Velamentous cord insertion, ischemic-hypoxic encephalopathy, and neurological rehabilitation: A case report
Abstract
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is a frequent and important cause of neurological problems in term and preterm newborns. A sentinel event of this entity is the vasa previa, specifically when there is an abnormality of the placenta such as a velamentous cord insertion. Some reports have shown the association between these two entities, but those regarding the recovery process and the neurological prognosis of children with both conditions are scarce.
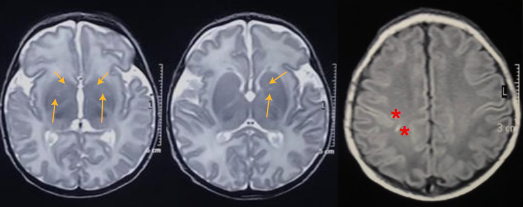
We present the case of a patient with a history of velamentous cord insertion and hypoxicischemic encephalopathy who received therapeutic hypothermia (cool cap). We describe his neurological rehabilitation process and we calculated the percentage of probability of presenting this condition compared to the population without these factors. The patient was a five-year-old boy with an Apgar index at birth equal to zero at one minute and equal to two at fifteen minutes who developed severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy secondary to a velamentous cord insertion without prenatal diagnosis and a marked initial neurological and multisystemic compromise. The recovery process included early multidisciplinary management in the neonatal intensive care unit and a focus on early neurological habilitation.
The patient is currently in school and he undergoes comprehensive therapies; on physical examination, he presents no motor or sensory deficiencies. His neuropsychological test suggests the risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Children with severe hypoxicischemic encephalopathy usually have disabilities due to motor, cognitive, and/or behavioral deficiencies.
Downloads
References
Lemyre B, Chau V. Hypothermia for newborns with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J.Paediatr Child Health. 2018;23:285-91. https://doi.org/10.1093/pch/pxy028
García-Alix A, Martínez M, Arnaez J, Valverde E, Quero J. Asfixia intraparto y encefalopatía hipóxico-isquémica. Asfixia intraparto y encefalopatía hipóxico-isquémica: protocolos diagnósticos terapéuticos de la AEP: Neonatología. Madrid: Asociación Española de Pediatría; 2008. p. 242-52.
Graham EM, Ruis KA, Hartman AL, Northington FJ, Fox HE. A systematic review of the role of intrapartum hypoxia-ischemia in the causation of neonatal encephalopathy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;199:587-95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2008.06.094
Nasiell J, Papadogiannakis N, Löf E, Elofsson F, Hallberg B. Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in newborns linked to placental and umbilical cord abnormalities. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;29:721-6. https://doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2015.1015984
Wiedaseck S, Monchek R. Placental and cord insertion pathologies: Screening, diagnosis, and management. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2014;59:328-35. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmwh.12189
Cunningham FG, Leveno KJ, Bloom SL, Dashe JS, Hoffman BL, Casey BM, et al. Placental abnormalities. Williams Obstetrics. 25th. edition. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2018. p. 111-23.
de Los Reyes S, Henderson J, Eke AC. A systematic review and meta-analysis of velamentous cord insertion among singleton pregnancies and the risk of preterm delivery. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2018;142:9-14. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijgo.12489
Thornberg E, Thiringer K, Odeback A, Milsom I. Birth asphyxia: Incidence, clinical course and outcome in a Swedish population. Acta Paediatr. 1995;84:927-32. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.1995.tb13794.x
Pappas A, Shankaran S, McDonald SA, Vohr BR, Hintz SR, Ehrenkranz RA, et al. Cognitive outcomes after neonatal encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 2015;135:e624-34. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2014-1566
Robertson C, Finer N. Term infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: Outcome at 3.5 years. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1985;27:473-84. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.1985.tb04571
Walsh BH, Neil J, Morey J, Yang E, Silvera MV, Inder TE, et al. The frequency and severity of magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities in infants with mild neonatal encephalopathy. J Pediatr. 2017;187:26-33.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.03.065
Holmes GL, Lombroso CT. Prognostic value of background patterns in the neonatal EEG. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1993;10:323-52. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004691-199307000-00008
Awal MA, Lai MM, Azemi G, Boashash B, Colditz PB. EEG background features that predict outcome in term neonates with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy: A structured review. Clin Neurophysiol. 2016;127:285-96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2015.05
Jain SV, Mathur A, Srinivasakumar P, Wallendorf M, Culver JP, Zempel JM. Prediction of neonatal seizures in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy using electroencephalograph power analyses. Pediatr Neurol. 2017;67:64-70.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2016.10.019
Kharoshankaya L, Stevenson NJ, Livingstone V, Murray DM, Murphy BP, Ahearne CE, et al. Seizure burden and neurodevelopmental outcome in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2016;58:1242-8. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.13215
Fitzgerald MP, Massey SL, Fung FW, Kessler SK, Abend NS. High electroencephalographic seizure exposure is associated with unfavorable outcomes in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Seizure. 2018;61:221-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2018.09.003
Pisani F, Spagnoli C. Monitoring of newborns at high risk for brain injury. Ital J Pediatr. 2016;42:48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-016-0261-8
Chiang MC, Jong YJ, Lin CH. Therapeutic hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Neonatol. 2017;58:475-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedneo.2016.11.001
Nariño O, Vera C, Carvajal J. Hipotermia corporal total en neonatos con encefalopatía hipóxico-isquémica (1). Rev Chil Obstet Ginecol. 2006;71:73-5. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-75262006000100013
Azzopardi DV, Strohm B, Edwards AD, Dyet L, Halliday HL, Juszczak E, et al. Moderate hypothermia to treat perinatal asphyxial encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1349-58. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0900854
Shankaran S, Laptook AR, McDonald SA, Hintz SR, Barnes PD, Das A, et al. Acute perinatal sentinel events, neonatal brain injury pattern and outcome of infants undergoing a trial of hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Pediatr. 2017;180:275-8.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.09.026
Hayes BC, Doherty E, Grehan A, Madigan C, McGarvey C, Mulvany S, et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome in survivors of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy without cerebral palsy. Eur J Pediatr. 2018;177:19-32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-017-3028-3
van Schie PEM, Schijns J, Becher JG, Barkhof F, van Weissenbruch MM, Vermeulen RJ. Long-term motor and behavioral outcome after perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2015;19:354-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2015.01.005
Parker SJ, Kuzniewicz M, Niki H, Wu YW. Antenatal and intrapartum risk factors for hypoxicischemic encephalopathy in a US birth cohort. J Pediatr. 2018;203:163-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.08.028
Ebbing C, Kiserud T, Johnsen SL, Albrechtsen S, Rasmussen S. Prevalence, risk factors and outcomes of velamentous and marginal cord insertions: A population-based study of 634,741 pregnancies. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e70380. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070380
Räisänen S, Georgiadis L, Harju M, Keski-Nisula L, Heinonen S. Risk factors and adverse pregnancy outcomes among births affected by velamentous umbilical cord insertion: A retrospective population-based register study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2012;165:231-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2012.08.021
del Riesgo-Prendes L, Salamanca-Matta A, Monterrey-Gutiérrez P, Bermúdez-Hernández PA, Vélez JL, Suárez-Rodríguez G. Hipoxia perinatal en el Hospital Mederi de Bogotá: comportamiento en los años 2007 a 2011. Rev Salud Pública. 2017;19:332-9. https://doi.org/10.15446/rsap.v19n3.65204
Zuleta-Tobón JJ, Salazar-Barrientos M. Aplicación del Sistema de Clasificación Internacional de Enfermedades para la Mortalidad Perinatal CIE-MP a partir de registros vitales para clasificar las muertes perinatales en Antioquia, Colombia. Rev Colomb Obstet Ginecol. 2019;70:228-42. https://doi.org/10.18597/rcog.3406
Vargas-Vaca Y, Devia C, Bertolotto AM, Suárez-Obando F. Caracterización de los recién nacidos con asfixia perinatal moderada o severa manejados con hipotermia cerebral selectiva en la Unidad de Recién Nacidos del Hospital Universitario San Ignacio desde junio de 2015 hasta marzo de 2017. Univ Med. 2019;60:4-13. https://doi.org/10.11144/javeriana.umed60-4.crna
Manotas H, Troncoso G, Sánchez J, Molina G. Descripción de una cohorte de pacientes neonatos con diagnóstico de asfixia perinatal, tratados con hipotermia terapéutica. 2017. Perinatol Reprod Hum. 2018;32:70-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rprh.2018.07.001
Torres-Muñoz J, Rojas C, Mendoza-Urbano D, Marín-Cuero D, Orobio S, Echandía C. Factores de riesgo asociados con el desarrollo de asfixia perinatal en neonatos en el Hospital Universitario del Valle, Cali, Colombia, 2010-2011. Biomédica. 2017;37:51-6. https://doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.v37i1.2844
Some similar items:
- Viviana Marcela Rodríguez, Adriana Cuéllar, Lyda Marcela Cuspoca, Carmen Lucía Contreras, Marcela Mercado, Alberto Gómez, Phenotypical determinants of stem cell subpopulations derived from human umbilical cord blood. , Biomedica: Vol. 26 No. 1 (2006)
- Valentina Duque , Laura Chaverra , Juanita Cury , María Carolina Portela , Juan Camilo Suárez-Escudero , Visual and neurological impairment post-dysfunction in the ventricle-peritoneal shunt system: A case report , Biomedica: Vol. 41 No. 1 (2021)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























