Real-time quantification to analyze historical Colombian samples detecting a short fragment of hypervariable region II of mitochondrial DNA
Abstract
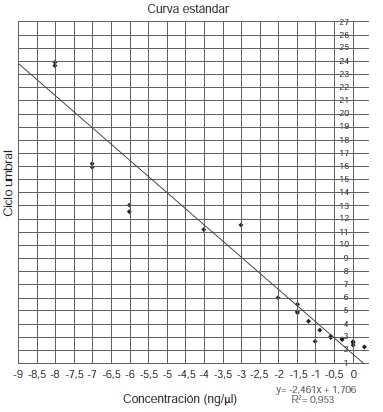
Introduction: Unlike other molecular biology studies, the analysis of ancient DNA (aDNA) requires special infrastructure and methodological conditions to guarantee the quality of the results. One of the main authenticity criteria is DNA quantification, where quantitative real-time PCR is often used given its sensitivity and specificity. Nevertheless, the implementation of these conditions and methodologies to fulfill authenticity criteria imply higher costs. Objective: To develop a simple and less costly method for mitochondrial DNA quantification suitable for highly degraded samples. Materials and methods: The proposed method is based on the use of mini-primers for the specific amplification of short fragments of mitochondrial DNA. The subsequent purification of these amplified fragments allows a standard curve to be constructed with concentrations in accordance to the state of degradation of the samples. Results: The proposed method successfully detected DNA from ancient samples including bone remains and mummified tissue. DNA inhibitory substances were also detected. Conclusion: The proposed method represents a simpler and cost-effective way to detect low amounts of aDNA, and a tool to differentiate DNA-free samples from samples with inhibitory substances.
Downloads
References
Hagelberg E, Hofreiter M, Keyser C. Ancient DNA: The first three decades. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015;370:20130371. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rstb. 2013.0371.
Kaestle FA, Horsburgh A. Ancient DNA in anthropology: Methods, applications, and ethics. Yearb Phys Anthr. 2002;130:92-130.
Willerslev E, Cooper A. Ancient DNA. Proc Biol Sci. 2005;272:3-16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2004.2813
Holliday R, Grigg GW. DNA methylation and mutation. Mutat Res. 1993;285:61-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0027-5107(93)90052-H
Höss M, Jaruga P, Zastawny TH, Dizdaroglu M, Pääbo S. DNA damage and DNA sequence retrieval from ancient tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996;24:1304-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/24.7.1304
Gilbert MTP, Bandelt HJ, Hofreiter M, Barnes I. Assessing ancient DNA studies. Trends Ecol Evol. 2005;20:541-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2005.07.005
Cooper A, Poinar H. Ancient DNA, do it right or not at all. Science. 2000;289:1139. http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science. 289.5482.1139b
Krings M, Stone A, Schmitz RW, Krainitzki H, Stoneking M, Pääbo S. Neanderthal DNA sequences and the origin of modern humans. Cell. 1997;90:19-30. http://dx.doi.org/10. 1016/S0092-8674(00)80310-4
Gabriel MN, Huffine EF, Ryan JH, Holland M, Parsons T. Improved MtDNA sequence analysis of forensic remains using a “ mini-primer set ” amplification strategy. J Forensic Sci. 2001;46:247-53.
Bio-Rad Laboratories. SsoFastTM EvaGreen ® Supermix 200. Hercules, CA, USA: Bio-Rad Laboratories; 2014.
Butler J. Forensic DNA typing. Biology, technology, and genetics of STR markers. Second edition. Burlington, MA: Academic Press; 2005.
QIAGEN. QIAamp® DNA Investigator. Sample and Assay Technologies. Valencia, CA: QIAGEN; 2010.
Loreille OM, Diegoli TM, Irwin JA, Coble MD, Parsons TJ. High efficiency DNA extraction from bone by total demineralization. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2007;1:191-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2007.02.006
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. GeneJET Gel Extraction Kit. Waltham, MA, USA: Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc; 2012.
Alonso A, Albarrán C, Martín P, García P, García O, De la Rúa C, et al. Multiplex – PCR of short amplicons for mtDNA sequencing from ancient DNA. Int Congr Ser. 2003;1239:585-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0531-5131(02) 00401-6
Kavlick MF, Lawrence HS, Merritt RT, Fisher C, Isenberg A, Robertson JM, et al. Quantification of human mitochondrial DNA using synthesized DNA standards. J Forensic Sci. 2011;56:1457-63. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-4029.2011.01871.x
Sprouse ML, Phillips NR, Kavlick MF, Roby RK. Internal validation of human mitochondrial DNA quantification using real-time PCR. J Forensic Sci. 2014;59:1049-56. http://dx. doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.12477
Young H, Jin M, Young N, Eun J, Ick W, Shin K. Simple and highly effective DNA extraction methods from old skeletal remains using silica columns. Forensic Sci Int Genet; 2010;4:275-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen. 2009.10.014
Yang DY, Eng B, Waye JS, Dudar JC, Saunders SR. Technical note: Improved DNA extraction from ancient bones using silica-based spin columns. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1998;105:539-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-8644 (199804)105:4<539::AID-AJPA10>3.0.CO;2-1
Anderung C, Persson P, Bouwman A. Fishing for ancient DNA. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2008;2:104-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2007.09.004
Robin ED, Wong R. Mitochondrial DNA molecules and virtual number of mitochondria per cell in mammalian cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988;136:507-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcp.1041360316
Stoneking M. Hypervariable sites in the mtDNA control region are mutational hotspots. Am J Hum Genet. 2000;67: 1029-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/303092
Keyser-Tracqui C, Ludes B. Methods for the study of ancient DNA. Methods Mol Biol. 2005;297:253-64.
Lee SB, Mccord B, Buel E. Advances in forensic DNA quantification. Electrophoresis. 2014;35:3044-52. http://dx. doi.org/10.1002/elps.201400187
Nielsen K, Smidt H, Hedman J, Parson W, Morling N, Niedersta H. Comparison of five DNA quantification methods. 2008;2:226-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen. 2008.02.008
Lamers R, Hayter S, Matheson CD. Postmortem miscoding lesions in sequence analysis of human ancient mitochondrial DNA. J Mol Evol. 2009;68:40-55. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00239-008-9184-3
Gotherstrom A, Collins MJ, Angerbjorn A, Liden K. Bone preservation and DNA amplification. Archeometry. 2002;44:395-404. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1475-4754.00072
Handt O, Krings M, Ward RH, Pääbo S. The retrieval of ancient human DNA sequences. Am J Hum Genet. 1996;59:368-76.
Pérez LA, Groot H, Langebaek CH. Aportes genéticos para el entendimiento de la organización social de la comunidad muisca Tibanica (Soacha, Cundinamarca) (tesis). Bogotá: Universidad de los Andes; 2016.
Some similar items:
- Adrián Peñata, Richard Salazar, Tatiana Castaño, Julián Bustamante, Sigifredo Ospina, Molecular diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis and sensitivity to rifampicin with an automated real-time method , Biomedica: Vol. 36 (2016): Suplemento 1, Microbiología médica
- Andrea Casas-Vargas, Liza M. Romero, William Usaquén, Sara Zea, Margarita Silva, Ignacio Briceño, Alberto Gómez, José Vicente Rodríguez, Mitochondrial DNA diversity in prehispanic bone remains on the eastern Colombian Andes , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. 4 (2017)
- Leonardo F. Jurado, Martha I. Murcia, Patricia Hidalgo, John E. Leguizamón, Lorena R. González, Phenotypic and genotypic diagnosis of bone and miliary tuberculosis in an HIV+ patient in Bogotá, Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 35 No. 1 (2015)
- Diana Carolina López, Carlos Jaramillo, Felipe Guhl, Population structure and genetic variability of Rhodnius prolixus (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) from different geographic areas of Colombia. , Biomedica: Vol. 27 No. 1esp (2007): Enfermedad de Chagas
- Martine Bonnaure-Mallet, Paula Juliana Pérez-Chaparro, Patrice Gracieux, Vincent Meuric, Zohreh Tamanai-Shacoori, Jaime Eduardo Castellanos, Distribution of Porphyromonas gingivalis fimA genotypes in isolates from subgingival plaque and blood sample during bacteremia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 2 (2009)
- Diego Fernando Zea, Martín Prager, Roger Adrian Figueroa, María Consuelo Miranda, Mucosal complication of cutaneous leishmaniasis , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 1 (2009)
- Norma B. Fernández, Adriana Toranzo, Luciana Farias, Cristina E. Canteros, Mycological diagnosis of paracoccidioidomycosis in a hospital from a nonendemic area: classical and molecular methods , Biomedica: Vol. 43 No. Sp. 1 (2023): Agosto, Micología médica
- Concepción Judith Puerta, Johana María Guevara, Paula Ximena Pavía, Marleny Montilla, Rubén Santiago Nicholls, Edgar Parra, Yuli Katherine Barrera, Evaluation of TcH2AF-R and S35-S36 primers in PCR tests for the detection of Trypanosoma cruzi in mouse cardiac tissue , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 4 (2008)
- Marcel Marín, Yudy Alexandra Aguilar, José Robinson Ramírez, Omar Triana, Carlos Enrique Muskus, Molecular and immunological analyses suggest the absence of hydrophilic surface proteins in Leishmania (Viannia) panamensis , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 3 (2008)
- Concepción Judith Puerta, Paula Ximena Pavia, Marleny Montilla, Carolina Flórez, Giomar Herrera, Juan Manuel Ospina, Fred Manrique, Rubén Santiago Nicholls, The first case of congenital Chagas’ disease analyzed by AP-PCR in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 4 (2009)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























