Vasoconstricción cerebral fatal, presentación inusual de una enfermedad inusual
Resumen
El síndrome de vasoconstricción cerebral reversible se produce por la constricción variable, segmentaria y multifocal, de las arterias cerebrales y, generalmente, es de curso benigno.
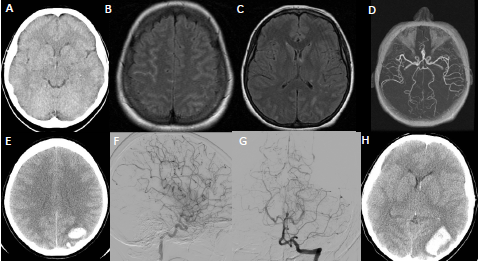
Se describe el caso de una mujer de 49 años que consultó por cefalea, síntomas visuales y convulsiones; tres días después, presentaba áreas de vasoconstricción en, por lo menos, dos territorios vasculares y dos segmentos de las mismas arterias. Fue internada en la unidad de cuidados intensivos para controlarle la presión arterial
y recibir tratamiento médico. Tuvo una evolución tórpida y, en el séptimo día de hospitalización, desarrolló edema cerebral maligno, tras lo cual ocurrió la muerte cerebral. Se inició entonces el plan de donación de órganos y, posteriormente, se practicó una autopsia guiada del cerebro. El estudio de patología descartó vasculitis y reveló áreas de hemorragia en la convexidad cerebral.
Se discuten los aspectos más relevantes de los casos con evolución fulminante informados en la literatura científica. El síndrome de vasoconstricción cerebral reversible se asocia con resultados fatales cuando los pacientes tienen una deficiencia neurológica focal, la neuroimagen inicial muestra alteraciones y hay un deterioro clínico rápido. Es importante conocer los factores asociados con un mal pronóstico, y establecer estrategias tempranas de intervención y prevención.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Choi HA, Lee MJ, Chung C-S. Cerebral endothelial dysfunction in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: A case-control study. J Headache Pain. 2017;18:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10194-017-0738-x
Pilato F, Distefano M, Calandrelli R. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: Clinical and radiological considerations. Front Neurol. 2020;11:34. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00034
Burton TM, Bushnell CD. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: A diagnostic imaging review. Stroke. 2019;50:2253-8. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.024416
Cappelen-Smith C, Calic Z, Cordato D. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: Recognition and treatment. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2017;19:21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-017-0460-7
Koopman K, Teune LK, Laan M, Uyttenboogaart M, Vroomen PC, De Keyser JD, et al. An often unrecognized cause of thunderclap headache: Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. J Headache Pain. 2008;9:389-91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10194-008-0068-0
Miller TR, Shivashankar R, Mossa-Basha M, Gandhi D. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome, part 1: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and clinical course. Am J Neuroradiol. 2015;36:1392-9. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4214
Bouvy C, Ackermans N, Maldonado-Slootjes S, Rutgers MP, Gille M. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome revealed by fronto-callosal infarctions. Acta Neurol Belg. 2020;120:1467-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-020-01319-0
Lee SH, Yun SJ, Choi YH. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome presenting as subarachnoid hemorrhage: A rare cause of postpartum seizure. Am J Emerg Med. 2017;35:807.e1-3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2016.12.021
Chen SP, Yang AC, Fuh JL, Wang SJ. Autonomic dysfunction in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. J Headache Pain. 2013;14:94. https://doi.org/10.1186/1129-2377-14-94
Calabrese LH, Dodick DW, Schwedt TJ, Singhal AB. Narrative review: Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146:34-44. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-146-1-200701020-00007
Singhal AB, Hajj-Ali RA, Topcuoglu MA, Fok J, Bena J, Yang D, et al. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes: Analysis of 139 cases. Arch Neurol. 2011;68:1005-12. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2011.68
Robert T, Kawkabani Marchini A, Oumarou G, Uske A. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome identification of prognostic factors. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013;115:2351-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2013.08.014
Lozupone E, Distefano M, Calandrelli R, Marca GD, Pedicelli A, Pilato F. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: A severe neurological complication in postpartum period. Neurol India.2020;68:192-8. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.279674
Abadía L, Castañeda C, Méndez JA, Coral J, Zarco LA. Síndrome de vasoconstricción cerebral reversible: revisión de tema. Universitas Médica. 2014;56:226-34.
Topcuoglu MA, Singhal AB. Hemorrhagic reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: Features and mechanisms. Stroke. 2016;47:1742-7. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.013136
Suchdev K, Norris G, Zak I, Mohamed W, Ibrahim M. Fulminant reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Neurohospitalist. 2018;8:NP5-8. https://doi.org/10.1177/1941874417692923
Enríquez P, Ariza-Varón M, Enríquez MN, Navarro CE. Síndrome de vasoconstricción cerebral reversible inducido por maniobra de Valsalva: reporte de caso y revisión de la literatura. Acta Neurológica Colombiana. 2020;36:81-6.
Pop A, Carbonnel M, Wang A, Josserand J, Auliac SC, Ayoubi J-M. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome associated with reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome in a patient presenting with postpartum eclampsia: A case report. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2019;48:431-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jogoh.2019.03.019
Singhal AB. Cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2004;11:1-6. https://doi.org/10.1310/ATK7-QTP7-7NE2-5G8X
Kunchok A, Castley HC, Aldous L, Hawke SH, Torzillo E, Parker GD, et al. Fatal reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 2018;385:146-50.
Singhal AB, Bernstein RA. Postpartum angiopathy and other cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Neurocrit Care. 2005;3:91-7. https://doi.org/10.1385/NCC:3:1:091
Ducros A. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11:906-17. ttps://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70135-7
Sattar A, Manousakis G, Jensen MB. Systematic review of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2010;8:1417-21. https://doi.org/10.1586/erc.10.124
Williams TL, Lukovits TG, Harris BT, Harker Rhodes C. A fatal case of postpartum cerebral angiopathy with literature review. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2007;275:67-77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-006-0194-3
Ducros A, Bousser M-G. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Pract Neurol. 2009;9:256-67. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2009.187856
Ducros A, Wolff V. The typical thunderclap headache of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome and its various triggers. Headache. 2016;56:657-73. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.12797
Calado S, Vale-Santos J, Lima C, Viana-Baptista M. Postpartum cerebral angiopathy: Vasospasm, vasculitis or both? Cerebrovasc Dis. 2004;18:340-1. https://doi.org/10.1159/000080976
Rocha EA, Topcuoglu MA, Silva GS, Singhal AB. RCVS(2) score and diagnostic approach for reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Neurology. 2019;92:e639-47. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000006917
Valencia-Mendoza M, Ramírez-Rodríguez N, Vargas-Ávila N, Peña-Ortiz A, Corzo-Villamizar M, Serna-Ramírez L, et al. Fatal reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: A systematic review of case series and case reports. J Clin Neurosci. 2019;70:183-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2019.08.014
Algunos artículos similares:
- Cristian Antony Ramos-Vera, Juan Camilo Motta, Carta al editor "Factores pronósticos en pacientes hospitalizados con diagnóstico de infección por SARS-CoV-2 en Bogotá, Colombia" , Biomédica: Vol. 41 Núm. 2 (2021)
- Juan Camilo Motta , Danny Novoa, Carmen Cecilia Gómez, Julian Moreno, Lina Vargas, Jairo Pérez, Henry Millán, Álvaro Ignacio Arango, Factores pronósticos en pacientes hospitalizados con diagnóstico de infección por SARS-CoV-2 en Bogotá, Colombia , Biomédica: Vol. 40 Núm. Supl. 2 (2020): SARS-CoV-2 y COVID-19
- Andrés Leonardo González, Ruth Aralí Martínez, Luis Ángel Villar, Evolución clínica de pacientes hospitalizados por dengue en una institución de salud de Bucaramanga, Colombia , Biomédica: Vol. 28 Núm. 4 (2008)
- Ignacio Zarante, Liliana Franco, Catalina López, Nicolás Fernández, Frecuencia de malformaciones congénitas: evaluación y pronóstico de 52.744 nacimientos en tres ciudades colombianas , Biomédica: Vol. 30 Núm. 1 (2010)
- Karen Melissa Ordóñez, Odismar Andrea Hernández, Jorge Alberto Cortés, María José López, Gladys Alfonso, Alejandro Junca, Endocarditis infecciosa izquierda por Pseudomonas aeruginosa tratada médicamente , Biomédica: Vol. 30 Núm. 2 (2010)
- Jairo Lizarazo, Melva Linares, Catalina de Bedout, Ángela Restrepo, Clara Inés Agudelo, Elizabeth Castañeda, Grupo Colombiano para el Estudio de la Criptococosis, Estudio clínico y epidemiológico de la criptococosis en Colombia: resultados de nueve años de la encuesta nacional, 1997-2005 , Biomédica: Vol. 27 Núm. 1 (2007)
- Álvaro J. Ruiz, Pablo J. Aschner, María Fernanda Puerta, Rafael Alfonso-Cristancho, Estudio IDEA (International Day for Evaluation of Abdominal Obesity): prevalencia de obesidad abdominal y factores de riesgo asociados en atención primaria en Colombia , Biomédica: Vol. 32 Núm. 4 (2012)
- Sergio Velásquez, Juan D. Matute, Laura Y. Gámez, Luis E. Enríquez, Iván D. Gómez, Fabiola Toro, Martha L. Valencia, Gisela De La Rosa, Pablo J. Patiño, Fabián A. Jaimes, Caracterización de la expresión de nCD64 en neutrófilos y de los niveles de s-TREM-1 y HMGB-1 en pacientes con sospecha de infección admitidos en el departamento de emergencias , Biomédica: Vol. 33 Núm. 4 (2013)
- Luis Eduardo Echeverría, Clara Saldarriaga, Sebastián Campbell-Quintero, Lisbeth Natalia Morales-Rodríguez, Juan David López-Ponce de León, Andrés Felipe Buitrago, Erika Martínez-Carreño, Jorge Alberto Sandoval-Luna, Alexis Llamas, Gustavo Adolfo Moreno-Silgado, Julián Vanegas-Eljach, Nelson Eduardo Murillo-Benítez, Ricardo Gómez-Paláu, Alex Arnulfo Rivera-Toquica, Juan Esteban Gómez-Mesa, RECOLFACA research group, Diabetes mellitus en pacientes con insuficiencia cardiaca y modificación del efecto de los factores de riesgo de mortalidad a corto plazo: un estudio observacional del Registro Colombiano de Falla Cardíaca (RECOLFACA) , Biomédica: Vol. 44 Núm. Sp. 1 (2024): Enfermedades crónicas no transmisibles
- Andrés Leonardo González, Aura Lucía Leal, Jorge Alberto Cortés, Ricardo Sánchez, Liliana Isabel Barrero, Juan Sebastián Castillo, Carlos Arturo Álvarez, Efecto del tratamiento antibiótico inicial adecuado sobre la mortalidad en pacientes en estado crítico con bacteriemia por Pseudomonas aeruginosa , Biomédica: Vol. 34 (2014): Abril, Suplemento 1, Resistencia bacteriana
| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |

























