Dengue virus induces apoptosis in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells
Abstract
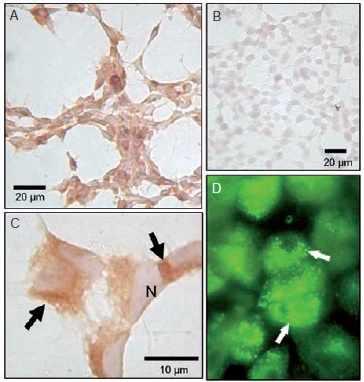
Introduction: Dengue is a human disease caused by a virus with the same name, which is transmitted by the bite of Aedes mosquitoes. The infection has a wide range of clinical presentations ranging from asymptomatic to fatal cases, with the pediatric population being the most susceptible. According to the new classification of the disease, the neurological manifestations are considered a criterion for the diagnosis of severe dengue. Objective: To evaluate the possible mechanisms involved in the onset of neurological signs in a cell line of human neurons as a model of infection with dengue virus type 2 (DENV-2). Materials and methods: Susceptibility and permissiveness of the SH-SY5Y line to infection by DENV-2 was analyzed, showing that the proportions of viral infection and production are similar to those of primate cells used as positive control for infection. Results: Infection induced a cytopathic effect on the neuroblastoma line characterized by apoptotic cell death process, increasing the proportion of annexin V and TUNEL positive cells and an upregulation of TNF-α. Treatment with anti-TNF-α antibody increased slightly cell survival of infected cells. The addition of exogenous TNF-α to the infected cultures enhanced cell death. Conclusion: These results as a whole suggest that the upregulation of TNF-α could be part of the process that induces cell damage and death in cases of dengue encephalitis.
Downloads
References
Velandia ML, Castellanos JE. Virus del dengue: estructura y ciclo viral. Infectio. 2011;15:33-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0123-9392(11)70074-1
Póvoa TF, Alves AM, Oliveira CA, Nuovo GJ, Chagas VL, Paes MV. The pathology of severe dengue in multiple organs of human fatal cases: Histopathology, ultrastructure and virus replication. PLoS One. 2014;9:e83386. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0083386
Villar L, Rojas D, Besada-Lombana S, Sarti E. Epidemiological trends of dengue disease in Colombia (2000-2011): A systematic review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9:e0003499. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd. 0003499
Organización Mundial de la Salud, Programa Especial para Investigación y Capacitación en Enfermedades Tropicales. Dengue. Guías para el diagnóstico, tratamiento, prevención y control. La Paz: OPS/OMS; 2010.
Castellanos J, Bello J, Velandia-Romero M. Manifes-taciones neurológicas durante la infección por el virus del dengue. Infectio. 2014;18:167-76. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j. infect.2014.02.006
Nimmagadda SS, Mahabala C, Boloor A, Raghuram PM, Nayak UA. Atypical manifestations of dengue fever (DF) - Where do we stand today? J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8:71-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2014/6885.3960
Méndez A, González G. Manifestaciones clínicas inusuales del dengue hemorrágico en niños. Biomédica. 2006;26:61-70. http://dx.doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.v26i1.1395
Neeraja M, Iakshmi V, Teja VD, Lavanya V, Priyanka EN, Subhada K, et al. Unusual and rare manifestations of dengue during a dengue outbreak in a tertiary care hospital in South India. Arch Virol. 2014;159:1567-73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2010-x
Jackson S, Hann-Chu J, Chia P, Morgan O, Ng L. Dengue encephalitis. En: Ruzek D, editor. Flavivirus encephalitis. Croatia: InTech; 2011. p. 71-88.
Tan LV, Thai LH, Phu NH, Nghia HD, Chuong LV, Sinh DX, et al. Viral etiology of central nervous system infections in adults admitted to a tertiary referral hospital in Southern Vietnam over 12 years. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e3127. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003127
Araújo F, Nogueira R, Araujo MS, Perdigão A, Cavalcante L, Brilhante R, et al. Dengue in patients with central nervous system manifestations, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:677-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid1804.111552
Solomon T, Dung NM, Vaughn DW, Kneen R, Thao LT, Raengsakulrach B, et al. Neurological manifestations of dengue infection. Lancet. 2000;355:1053-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02036-5
Desprès P, Frenkiel M, Ceccaldi P, Dos Santos CD, Deubel V. Apoptosis in the mouse central nervous system in response to infection with mouse-neurovirulent dengue viruses. J Virol. 1998;72:823-9.
Sánchez-Burgos G, Hernández-Pando R, Campbell IL, Ramos-Castañeda J, Ramos C. Cytokine production in brain of mice experimentally infected with dengue virus. Neuroreport. 2004;15:37-42.
García-Rivera EJ, Rigau-Pérez JG. Encephalitis and dengue. Lancet. 2002;360:261. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09481-3
Rincón V, Alvear D, Solano O, Prada-Arismendy J, Castellanos JE. La infección por virus dengue induce la disminución de marcadores de diferenciación en células de neuroblastoma. Iatreia. 2011;24:126-35.
Padilla J, Rojas D, Sáenz-Gómez R. Dengue en Colombia. Epidemiología de la reemergencia a la hiperendemia. Bogotá, D.C.: Guías de Impresión Ltda; 2012. p. 249.
Ramos-Castañeda J, Imbert JL, Barron BL, Ramos C. A 65-kDa trypsin-sensible membrane cell protein as a possible receptor for dengue virus in cultured neuroblastoma cells. J Neurovirol. 1997;3:435-40.
Reyes-Del Valle J, Chávez-Salinas S, Medina F, Del Angel RM. Heat shock protein 90 and heat shock protein 70 are components of dengue virus receptor complex in human cells. J Virol. 2005;79:4557-67. http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.79.8.4557-4567.2005
Huelseweh B, Ehricht R, Marschall HJ. A simple and rapid protein array based method for the simultaneous detection of biowarfare agents. Proteomics. 2006;6:2972-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200500721
Velandia-Romero ML, Acosta-Losada O, Castellanos JE. In vivo infection by a neuroinvasive neurovirulent dengue virus. J Neurovirol. 2012;18:374-87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13365-012-0117
Chingsuwanrote P, Suksanpaisan L, Smith DR. Adaptation of the plaque assay methodology for dengue virus infected HepG2 cells. J Virol Methods. 2004;116:119-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2003.11.002
Prada-Arismendy J, Castellanos JE. Real time PCR. Appli-cation in dengue studies. Colomb Med. 2011;42:243-58.
Lanciotti RS, Calisher CH, Gubler DJ, Chang GJ, Vorndam AV. Rapid detection and typing of dengue viruses from clinical samples by using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992;30:545-51.
Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S. Assessment of apoptosis and necrosis by DNA fragmentation and morphological criteria. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2001;18. http://dx.doi.org/10. 1002/0471143030.cb1803s12
Kweon SM, Lee ZW, Yi SJ, Kim YM, Han JA, Paik SG, et al. Protective role of tissue transglutaminase in the cell death induced by TNF-α in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2004;37:185-91.
Solbrig M, Perng G. Current neurological observations and complications of dengue virus infection. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2015;15:29. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11910- 015-0550-4
Carod-Artal FJ, Wichmann O, Farrar J, Gascón J. Neurological complications of dengue virus infection. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12:906-19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70150-9
Domínguez R, Kuster G, Onuki-Castro F, Souza V, Levi J, Pannuti C. Involvement of the central nervous system in patients with dengue virus infection. J Neurol Sci. 2008;267:36-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2007.09.040
Velandia M, Castellanos JE. Flavivirus neurotropism, neuroinvasion, neurovirulence and neurosusceptibility: Clues to understanding flavivirus- and dengue-induced encephalitis. In: García ML, Romanowski V, editors. Viral genomes - molecular structure, diversity, gene expression mechanisms and host-virus interactions. Croacia: InTech; 2012. p. 219-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/26571
Charlier N, Leyssen P, De Clercq E, Neyts J. Rodent models for the study of therapy against flavivirus infections. Antiviral Res. 2004;63:67-77. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2004.06.007
Imbert J, Guevara P, Ramos-Castañeda J, Ramos C, Sotelo J. Dengue virus infects mouse cultured neurons but not astrocytes. J Med Virol. 1994;42:228-33.
Guzmán MG, Kouri G. Advances in dengue diagnosis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1996;3:621-7.
Catteau A, Kalinina O, Wagner MC, Deubel V, Courageot MP, Desprès P. Dengue virus M protein contains a proapoptotic sequence referred to as ApoptoM. J Gen Virol. 2003;84:2781-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.19163-0
Desprès P, Flamand M, Ceccaldi PE, Deubel V. Human isolates of dengue type 1 virus induce apoptosis in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Virol. 1996;70:4090-6.
Jan JT, Chen BH, Ma SH, Liu CI, Tsai HP, Wu HC, et al. Potential dengue virus-triggered apoptotic pathway in human neuroblastoma cells: Arachidonic acid, superoxide anion, and NF-kappaB are sequentially involved. J Virol. 2000;74:8680-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.74.18.8680-8691.2000
Marianneau P, Flamand M, Deubel V, Despres P. Apoptotic cell death in response to dengue virus infection: The pathogenesis of dengue haemorrhagic fever revisited. Clin Diagn Virol. 1998;10:113-9.
Su HL, Lin YL, Yu HP, Tsao CH, Chen LK, Liu YT, et al. The effect of human bcl-2 and bcl-X genes on dengue virus-induced apoptosis in cultured cells. Virology. 2001;282:141-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/viro.2000.0820
Lee CJ, Liao CL, Lin YL. Flavivirus activates phos-phatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling to block caspase-dependent apoptotic cell death at the early stage of virus infection. J Virol. 2005;79:8388-99. http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.79.13.8388-8399.2005
Long X, Li Y, Qi Y, Xu J, Wang Z, Zhang X, et al. XAF1 contributes to dengue virus-induced apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2013;27:1062-73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1096/fj.12-213967
Chaturvedi UC. Tumour necrosis factor and dengue. Indian J Med Res. 2006;123:11-4.
Houghton N, Martín K, Giaya K, Rodríguez J, Bosch I, Castellanos JE. Comparación de los perfiles de transcripción de pacientes con fiebre de dengue y fiebre hemorrágica por dengue que muestra diferencias en la respuesta inmunitaria y claves en la inmunopatogénesis. Biomédica. 2010;30:587-97. http://dx.doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.v30i4.297
Sriram K, O’Callaghan JP. Divergent roles for tumor necrosis factor-α in the brain. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2007;2: 140-53. http://dx.doi.org/1010.1007/s11481-007-9070-6
Deng M, Zhao JY, Ju XD, Tu PF, Jiang Y, Li ZB. Protective effect of tubuloside B on TNFalpha-induced apoptosis in neuronal cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2004;25:1276-84.
Hopkins-Donaldson S, Bodmer JL, Bourloud KB, Brognara CB, Tschopp J, Gross N. Loss of caspase-8 expression in highly malignant human neuroblastoma cells correlates with resistance to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2000;60:4315-9.
Eggert A, Grotzer MA, Zuzak TJ, Wiewrodt BR, Ho R, Ikegaki N, et al. Resistance to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells correlates with a loss of caspase-8 expression. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1314-9.
Some similar items:
- Iveth J. González, Metacaspases and their role in the life cycle of human protozoan parasites , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
- Clara Beatriz Ocampo, Camila González, Carlos A. Morales, Mauricio Pérez, Dawn Wesson, Charles S. Apperson, Evaluation of community-based strategies for Aedes aegypti control inside houses , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 2 (2009)
- María Elena Cuéllar-Jiménez, Olga Lucía Velásquez-Escobar, Ranulfo González-Obando, Carlos Andrés Morales-Reichmann, Detection of Aedes albopictus (Skuse) (Diptera: Culicidae) in the city of Cali, Valle del Cauca, Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 27 No. 2 (2007)
- María Elena Maldonado, Souad Bousserouel, Francine Gossé, Annelise Lobstein, Francis Raul, Implication of NF-κB and p53 in the expression of TRAIL-death receptors and apoptosis by apple procyanidins in human metastatic SW620 cells , Biomedica: Vol. 30 No. 4 (2010)
- Natalia Houghton-Triviño, Katherine Martín, Kris Giaya, Jairo A. Rodríguez, Irene Bosch, Jaime E. Castellanos, Comparison of the transcriptional profiles of patients with dengue fever and dengue hemorrhagic fever reveals differences in the immune response and clues in immunopathogenesis , Biomedica: Vol. 30 No. 4 (2010)
- María Teresa Rugeles, Paula A. Velilla, Carlos J. Montoya, Mechanisms of human natural resistance to HIV: A summary of ten years of research in the Colombian population , Biomedica: Vol. 31 No. 2 (2011)
- Berta Nelly Restrepo, Margarita Arboleda, Ruth Ramírez, Gonzalo Álvarez, Serum platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase activity in dengue patients of African or mestizo descendency , Biomedica: Vol. 31 No. 4 (2011)
- Sandy Milena Caldera, María Cristina Jaramillo, Suljey Cochero, Alveiro Pérez-Doria, Eduar Elías Bejarano, Genetic differences between populations of Aedes aegypti from municipalities in northern Colombia, with high and low dengue incidence , Biomedica: Vol. 33 (2013): Suplemento 1, Fiebres hemorrágicas
- Raquel E. Ocazionez-Jiménez, Ayda Susana Ortiz-Báez, Sergio Yebrail Gómez-Rangel, Daniel R. Miranda-Esquivel, Dengue virus serotype 1 (DENV-1) from Colombia: its contribution to dengue occurrence in Santander , Biomedica: Vol. 33 (2013): Suplemento 1, Fiebres hemorrágicas
- Mabel Carabalí, Clara Beatriz Ocampo, María Eugenia Toledo, Lyda Osorio, Mass communication of dengue surveillance data: effect of an intervention in Guadalajara de Buga, Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 33 (2013): Suplemento 1, Fiebres hemorrágicas
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























