Thromboembolic complications associated with tuberculosis: A pediatric case report
Abstract
Tuberculosis is one of the most common infectious diseases around the world. With timely diagnosis and treatment, mortality in children is practically zero. It is usually associated with a diverse number of complications that can cause significant morbidity and mortality, such as deep and superficial vein thrombosis. This event has been associated with a procoagulant state caused by the systemic inflammatory response to infection.
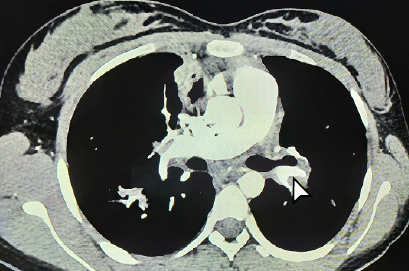
We report the case of a 14-year-old adolescent with pulmonary tuberculosis under the initial four-drug regimen. She presented two episodes of venous thromboembolism, the first in the kidneys and the second in the lungs. After ruling out diseases such as nephrotic and antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, chest and abdomen tomographies were performed as a fundamental tool for the diagnosis. Thereafter, treatment with low molecular weight heparin was initiated and the symptoms improved. Given the requirement for anticoagulation, further image studies could not be done.
Thromboembolic complications in patients with no other risk factors, associated only with a previous pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis, offer evidence to consider the procoagulant effect resulting from the systemic inflammatory response that, by itself, could be the cause of a serious complication, often underdiagnosed but also preventable. Therefore, it is recommended to consider the predisposition for venous thromboembolism in these patients and to establish strict surveillance so early anticoagulant therapy can be provided to prevent adverse outcomes.
Downloads
References
Holmberg PJ, Temesgen Z, Banerjee R. Tuberculosis in children. Pediatr Rev. 2019;40:168-78. https://doi.org/10.1542/pir.2018-0093
Pérez-Vélez CM, Marais BJ. Tuberculosis in children. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:348-61. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1008049
Posada A, Echeverri D, Bolaño, J, Ramírez H, García J. Embolismo pulmonar masivo en un paciente con tuberculosis pulmonar: una entidad más que una asociación. Acta Colombiana de Cuidado Intensivo. 2015;15:143-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acci.2015.02.003
Kwas H, Habibech S, Zendah I, Elmjendel I, Ghedira H. Pulmonary embolism and tuberculosis. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2014;22:487-90. https://doi.org/10.1177/0218492313485071
Dentan C, Epaulard O, Seynaeve D, Genty C, Bosson J-L. Active tuberculosis and venous thromboembolism: Association according to International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision Hospital Discharge Diagnosis Codes. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;58:495-501. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cit780
Park H, Cha SI, Lim JK, Lee SY, Kim CH, Park JY, et al. Clinical characteristics of coexisting pulmonary thromboembolism in patients with respiratory tuberculosis. Am J Med Sci. 2017;353:166-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjms.2016.11.025
Bessis S, Bertin D, Million M, Meddeb L, Drancourt M, Lagier JC, et al. Thromboses in tuberculosis are linked to antiphosphatidylethanolamine antibodies levels: A cross-sectional study. J Clin Tuberc Mycobact Dis. 2019;15:100092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jctube.2019.100092
Kager LM, Blok DC, Lede IO, Rahman W, Afroz R, Bresser P, et al. Pulmonary tuberculosis induces a systemic hypercoagulable state. J Infect. 2015;70:324-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2014.10.006
Shah PA. Pulmonary tuberculosis with deep venous thrombosis. Webmed Central. 2011;2. https://doi.org/10.9754/journal.wmc.2011.002093
Huei TJ, Henry TCL, Ho CA, Mohamad Y. A rare case of ileocecal tuberculosis with pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11:PD03-4. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2017/27923.10192
White N. Venous thrombosis and rifampicin. Lancet. 1989;334:434-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90603-x
Naithani R, Agrawal N, Choudhary VP. Deep venous thrombosis associated with tuberculosis. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2007;18:377-80. https://doi.org/10.1097/MBC.0b013e3280d942b4
Goncalves IM, Alves DC, Carvalho A, do Ceu Brito M, Calvario F, Duarte R. Tuberculosis and venous thromboembolism: A case series. Cases J. 2009;2:9333. https://doi.org/10.1186/1757-1626-2-9333
Suárez S, Artilez J, Balda I, Melado P, Arkuch ME, Ayala E, et al. La tuberculosis como factor de riesgo de trombosis venosa. Anales de Medicina Interna. 1993;10:398-400.
Kechaou I, Cherif E, Ben Hassine L, Khalfallah N. Deep vein thrombosis and tuberculosis: A causative link? BMJ Case Rep. 2014;2014:bcr2013200807. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2013-200807
Nkoke C, Bain LE, Jingi AM, Kotta S, Mintom P, Menanga A. Bilateral pulmonary embolism in a patient with pulmonary tuberculosis: A rare association in Yaoundé, Cameroon. Pan Afr Med J. 2014;17:262. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2014.17.262.4107
Ekukwe NC, Bain LE, Jingi AM, Sylvia K, Mintom P, Menanga A. Bilateral pulmonary embolism in a patient with pulmonary tuberculosis: A rare association in Yaoundé, Cameroon. Pan Afr Med J. 2014;17:262. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2014.17.262.4107
Monagle P, Newall F. Management of thrombosis in children and neonates: Practical use of anticoagulants in children. Hematology. 2018;2018:399-404. https://doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2018.1.399
Kumarihamy KW, Ralapanawa DM, Jayalath WA. A rare complication of pulmonary tuberculosis: A case report. BMC Res Notes. 2015;8:39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-015-0990-6
Kouismi H, Laine M, Bourkadi J-E, Iraqi G. Association of deep venous thrombosis with pulmonary tuberculosis. Egypt J Chest Dis Tuberc. 2013;62:541-3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcdt.2013.06.001
Monagle P, Chan AKC, Goldenberg NA, Ichord RN, Journeycake JM, Nowak-Göttl U, et al. Antithrombotic therapy in neonates and children. Chest. 2012;141:e737S-e801S. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.11-2308
Sangani J, Mukherjee S, Biswas S, Chaudhuri T, Ghosh G. Tuberculosis and acute deep vein thrombosis in a paediatric case. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9:SD01-02. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2015/11809.6078
Some similar items:
- Nelson José Alvis-Zakzuk, María de los Ángeles Carrasquilla, Verónica Jhajaira Gómez, Jaime Robledo, Nelson Rafael Alvis-Guzmán, José Mauricio Hernández, Diagnostic accuracy of three technologies for the diagnosis of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. 3 (2017)
- Helena Hernández-Cuervo, Solangy Usme, Juan José Yunis, Frequently associated genotypes to thrombophilia , Biomedica: Vol. 34 No. 1 (2014)
- Nelsy Loango, Martha Lucía Gallego, Beatriz Restrepo, Patricia Landázuri, Gender, age and plasma lipids differences associated with apolipoprotein E polymorphism in school children , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
- Juan Gabriel Bueno-Sánchez, Jairo René Martínez-Morales, Elena E. Stashenko, Wellman Ribón, Anti-tubercular activity of eleven aromatic and medicinal plants occurring in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 1 (2009)
- Andrés Leonardo González, Ruth Aralí Martínez, Luis Ángel Villar, Clinical evolution of dengue in hospitalized patients , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 4 (2008)
- María Consuelo Garzón, Dailyn Yorledy Angée, Claudia Llerena, Dora Leticia Orjuela, Jorge Ernesto Victoria, Surveillance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistance to antituberculosis drugs , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 3 (2008)
- Elpidia Poveda, Ney E. Callas, César M. Baracaldo, Carlina Castillo, Patricia Hernández, Leptin levels in school age children associated with anthropometric measurements and lipid profiles , Biomedica: Vol. 27 No. 4 (2007)
- Leandro Galvis, Ángel Y. Sánchez, Leonardo F. Jurado, Martha I. Murcia, Tuberculosis associated with tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists, case description and analysis of reported cases in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 38 No. 1 (2018)
- Yordanis Enríquez, Claudia Rebeca Cahui , Giovani Martín Díaz , An ecological approach to the characteristics and determinants of adolescent sexual violence in Perú , Biomedica: Vol. 44 No. 2 (2024): Publicación anticipada, junio
- María Imaz, Sonia Allassia, Mónica Aranibar, Alba Gunia, Susana Poggi, Ana Togneri, Lidia Wolff, Group of Implementation of Fluorescence, Performance of LED fluorescence microscopy for the detection of acid-fast bacilli from respiratory samples in peripheral laboratories in Argentina , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. 2 (2017)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























