Phylogenetic signal at the Cytb-SertRNA-IG1-ND1 mitochondrial region in Anopheles (Kerteszia) neivai Howard, Dyar & Knab, 1913
Abstract
Introduction: Mitochondrial DNA has proven its utility for the study of insect evolution. Genes such as cytochrome b (Cytb) and the transfer gene for serine (SertRNA) can be used to compare closely related organisms.
Objective: The phylogenetic utility of Cytb-SertRNA-IG1-ND1 was tested for polymorphisms, and secondary structure modeling in SertRNA was done to detect possible cryptic species in Anopheles neivai.
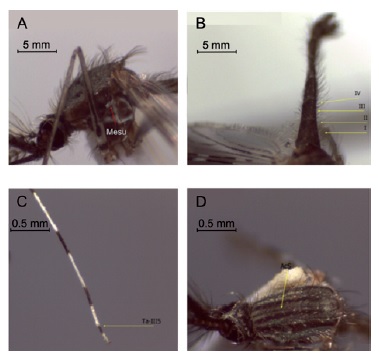
Materials and methods: Specimens from Colombia, Guatemala, and the type locality in Panamá were collected and sequenced for specimen comparison based on DNA polymorphisms, and secondary structure modeling for the SertRNA gene.
Results: Thirty-six sequences for A. neivai and A. pholidotus were obtained.
Conclusions: Polymorphic variants were detected in A. neivai for Cytb-SertRNA-IG1- ND1. Despite this variation in A. neivai, cryptic species could not be detected.
Downloads
References
Zavortink TJ. Mosquito studies (Diptera, Culicidae) XXIX. A review of the subgenus Kerteszia of Anopheles. Contrib Am Entomol Inst. 1973;9:1-54.
Escovar J, González R, Quiñones ML. Anthropophilic biting behaviour of Anopheles (Kerteszia) neivai Howard, Dyar & Knab associated with Fishermen’s activities in a malaria-endemic area in the Colombian Pacific. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2013;108:1057-64. https://doi.org/ 10. 1590/0074-0276130256
Murillo C, Jaramillo C, Quintero J, Suárez M. Biología de Anopheles (Kerteszia) neivai H., D. & K., 1913 (Diptera: Culicidae) en la costa pacífica de Colombia. IV Estructura etárea y transmisión de malaria. Rev Saúde Pública. 1989;23:363-7. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-8910198900 0500001
González R, Carrejo N. Introducción al estudio taxonómico de Anopheles de Colombia: claves y notas de distribución. Cali: Programa Editorial Universidad del Valle; 2009. p. 260.
Gutiérrez LA, Naranjo N, Jaramillo LM, Muskus C, Luckhart S, Conn JE, et al. Natural infectivity of Anopheles species from the Pacific and Atlantic Regions of Colombia. Acta Trop. 2008; 107:99-105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2008.04.019
Murillo C, Astaiza R, Fajardo P. Biología de Anopheles (Kerteszia) neivai H., D. & K., 1913 (Diptera:Culicidae) en la Costa Pacífica de Colombia. III Medidas de luminosidad y el comportamiento de picadura. Rev Saúde Pública. 1988;22: 109-12. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-89101988000200006
Astaiza R, Murillo C, Fajardo P. Biología de Anopheles (Kerteszia) neivai H., D. & K., 1913 (Diptera: Culicidae) en la Costa Pacífica de Colombia. II Fluctuación de la población adulta. Rev Saúde Pública. 1988;22:101-8. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-89101988000200005
Collins FH, Paskewitz SM. A review of the use of ribosomal DNA (rDNA) to differentiate among cryptic Anopheles species. Insect Mol Biol. 1996;5:1-9. https://doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1365-2583.1996.tb00034.x
Rosero DA, Jaramillo LM, Gutiérrez LA, Conn JE, Correa MM. Genetic diversity of Anopheles triannulatuss. l. (Diptera: Culicidae) from Northwestern and Southeastern Colombia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012;87:910-20. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.2012.12-0285
Lehr MA, Kilpatrick CW, Wilkerson RC, Conn JE. Cryptic species in the Anopheles (Nyssorhynchus) albitarsis (Diptera: Culicidae) complex: Incongruence between random amplified polymorphic DNA-polymerase chain reaction identification and analysis of mitochondrial DNA COI gene. Ann Entomol Soc Am. 2005;98:908-17. https://doi.org/10.1603/0013-8746(2005)098[0908:CSITAN]2.0.CO;2
Montoya-Lerma J, Solarte Y, Giraldo-Calderón GI, Quiñones ML, Ruiz-López F, Wilkerson RC, et al. Malaria vector species in Colombia: A review. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2011;106:223-38. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0074-0276 2011000900028
Linton Y-MM. Mosquito Barcoding Initiative. The first barcode release paper. Third International Barcode of Life Conference. México: Consortium for the Barcoding of Life-CBOL. – 2009. Accessed: January 15th, 2017. Available from: https://vimeo.com/8996184
Krzywinski J, Wilkerson RC, Besansky NJ. Evolution of mitochondrial and ribosomal gene sequences in Anophelinae (Diptera: Culicidae): Implications for phylogeny recons-truction. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2001;18:479-87. https://doi.org/10.1006/mpev.2000.0894
Freitas LA, Russo CA, Voloch CM, Mutaquiha OC, Marques LP, Schrago CG. Diversification of the genus Anopheles and a neotropical clade from the late Cretaceous. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0134462. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0134462
Foster PG, Bergo ES, Bourke BP, Oliveira TM, Nagaki SS, Sant’Ana DC, et al. Phylogenetic analysis and DNA-based species confirmation in Anopheles (Nyssorhynchus). PLoS One. 2013;8:e54063. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054063
Ruiz-López F, Wilkerson RC, Conn JE, McKeon SN, Levin DM, Quiñones ML, et al. DNA barcoding reveals both known and novel taxa in the Albitarsis group (Anopheles: Nyssorhynchus) of Neotropical malaria vectors. Parasit Vectors. 2012;5:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-5-44
Moreno M, Bickersmith S, Harlow W, Hildebrandt J, McKeon SN, Silva-do-Nascimento TF, et al. Phylogeo-graphy of the neotropical Anopheles triannulatus complex (Diptera: Culicidae) supports deep structure and complex patterns. Parasit Vectors. 2013;6:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/ 1756-3305-6-47
Hoy AM. Insect Molecular Genetics. An introduction to principles and applications. 3rd edition. Boston, MA: Academic Press; 2013. p. 364.
Rubinoff D, Holland BS. Between two extremes: Mito-chondrial DNA is neither the panacea nor the nemesis of phylogenetic and taxonomic inference. Syst Biol. 2005;54: 952-61. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150500234674
Hurst GD, Jiggins FM. Problems with mitochondrial DNA as a marker in population, phylogeographic and phyloge-netic studies: The effects of inherited symbionts. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci. 2005;272:1525-34. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2005.3056
Norris LC, Norris DE. Phylogeny of anopheline (Diptera: Culicidae) species in southern Africa, based on nuclear and mitochondrial genes. J Vector Ecol. 2015;40:16-27. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvec.12128
Harbach RE. The phylogeny and classification of Anopheles. In: Manguin S, editor. Anopheles mosquitoes - New insights into malaria vectors. Rijeka: InTech; 2013.
López-Rubio A, Suaza-Vasco J, Marcet PL, Ruiz-Molina N, Cáceres L, Porter C, Uribe S. Use of DNA barcoding to distinguish the malaria vector Anopheles neivai in Colom-bia. Zootaxa. 2016;4175:377-89. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4175.4.7
Danforth BN, Lin CP, Fang J. How do insect nuclear ribosomal genes compare to protein-coding genes in phylo-genetic utility and nucleotide substitution patterns? Syst Entomol. 2005;30:549-62. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3113.2005.00305.x
Krzywinski J, Wilkerson RC, Besansky NJ. Toward understanding Anophelinae (Diptera, Culicidae) phylogeny: Insights from nuclear single-copy genes and the weight of evidence. Syst Biol. 2001;50:540-56. https://doi.org/10. 1080/10635150119931
Vivero RJ, Contreras-Gutiérrez MA, Bejarano EE. Análisis de la estructura primaria y secundaria del ARN de transferencia mitocondrial para serina en siete especies de Lutzomyia. Biomédica. 2007;27:429-38. https://doi.org/10. 7705/biomedica.v27i3.205
Yona AH, Bloom-Ackermann Z, Frumkin I, Hanson-Smith V, Charpak-Amikam Y, Feng Q, et al. tRNA genes rapidly change in evolution to meet novel translational demands. Elife. 2013;2:e01339. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.01339.001
Kumazawa Y, Nishida M. Sequence evolution of mito-chondrial tRNA genes and deep-branch animal phylo-genetics. J Mol Evol. 1993;37:380-98. https://doi.org/10. 1007/BF00178868
Marín MA, López A, Uribe SI. Interspecific variation in mitochondrial serine transfer RNA (UCN) in Euptychiina butterflies (Lepidoptera: Satyrinae): Structure and alignment. Mitochondrial DNA. 2012;23:208-15. https://doi.org/10.3109/19401736.2012.668895
Keller A, Förster F, Müller T, Dandekar T, Schultz J, Wolf M. Including RNA secondary structures improves accuracy and robustness in reconstruction of phylogenetic trees. Biol Direct. 2010;5:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6150-5-4
Pecor J, Gaffigan T. Collecting, rearing, preserving, mounting and shipping techniques for mosquitoes. Walter Reed Bio-systematics Unit. 1997. Accessed: January 4th, 2017. Available from: http://www.wrbu.org/about/techniques.html
González R, Carrejo N. Introducción al estudio taxonómico de Anopheles de Colombia: claves y notas de distribución. Cali: Programa Editorial Universidad del Valle; 2009. p. 260.
Harrison BA, Ruiz-López F, Falero GC, Savage HM, Pecor JE, Wilkerson RC. Anopheles (Kerteszia) lepidotus (Diptera: Culicidae), not the malaria vector we thought it was: Revised male and female morphology; larva, pupa, and male genitalia characters; and molecular verification. Zootaxa. 2012;3218:1-17.
Uribe SI, Porter CH, Vélez ID. Amplificación y obtención de secuencias de rRNA mitocondrial en Lutzomyia spp. (Diptera: Psychodidae), vectores de leishmaniosis. Rev Colomb Entomol. 1998;23:177-85.
Ready PD, Day JC, de Souza A, Rangel EF, Davies CR. Mitochondrial DNA characterization of populations of Lutzomyia whitmani (Diptera: Psychodidae) incriminated in the peri-domestic and silvatic transmission of Leishmania species in Brazil. Bull Entomol Res. 1997;87:187-95. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485300027346
Simon C, Frati F, Beckenbach A, Crespi B, Liu H, Flook P. Evolution, weighting, and phylogenetic utility of mito-chondrial gene sequences and a compilation of conserved polymerase chain reaction primers. Ann Entomol Soc Am. 1994;87:651-701. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/87.6.651
Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A, Stones-Havas S, Cheung M, Sturrock S, et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2012;28: 1647-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199
Johnson M, Zaretskaya I, Raytselis Y, Merezhuk Y, McGinnis S, Madden TL. NCBI BLAST: A better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:W5-9. https://doi.org/10.1093%2Fnar%2Fgkn201
Hlaing T, Tun-Lin W, Somboon P, Socheat D, Setha T, Min S, et al. Mitochondrial pseudogenes in the nuclear genome of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes: Implications for past and future population genetic studies. BMC Genet. 2009;10:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-10-11
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, Mcgettigan PA, McWilliam H, et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:2947-8. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Librado P, Rozas J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics. 2009; 25:1451-2. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187
Lorenz R, Bernhart SH, Höner-zuSiederdissen C, Tafer H, Flamm C, Stadler PF, et al. ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol Biol. 2011;6:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-7188-6-26
Mathews DH, Disney MD, Childs JL, Schroeder SJ, Zuker M, Turner DH. Incorporating chemical modification constraints into a dynamic programming algorithm for prediction of RNA secondary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:7287-92. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas. 0401799101
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33:1870-4. https://doi.org/10. 1093/molbev/msw054
Tavaré S. Some probabilistic and statistical problems in the analysis of DNA sequences. Lect Math Life Sci. 1986;17: 57-86.
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol. 2010;59:307-21. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syq010
Yule GU. A mathematical theory of evolution based on the conclusions of Dr. J.C. Willis, F.R.S. J R Stat Soc. 1925;88:433-6. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.1925.0002
Bouckaert RR, Heled J, Kühnert D, Vaughan T, Wu C-H, Xie D, et al. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014;10:e1003537. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003537
Münkemüller T, Lavergne S, Bzeznik B, Dray S, Jombart T, Schiffers K, et al. How to measure and test phyloge-netic signal. Methods Ecol Evol. 2012;3:743-56. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2041-210X.2012.00196.x
Blomberg SP, Garland T, Ives AR. Testing for phyloge-netic signal in comparative data: Behavioural traits are more labile. Evolution (N Y). 2003;57:717-45. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0014-3820.2003.tb00285.x
Felsenstein J. Inferring Phylogenies. Sunderland: Sinauer Associates; 2004. p. 664.
Kolaczkowski B, Thornton JW. Long-branch attraction bias and inconsistency in Bayesian phylogenetics. PLoS One. 2009;4:e7891. https://doi.org10.1371/journal.pone. 0007891
Susko E. Bayesian long branch attraction bias and correc-tions. Syst Biol. 2015;64:243-55. https://doi.org10.1093/sysbio/syu099
Caetano-Anollés G, Sun FJ. The natural history of transfer RNA and its interactions with the ribosome. Front Genet. 2014;5:1-5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2014.00127
Sun FJ, Caetano-Anollés G. The origin and evolution of tRNA inferred from phylogenetic analysis of structure. J Mol Evol. 2008;66:21-35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-007-9050-8
Meer M V, Kondrashov AS, Artzy-Randrup Y, Kondrashov FA. Compensatory evolution in mitochondrial tRNAs navigates valleys of low fitness. Nature. 2010;464:279-82. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08691
Zhang J, Ferré-D’Amaré A. The tRNA elbow in structure, recognition and evolution. Life. 2016;6:3. https://doi.org/10. 3390/life6010003
Meiklejohn CD, Holmbeck MA, Siddiq MA, Abt DN, Rand DM, Montooth KL. An incompatibility between a mitochondrial tRNA and its nuclear-encoded trnasynthetase compromises development and fitness in Drosophila. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003238. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003238
Pérez-Doria A, Bejarano EE, Sierra D, Vélez ID. Molecular evidence confirms the taxonomic separation of Lutzomyia tihuiliensis from Lutzomyia pia (Diptera: Psychodidae) and the usefulness of pleural pigmentation patterns in species identification. J Med Entomol. 2008;45:653-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/45.4.653
Dotson EM, Beard CB. Sequence and organization of the mitochondrial genome of the Chagas disease vector, Triatoma dimidiata. Insect Mol Biol. 2001;10:205-15. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2583.2001.00258.x
Kim I, Lee EM, Seol KY, Yun EY, Lee YB, Hwang JS, et al. The mitochondrial genome of the Korean hairstreak, Coreana raphaelis (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae). Insect Mol Biol. 2006;15:217-25. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2583. 2006.00630.x
Beard CB, Hamm DM, Collins FH. The mitochondrial genome of the mosquito Anopheles gambiae: DNA sequence, genome organization, and comparisons with mitochondrial sequences of other insects. Insect Mol Biol. 1993;2:103-24. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2583.1993.tb00131.x
Cameron SL, Whiting MF. The complete mitochondrial genome of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta, (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Sphingidae), and an examination of mitochondrial gene variability within butterflies and moths. Gene. 2008;408:112-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2007. 10.023
Sheffield NC, Song H, Cameron SL, Whiting MF. A comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes in coleoptera (Arthropoda: Insecta) and genome descriptions of six new beetles. Mol Biol Evol. 2008;25:2499-509. https://doi.org/ 10.1093/molbev/msn198
Dayrat B. Towards integrative taxonomy. Biol J Linn Soc. 2005;85:407-15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2005. 00503.x
Some similar items:
- Lorena I. Orjuela, Manuela Herrera, Holmes Erazo, Martha L. Quiñones, Anopheles species present in the department of Putumayo and their natural infectivity with Plasmodium , Biomedica: Vol. 33 No. 1 (2013)
- Sandy Milena Caldera, María Cristina Jaramillo, Suljey Cochero, Alveiro Pérez-Doria, Eduar Elías Bejarano, Genetic differences between populations of Aedes aegypti from municipalities in northern Colombia, with high and low dengue incidence , Biomedica: Vol. 33 (2013): Suplemento 1, Fiebres hemorrágicas
- Carolina Montoya, Priscila Bascuñán, Julián Rodríguez-Zabala, Margarita M. Correa, Abundance, composition and natural infection of Anopheles mosquitoes from two malaria-endemic regions of Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. Sup. 2 (2017): Suplemento 2, Entomología médica, 2017
- Pilar Jiménez, Jan E. Conn, Robert Wirtz, Helena Brochero, Anopheles (Díptera: Culicidae) vectors of malaria in Puerto Carreño municipality, Vichada, Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 32 (2012): Suplemento 1, Malaria
- Lyda Osorio, Ligia del Pilar Pérez, Iveth J. González, Assessment of the efficacy of antimalarial drugs in Tarapacá, in the Colombian Amazon basin , Biomedica: Vol. 27 No. 1 (2007)
- Liliana Santacoloma, Tania Tibaduiza, Marcela Gutiérrrez, Helena Brochero, Susceptibility to insecticides of Anopheles darlingi Root 1840, in two locations of the departments of Santander and Caquetá, Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 32 (2012): Suplemento 1, Malaria
- Sandra Milena Barrera, Manuel Alberto Pérez, Angélica Knudson, Rubén Santiago Nicholls, Ángela Patricia Guerra, Genotypic survery of Plasmodium falciparum based on the msp1, msp2 and glurp genes by multiplex PCR , Biomedica: Vol. 30 No. 4 (2010)
- Margarita Arboleda, María Fernanda Pérez, Diana Fernández, Luz Yaned Usuga, Miler Meza, Clinical and laboratory profile of Plasmodium vivax malaria patients hospitalized in Apartadó, , Biomedica: Vol. 32 (2012): Suplemento 1, Malaria
- Amanda Maestre, Jaime Carmona-Fonseca, Amanda Maestre, Alta frecuencia de mutaciones puntuales en pfcrt de Plasmodium falciparum y emergencia de nuevos haplotipos mutantes en Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 4 (2008)
- Rosa Magdalena Uscátegui, Adriana M. Correa, Jaime Carmona-Fonseca, Changes in retinol, hemoglobin and ferritin concentrations in Colombian children with malaria , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 2 (2009)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























