Association of polymorphic variants of PTPN22, TNF and VDR genes in children with lupus nephritis: A study in Colombian family triads
Abstract
Introduction: Systemic lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease in which the severity varies according to race, sex and age of onset. This variation is also observed in the genetic markers associated with the disease, including PTPN22, VDR and TNF genes. The genetic stratification in different populations worldwide can influence the variability.
Objective: To analyze the heritability of PTPN22, VDR and TNF genetic variants and their association with pediatric lupus nephritis in Colombian families.
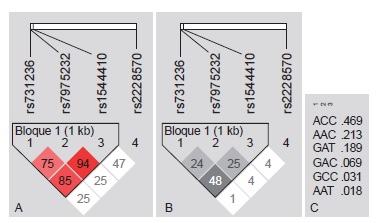
Materials and methods: We conducted a family-based study including 46 triads (case, father and mother). The variants rs2476601 of PTPN22; rs361525 and rs1800629 of TNF, and TaqI [rs731236], ApaI [rs7975232], BsmI [rs1544410] and FokI [rs2228570] of VDR were genotyped by qPCR. The effects of overtransmission of the risk allele from parents to children and linkage disequilibrium at the VDR and TNF loci were estimated.
Results: We found that allele A of rs2476601 in PTPN22 was distributed among 8.69 % (n=16) of the parents and 19.5 % (n=18) of the cases; this allele was overtransmitted from parents to children 17 times more often than the G allele (p=0.028). TNF and VDR polymorphisms did not exhibit transmission disequilibrium. VDR TaqI, ApaI and BsmI variants exhibited linkage disequilibrium.
Conclusion: These findings showed an association between the PTPN22 rs2476601 polymorphism and pediatric lupus nephritis due to its overtransmission in the group of families studied.
Downloads
References
Bonanni A, Vaglio A, Bruschi M, Sinico RA, Cavagna L, Moroni G, et al. Multi-antibody composition in lupus nephritis: Isotype and antigen specificity make the difference. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14:692-702. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2015.04.004
Mohan C, Putterman C. Genetics and pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015;11:329-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2015.33
Pons-Estel BA, Catoggio LJ, Cardiel MH, Soriano ER, Gentiletti S, Villa AR, et al. The GLADEL multinational Latin American prospective inception cohort of 1,214 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Ethnic and disease heterogeneity among “Hispanics”. Medicine (Baltimore). 2004;83:1-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.md.0000104742.42401.e2
Ramírez-Gómez LA, Uribe-Uribe O, Osio-Uribe O, Grisales-Romero H, Cardiel MH, Wojdyla D, et al. Childhood systemic lupus erythematosus in Latin America. The GLADEL experience in 230 children. Lupus. 2008;17:596-604. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0961203307088006
Makashir SB, Kottyan LC, Weirauch MT. Meta-analysis of differential gene co-expression: Application to lupus. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2015:443-54. http://dx.doi.org/10.1142/9789814644730_0042
Dema B, Charles N. Advances in mechanisms of systemic lupus erythematosus. Discov Med. 2014;17:247-55.
Kunz M. Lupus erythematosus. Part I: Epidemiology, genetics and immunology. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:709-19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/ddg.12165
Sinha R, Raut S. Pediatric lupus nephritis: Management update. World J Nephrol. 2014;3:16-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v3.i2.16
Ortega LM, Schultz DR, Lenz O, Pardo V, Contreras GN. Review: Lupus nephritis: Pathologic features, epidemiology and a guide to therapeutic decisions. Lupus. 2010;19:557-74. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0961203309358187
Shi L, Wei Y, Xun W, Han D. Meta-analysis of the correlation between PTPN22 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2013;25(Suppl.4):22S-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1010539513496268
Ramírez M, Quintana G, Díaz-Gallo LM, Caminos J, Garcés M, Cepeda L, et al. The PTPN22 C1858T variant as a risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus but not for systemic sclerosis in the Colombian population. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012;30:520-4.
Hu W, Niu G, Lin Y, Chen X, Lin L. Impact of the polymorphism in vitamin D receptor gene BsmI and the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus: An updated metaanalysis. Clin Rheumatol. 2015;35:927-34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3157-x
Mao S, Huang S. Association between vitamin D receptor gene BsmI, FokI, ApaI and TaqI polymorphisms and the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus: A meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int. 2014;34:381-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2898-6
Pan HF, Leng RX, Wang C, Qin WZ, Chen LL, Zha ZQ, et al. Association of TNF-alpha promoter-308 A/G polymorphism with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus: A metaanalysis. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32:2083-92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-1924-9
Zou YF, Feng XL, Pan FM, Su H, Tao JH, Ye DQ. Metaanalysis of TNF-alpha promoter - 238A/G polymorphism and SLE susceptibility. Autoimmunity. 2010;43:264-74.
http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/08916930903509049
Niu Z, Zhang P, Tong Y. Value of HLA-DR genotype in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis: A metaanalysis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2015;18:17-28. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.12528
Pan CF, Wu CJ, Chen HH, Dang CW, Chang FM, Liu HF, et al. Molecular analysis of HLA-DRB1 allelic associations with systemic lupus erythematous and lupus nephritis in Taiwan. Lupus. 2009;18:698-704. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0961203308101955
Ghodke-Puranik Y, Niewold TB. Immunogenetics of systemic lupus erythematosus: A comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 2015;64:125-36. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2015.08.004
Lewis CM. Genetic association studies: Design, analysis and interpretation. Brief Bioinform. 2002;3:146-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bib/3.2.146
Campbell H, Rudan I. Interpretation of genetic association studies in complex disease. Pharmacogenomics J. 2002;2:349-60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500132
Robinson MR, Wray NR, Visscher PM. Explaining additional genetic variation in complex traits. Trends Genet. 2014;30124-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2014.02.003
Kaufman JS, Cooper RS. Commentary: Considerations for use of racial/ethnic classification in etiologic research. Am J Epidemiol. 2001;154:291-8. http://dx.doi.org/0.1093/aje/154.4.291
Jenkins JM, McGowan P, Knafo-Noam A. Parentoffspring transaction: Mechanisms and the value of within family designs. Horm Behav. 2016;77:53-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.06.018
Infante-Rivard C, Mirea L, Bull SB. Combining case control and case-trio data from the same population in genetic association analyses: Overview of approaches and illustration with a candidate gene study. Am J Epidemiol.2009;170:657-64. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwp180
Santos JL, Pérez F, Carrasco E, Albala C. Uso de tríos caso-padres en estudios epidemiológicos de asociación entre polimorfismos genéticos y enfermedades complejas. Rev Med Chil. 2002;130:1307-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0034-98872002001100016
Guo W, Fung WK. Combining the case-control methodology with the small size transmission/disequilibrium test for multiallelic markers. Eur J Hum Genet. 2005;13:1007-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201453
Hochberg MC. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:1725. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(199709)40:9<1725::AIDART29>3.0.CO;2-Y
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16:1215. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/16.3.1215
Laird NM, Lange C. Family-based designs in the age of large-scale gene-association studies. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:385-94. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrg1839
Some similar items:
- Carolina Gómez, Ruth María Eraso, Carlos A. Aguirre, María del Pilar Pérez, Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: pediatric case presentation , Biomedica: Vol. 30 No. 4 (2010)
- Gustavo Adolfo Guerrero, Luis Francisco Guerrero, Tatiana González , Non-lupus full house nephropathy in pediatrics: Case reports , Biomedica: Vol. 40 No. 2 (2020)
- Ana Victoria Valencia, Ana Lucía Páez, María Elena Sampedro, Clara Ávila, Julio Cesar Cardona, Catalina Mesa, Lina Galvis, Jaime Carrizosa, Mauricio Camargo, Andrés Ruíz, William Cornejo, Gabriel Bedoya, Evidence for association and epistasis between the genetic markers SLC6A4 and HTR2A in autism etiology , Biomedica: Vol. 32 No. 4 (2012)
- Juan Manuel Anaya, Mauricio Uribe, Adriana Pérez, Juan F. Sánchez, Luis F. Pinto, José F. Molina, María C. Londoño, Martha E. Cadavid, Gustavo Matute, Clinical and immunological factors associated with lupus nephritis in patients from northwestern Colombia. , Biomedica: Vol. 23 No. 3 (2003)
- Diana María Valencia, Carlos Andrés Naranjo, María Victoria Parra, María Antonieta Caro, Ana Victoria Valencia, Carlos José Jaramillo, Gabriel Bedoya, Association and interaction of AGT, AGTR1, ACE, ADRB2, DRD1, ADD1, ADD2, ATP2B1, TBXA2R and PTGS2 genes on the risk of hypertension in Antioquian population , Biomedica: Vol. 33 No. 4 (2013)
- Mauricio Restrepo, Lilliana María Giraldo, Luisa Fernanda Montoya, Adriana Lucía Vanegas, Carlos Horacio Muñoz, Gloria María Vásquez, Luis Alonso González, Pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in a pregnant woman with systemic lupus erythematous , Biomedica: Vol. 38 No. Sup.1 (2018): Suplemento 1, Enfermedades crónicas
- Diana Clobeth Sarrazola, Alejandra Marcela Rodríguez, Martín Toro, Alejandra Vélez, Jorge García-Ramírez, María Victoria Lopera, Cristiam M. Álvarez, Vital Balthazar González †, Juan Manuel Alfaro, Nicolás Pineda-Trujillo, Classical HLA alleles tag SNP in families from Antioquia with type 1 diabetes mellitus , Biomedica: Vol. 38 No. 3 (2018)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























