Phospholipase and proteinase activities of isolates of colonizing Candida spp. causing vulvovaginitis in pregnant women
Abstract
Introduction. Proteases and phospholipases are virulence factors of Candida spp. that play an important role in tissue invasion. Among the factors related to the host some are associated with environmental characteristics and others with Candida colonization.
Objectives. To determine phospholipase and protease activities in colonizing and pathogenic strains, isolated from pregnant women in Cartagena de Indias.
Materials and methods. Phospholipase and protease activity was determined in 56 isolates, evaluating substrate degradation and calculating the enzyme activity coefficient. Phospholipase and protease activities were compared between colonizing and pathogenic strains.
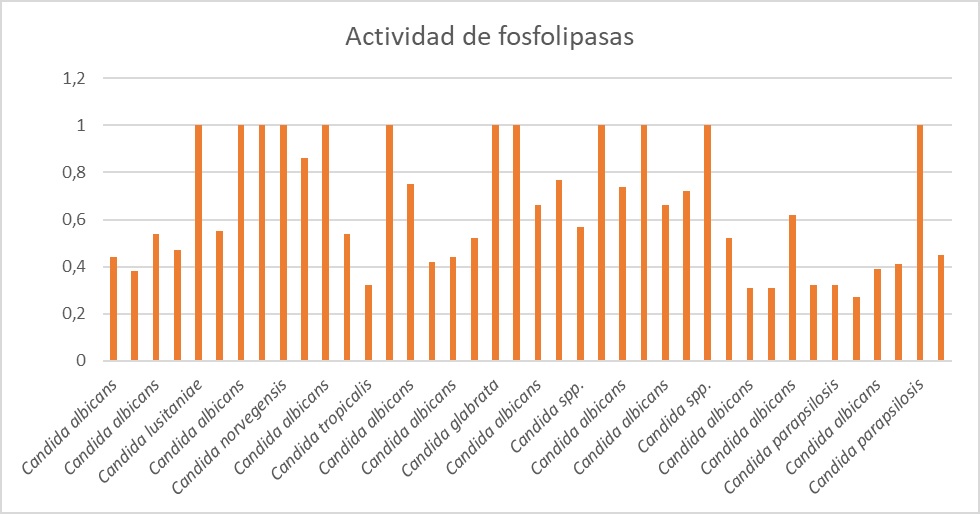
Results. “Very high” (<0.69) phospholipase and protease activity was found in 34 and 14 isolates, respectively. There was no significant difference when comparing phospholipase and protease activities between colonizing and pathogenic isolates.
Conclusions. Phospholipase activity predominated as a virulence factor in the studied strains, but no significant difference found between colonizing and pathogenic strains for phospholipase and protease activities.
Downloads
References
Mroczyńska M, Brillowska-Dabrowska A. Virulence of clinical Candida isolates. Pathogens. 2021;10:466-78. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10040466
Kotey FC, Dayie NT, Tetteh-Uarcoo PB, Donkor ES. Candida bloodstream infections: changes in epidemiology and increase in drug resistance. Infect Dis Res Treat. 2021;14:1-5. https://doi.org/10.1177/11786337211026927
Suárez P, Bello AM, Puello M, Young G, Durán M, Arechavala AI. Vaginal colonization and vulvovaginitis by Candida species in pregnant women from northern Colombia. Arch Med. 2018;18:51-9. https://doi.org/10.30554/archmed.18.1.2010.2018
Fule SR, Das D, Fule RP. Detection of phospholipase activity of Candida albicans and non albicans isolated from women of reproductive age with vulvovaginal candidiasis in rural area. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2015;33:92-5. https://doi.org/10.4103/0255-0857.148392
Tanju K, Birsay G, Banu UC. Phospholipases of Candida albicans. Mycoses. 2001;44:361-7. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0507.2001.00685.x
Panizo M, Reviákna V, Flores Y, Montes W, Gonzales G. Actividad de fosfolipasas y proteasas en aislados clínicos de Candida spp. Revista de la Sociedad Venezolana de Microbiología. 2005;25:217-28.
Ombrella AM, Racca L, Ramos L. Actividades proteinasa y fosfolipasa de aislamientos de Candida albicans provenientes de secreciones vaginales con distintos valores de pH. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2008;25:12-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1130-1406(08)70004-4
Price MF, Wilkinson ID, Gentry LO. Plate method for detection of phospholipase activity in Candida albicans. Med Mycol. 1982;20:7-14. https://doi.org/10.1080/00362178285380031
Tunç B, Demiray Gürbüz E, Doluca-Dereli M. Investigation of phospholipase activity in Candida albicans strains isolated from blood and oral cavity specimens. Turk Mikrobiyol Cemiy Derg. 2021;51:50-60. https://doi.org/10.5222/tmcd.2021.84429
Tokak S, Kılıç İH, Horasanlı JE, Mutlu EG, Taşbent FE, Karagöz ID. Vaginal candidiasis in Konya area: Etiology, risk factors, virulence patterns, and antifungal susceptibility. Rev Rom Med Lab. 2021;29:201-15. https://doi.org/10.2478/rrlm-2021-0012
Bassyouni RH, Wegdan AA, Abdelmoneim A, Said W, Aboelnaga F. Phospholipase and aspartyl proteinase activities of Candida species causing vulvovaginal candidiasis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;25:173441. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1504.04009
Abu-Lubad MA, Helaly GF, Aqel AA, Jarajreh DA, Al-Kharabsheh AM, Abufraijeh SM, et al. Putative virulence factors of candida species colonising asymptomatic pregnant jordanian women. New Zeal J Med Lab Sci. 2021;75:51-6.
Shirkhani S, Sepahvand A, Mirzaee M, Anbari K. Phospholipase and proteinase activities of Candida spp. isolates from vulvovaginitis in Iran. J Med Mycol. 2016;26:255-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycmed.2016.05.001
Some similar items:
- Catalina de Bedout, Julio Ayabaca, Ricardo Vega, Matilde Méndez, Axel R. Santiago, María Lucrecia Pabón, Angela Tabares, Myrtha Arango, Angela Restrepo, Vance Newell, Evaluation of Candida species' susceptibility to fluconazole with the disk diffusion method. , Biomedica: Vol. 23 No. 1 (2003)
- Sandra Moreno, Beatriz Parra, Javier E. Botero, Freddy Moreno, Daniel Vásquez, Hugo Fernández, Sandra Alba, Sara Gallego, Gilberto Castillo, Adolfo Contreras, Periodontal microbiota and microorganisms isolated from heart valves in patients undergoing valve replacement surgery in a clinic in Cali, Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. 4 (2017)
- Javier Araiza , Valentín Sánchez-Pedraza, Ana Karen Carrillo , Denise Fernández-Samar, Jazmín Tejeda, Alexandro Bonifaz, Mixed oral candidiasis in type 2 diabetic patients: Identification and spectrum of sensitivity , Biomedica: Vol. 43 No. Sp. 1 (2023): Agosto, Micología médica
- Mónica Gabriela Huertas , Miguel Rodríguez, Patricia Castro, Sergio Danilo Cruz, Erika Alejandra Cifuentes, Andrés Felipe Yepes, María Mercedes Zambrano , Ana Margarita Baldión, Description of the colonizing mycobiota of endotracheal tubes from patients admitted to two intensive care units in Bogotá, Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 43 No. Sp. 1 (2023): Agosto, Micología médica
Copyright (c) 2023 Biomedica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























