite medical and surgical treatment the patient died after multiple complications.
The second case involved a patient with a history of neurocysticercosis, who consulted for chronic intractable vomiting. She required multiple paraclinical tests that led to the diagnosis of vomiting of central origin secondary to racemose neurocysticercosis and entrapment of the fourth ventricle. After medical and surgical treatment the patient showed slight improvement.
In these two cases it was evident how proper interpretation of neuroimages is essential for the diagnosis of racemose neurocysticercosis.
Downloads
References
Del Brutto OH. Neurocysticercosis: A review. Scientific World Journal. 2012;2012:159821. http://dx.doi.org/10.1100/2012/159821
Singh G, Burneo JG, Sander JW. From seizures to epilepsy and its substrates: Neurocysticercosis. Epilepsia. 2013;54:783-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/epi.12159
Hawk M, Shahlaie K, Kim K, Theis J. Neurocysticercosis: A review. Surg Neurol. 2005;63:123-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2004.02.033
Fabiani S, Bruschi F. Neurocysticercosis in Europe: Still a public health concern not only for imported cases. Acta Trop. 2013;128:18-26. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.06.020
Del Brutto OH. Neurocysticercosis. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;121:1445-59. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-7020-4088-7.00097-3
Del Brutto OH. Neurocysticercosis. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2012;18:1392-416. http://dx.doi.org/10.1212/01.CON.0000423853.47770.90
Flisser A. Taeniasis and cysticercosis due to Taenia solium. Prog Clin Parasitol. 1994;4:77-116. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-5-18
Takayanagui OM, Odashima NS. Clinical aspects of neurocysticercosis.Parasitol Int. 2006;55(Suppl.):S111-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2005.11.016
Carabin H, Ndimubanzi PC, Budke CM, Nguyen H, Qian Y, Cowan LD, et al. Clinical manifestations associated with neurocysticercosis: A systematic review. PLoS Negl
Trop Dis. 2011;5:e1152. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0001152
Mahale R, Mehta A, Rangasetty S. Extraparenchymal (racemose) neurocysticercosis and its multitude manifestations: A comprehensive review. J Clin Neurol. 2015;11:203-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2015.11.3.203
Sarria S, Frascheri L, Siurana S, Auger C, Rovira A. Imaging findings in neurocysticercosis. Radiología. 2013;55:130-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rxeng.2011.11.003
Fleury A, Escobar A, Fragoso G, Sciutto E, Larralde C. Clinical heterogeneity of human neurocysticercosis results from complex interactions among parasite, host
and environmental factors. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg.2010;104:243-50. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.trstmh.2010.01.005
Del Brutto OH, Rajshekhar V, White AC Jr, Tsang VC, Nash TE, Takayanagui OM, et al. Proposed diagnostic criteria for neurocysticercosis. Neurology. 2001;57:177-83.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1212/WNL.57.2.177
Zhao JL, Lerner A, Shu Z GX. Imaging spectrum of neurocysticercosis. Radiol Infect Dis. 2015;1:94-102. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jrid.2014.12.001
Zee CS, Go JL, Kim PE DC. Imaging of neurocysticercosis. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2000;10:391-407. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nic.2012.05.004
Lerner A, Shiroishi MS, Zee CS, Law M, Go JL. Imaging of neurocysticercosis. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2012;2:659-76. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nic.2012.05.004
Kimura-Hayama ET, Higuera JA, Corona-Cedillo R, Chávez-Macías L PA, Quiroz-Rojas LY, et al. Neurocysticercosis: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2010;30:1705-19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/rg.306105522
Shandera WX, White AC, Chen JC, Díaz P, Armstrong R. Neurocysticercosis in Houston, Texas. A report of 112 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 1994;73:37-52.
Barinagarrementeria F, Cantú C. Frequency of cerebral arteritis in subarachnoid cysticercosis: An angiographic study. Stroke. 1998;29:123-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.29.1.123
Góngora-Rivera F, Soto-Hernández JL, González D, Cook HJ, Márquez-Caraveo C, Hernández R, et al. Albendazole trial at 15 or 30 mg/kg/day for subarachnoid and
intraventricular cysticercosis. Neurology. 2006;66:436-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000195887.63124.dc
Mitre E, Talaat KR, Sperling MR, Nash NT. Methotrexate as a corticosteroid-sparing agent in complicated neurocysticercosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:549-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/511040
Torres-Corzo JG, Tapia-Pérez JH, Rodríguez-Della Vecchia RR, Chalita-Williams JC, Sánchez-Aguilar M, Sánchez-Rodríguez JJ. Endoscopic management of hydrocephalus
due to neurocysticercosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2010;112:11-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2009.08.022
Husain M, Jha DK, Rastogi M, Husain N, Gupta RK. Neuro-endoscopic management of intraventricular neurocysticercosis (NCC). Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2007;149:341-6.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00701-006-1059-z
Torres-Corzo J, Rodríguez-Della Vecchia R, Rangel-Castilla L. Bruns syndrome caused by intraventricular neurocysticercosis treated using flexible endoscopy. J
Neurosurg. 2006;104:746-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.3171/jns.2006.104.5.746
García HH, Evans CA, Nash TE, Takayanagui OM, White AC Jr, Botero D, et al. Current consensus guidelines for treatment of neurocysticercosis. Clin Microbiol Rev.
;15:747-56. http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/CMR.15.4.747-756.2002
Proaño JV, Torres-Corzo J, Rodríguez-Della Vecchia R, Guizar-Sahagun G, Rangel-Castilla L. Intraventricular and subarachnoid basal cisterns neurocysticercosis: A
comparative study between traditional treatment versus neuroendoscopic surgery. Childs Nerv Syst. 2009;25:1467-75. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00381-009-0933-4
Sotelo J, Marín C. Hydrocephalus secondary to cysticercotic arachnoiditis. A long-term follow-up review of 92 cases. J Neurosurg. 1987;66:686-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.3171/jns.1987.66.5.0686
Matushita H, Pinto FC, Cardeal DD, Teixeira MJ. Hydrocephalus in neurocysticercosis. Childs Nerv Syst. 2011;27:1709-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1500-3
Some similar items:
- Piedad Agudelo, David Botero, Luis Guillermo Palacio, Evaluation of the ELISA method for diagnosis of human cysticercosis in an endemic region. , Biomedica: Vol. 25 No. 4 (2005)
- Jenny Fabiola Hernández, Sofía Duque, Adriana Arévalo, Rafael Guerrero, Rubén Santiago Nicholls, Identification of antigens of Colombian Giardia duodenalis isolates recognized by total IgG and subclasses. , Biomedica: Vol. 23 No. 3 (2003)
- Rosana Natalia Olmos, Sofía Duque, Myriam Consuelo López, Adriana Arévalo, Rafael Guerrero, Martha Patricia Velandia, Ruben Santiago Nicholls, Identification of cyst and trophozoite antigens from Colombian Giardia duodenalis isolates recognized by IgA. , Biomedica: Vol. 23 No. 3 (2003)
- Manuel Toquero, Antonio Morocoima, Elizabeth Ferrer, Seroprevalence and risk factors of cysticercosis in two rural communities in Anzoátegui state, Venezuela , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. Sup.1 (2017): Suplemento 1, Alteraciones del sistema nervioso
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























