Tuberculosis in the era of anti-TNF-alpha therapy: Why does the risk still exist?
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune systemic disease characterized mainly by inflammatory compromise of diarthrodial joints. Multiple drug therapies have been developed to control the activity of rheumatoid arthritis, among them, the first line of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARD), and novel drug therapies such as the anti-TNF alpha therapy, with satisfactory clinical outcomes.
Despite this positive fact, the use of this therapy implies the risk of producing negative effects due to its mechanism of action, which has been associated with multiple infections, especially tuberculosis, making it necessary to use screen tests before resorting to this kind of drugs.
We present the case of a 58-year-old female patient, with a six-year history of rheumatoid arthritis.
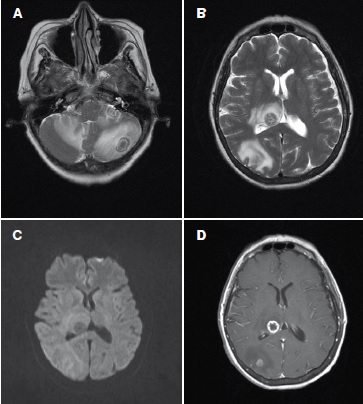
The patient developed disseminated tuberculosis with compatible radiological and histological findings after receiving treatment with infliximab (anti-TNF therapy). No test was performed to screen for latent tuberculosis infection prior to the administration of infliximab.
The performance of routine screenings tests for tuberculosis prior to anti-TNF alpha therapy plays an essential role in the detection of asymptomatic patients with latent tuberculosis. This is the only way to identify those patients who would benefit from anti-tuberculosis drugs before the initiation of anti-TNF alpha therapy, which makes the difference in the search of a significant reduction in the incidence of tuberculosis and its associated morbidity and mortality.
Downloads
References
Anaya JM, Shoenfeld Y, Rojas-Villarraga A, Levy RA, Cervera R. Autoimmunity from bench to bedside. First edition. Bogotá: Universidad del Rosario; 2013. p. 381-2.
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Bijlsma JWJ, Breedveld FC, Boumpas D, Burmester G, et al. Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: Recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:631-7. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.123919
Gorter SL, Bijlsma JM, Cutolo M, Gómez-Reino J, Kouloumas M, Smolen JS, et al. Current evidence for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with glucocorticoids: A systematic literature review informing the EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;69:1010-14. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.127332
Monaco C, Nanchahal J, Taylor P, Feldmann M. Anti-TNF therapy: Past, present and future. Int Immunol. 2015;27:55-62. https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/dxu102
Cantini F, Nannini C, Niccoli L, Iannone F, Delogu G, Garlaschi G, et al. Guidance for the management of patients with latent tuberculosis infection requiring biologic therapy in rheumatology and dermatology clinical practice. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14:503-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2015.01.011
Vivar N, van Vollenhoven RF. Advances in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. F1000Prime Rep. 2014;6:31. https://doi.org/10.12703/P6-31
Ali T, Kaitha S, Mahmood S, Ftesi A, Stone J, Bronze MS. Clinical use of anti-TNF therapy and increased risk of infections. Drug Healthc Patient Saf. 2013;5:79-99. https://doi.org/10.2147/DHPS.S28801
Murdaca G, Spanò F, Contatore M, Guastalla A, Penza E, Magnani O, et al. Infection risk associated with anti-TNF-α agents: A review. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2015;14:571-82.
https://doi.org/10.1517/14740338.2015.1009036
Joshi P, Dhaneshwar SS. An update on disease modifying antirheumatic drugs. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2014;
:249-61. https://doi.org/10.2174/187152811304140915152102
Tracey D, Klareskog L, Sasso EH, Salfeld JG, Tak PP. Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanisms of action: A comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther. 2008;117:244-79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.10.001
Koo S, Marty FM, Baden LR. Infectious complications associated with immunomodulating biologic agents. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2011;25:117-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hoc.2010.11.009
Solovic I, Sester M, Gómez-Reino JJ, Rieder HL, Ehlers S, Milburn HJ, et al. The risk of tuberculosis related to tumour necrosis factor antagonist therapies: A TBNET consensus statement. Eur Respir J. 2010;36:1185-206. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00028510
Maini RN, Feldmann M. How does infliximab work in rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Res. 2002;4:S22-8. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar549
Goel N, Stephens S. Certolizumab pegol. MAbs. 2010;2:137-47.
Wallis RS. Tumour necrosis factor antagonists: Structure, function, and tuberculosis risks. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008;8:601-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(08)70227-5
Cheifetz A, Smedley M, Martin S, Reiter M, Leone G, Mayer L, et al. The incidence and management of infusion reactions to infliximab: A large center experience. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:1315-24. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07457.x
Rosenblum H, Amital H. Anti-TNF therapy: Safety aspects of taking the risk. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10:563-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2011.04.010
Cacciapaglia F, Navarini L, Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Minotti G, Afeltra A. Cardiovascular safety of anti-TNFalpha therapies: Facts and unsettled issues. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10:631-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2011.04.014
Xie X, Li F, Chen J-W, Wang J. Risk of tuberculosis infection in anti-TNF-α biological therapy: From bench to bedside. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2014;47:268-74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2013.03.005
Yasui K. Immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the risk of biologic anti-TNF-α reagents. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2014;12:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1546-0096-12-45
Winthrop KL. Risk and prevention of tuberculosis and other serious opportunistic infections associated with the inhibition of tumor necrosis factor. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006;2:602-10. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncprheum0336
Wallis RS, Broder M, Wong J, Beenhouwer D. Granulomatous
infections due to tumor necrosis factor blockade: Correction. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:1254-5. https://doi.org/10.1086/424455
World Health Organization. Tuberculosis. First edition. Accessed: 12 de octubre de 2015. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs104/en/
World Health Organization. Tuberculosis, Colombia 2012. First edition. Accessed: 25 de noviembre de 2015. Available from: https://extranet.who.int/sree/Reports?op=Replet&name=
%2FWHO_HQ_Reports%2FG2%2FPROD%2FEXT%2FTBCou
ntryProfile&ISO2=CO&LAN=EN&outtype=html
Shim TS. Diagnosis and treatment of latent tuberculosis
infection due to initiation of anti-TNF therapy. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2014;76:261-8. https://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.76.6.261
Dixon WG, Hyrich KL, Watson KD, Lunt M, Galloway J, Ustianowski A, et al. Drug-specific risk of tuberculosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF therapy: Results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register (BSRBR). Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:522-8. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.118935
Tubach F, Salmon D, Ravaud P, Allanore Y, Goupille P, Bréban M, et al. Risk of tuberculosis is higher with antitumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody therapy than with soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor therapy: The three-year prospective French Research Axed on Tolerance of Biotherapies registry. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:1884-94. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24632
Lee H, Park HY, Jeon K, Jeong B-H, Hwang J-W, Lee J, et al. QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube assay for screening arthritis patients for latent tuberculosis infection before starting anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0119260. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119260
Rojas-Villarraga A, Agudelo CA, Pineda-Tamayo R, Porras A, Matute G, Anaya JM. Tuberculosis in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists living in an endemic area. Is the risk worthwhile? Biomédica. 2007;27:159-71. https://doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.v27i2.212
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Tuberculosis
associated with blocking agents against tumor necrosis factor-alpha--California, 2002-2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2004;53:683-6.
Carmona L, Gómez-Reino JJ, Rodríguez-Valverde V, Montero D, Pascual-Gómez E, Mola EM, et al. Effectiveness of recommendations to prevent reactivation of latent tuberculosis infection in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:1766-72.https://doi.org/10.1002/art.21043
Mariette X, Salmon D. French guidelines for diagnosis and treating latent and active tuberculosis in patients with RA treated with TNF blockers. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:791.
https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.62.8.791
Fonseca JE, Canhão H, Silva C, Miguel C, Mediavilla MJ, Teixeira A, et al. Tuberculosis in rheumatic patients treated with tumour necrosis factor alpha antagonists: The Portuguese experience. Acta Reumatol Port. 2006;31:247-53.
Caballero CV, Pinzón L. Artritis reumatoide tratada con inhibidores del factor de necrosis tumoral α (Anti-TNF-α) y tuberculosis pulmonar. Salud Uninorte. 2006;22:29-39.
Hidalgo P, Echeverri J, Gutiérrez JM. Tuberculosis pleural asociada con adalimumab, en un paciente con artritis reumatoide. Infectio. 2010;14:47-54. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0123-9392(10)70092-8
Londoño P, Fernández D, Salazar J, Saiibi D, Molina J, Valle R, et al. Cambio en la capacidad funcional, calidad de vida y actividad de la enfermedad, en un grupo de pacientes colombianos con artritis reumatoide refractaria (sic) al tratamiento convencional, que recibieron terapia con infliximab como medicamento de rescate. Rev Fac Med. 2009;17:40-9.
Machado J, Moncada JC, Pineda R. Perfil de utilización de los anti-factor de necrosis tumoral en pacientes de Colombia. Biomédica. 2011;31:250-7. https://doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.v31i2.319
Martínez JB, Medina Y, Parga R, Restrepo JF, Iglesias A, Rondón F. Reactivación de tuberculosis pulmonar (TBC) con el uso de antagonistas del factor de necrosis tumoral alfa (FNTa) en artritis reumatoide. A propósito de un caso. Rev Colomb Reumatol. 2005;12:54-61.
Muñoz OM, Hurtado M, Fernández D, Hidalgo P, Gutiérrez JM. Conversión de tuberculosis latente en un grupo de pacientes tratados con terapia biológica en una unidad de Reumatología. Rev Colomb Neumol. 2014;26:116-22.
Insuasty JS, Bolívar A, Calvo LS, Roberto SL. Tuberculosis peritoneal simulando cáncer de ovario. Acta Med Colomb. 2014;39:383-7.
Vega J, Pinto LF, Muñoz C, Márquez JD, Rodríguez LM, Velázquez CJ. Infecciones en pacientes con artritis reumatoide:
medicamentos moduladores de la respuesta biológica versus fármacos modificadores de la enfermedad. Seguimiento a un año. Rev Colomb Reumatol. 2013;21:27-34.
Wang MH, Liu X, Shen B. Disseminated tuberculosis in a
patient taking anti-TNF therapy for Crohn’s disease. ACG Case Reports J. 2015;3:45-8. https://doi.org/10.14309/crj.2015.97
Tanaka T, Sekine A, Tsunoda Y, Takoi H, Lin S-Y, Yatagai Y, et al. Central nervous system manifestations of tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome during adalimumab therapy: A case report and review of the literature. Intern Med. 2015;54:847-51. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.54.2828
van der Have M, Belderbos TD, Fidder HH, Leenders M, Dijkstra G, Peters CP, et al. Screening prior to biological therapy in Crohn’s disease: Adherence to guidelines and prevalence of infections. Results from a multicentre retrospective study. Dig Liver Dis. 2014;46:881-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2014.07.006
Raval A. Brief communication: Characteristics of spontaneous
cases of tuberculosis associated with infliximab. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147:699-702. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-147-10-200711200-00006
Keane J, Gershon S, Wise RP, Mirabile-Levens E, Kasznica J, Schwieterman WD, et al. Tuberculosis associated with infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor alphaneutralizing agent. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1098-104. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa011110.
Elbek O, Uyar M, Aydin N, Börekçi S, Bayram N, Bayram H, et al. Increased risk of tuberculosis in patients treated with antitumor necrosis factor alpha. Clin Rheumatol. 2009;28:421-6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-1067-x
Jick SS, Lieberman ES, Rahman MU, Choi HK. Glucocorticoid
use, other associated factors, and the risk of tuberculosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;55:19-26. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.21705
Lorenzetti R, Zullo A, Ridola L, Diamanti AP, Laganà B, Gatta L, et al. Higher risk of tuberculosis reactivation when anti-TNF is combined with immunosuppressive agents: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Ann Med. 2014;46:547-54. https://doi.org/10.3109/07853890.2014.941919
Brode SK, Jamieson FB, Ng R, Campitelli MA, Kwong JC, Paterson JM, et al. Increased risk of mycobacterial infections associated with anti-rheumatic medications. Thorax. 2015;70:677-82. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206470
Ledingham J, Wilkinson C, Deighton C. British Thoracic Society (BTS) recommendations for assessing risk and managing tuberculosis in patients due to start anti-TNFalpha treatments. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005;44:1205-6. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kei103
Beglinger C, Dudler J, Mottet C, Nicod L, Seibold F, Villiger PM, et al. Screening for tuberculosis infection before the initiation of an anti-TNF-alpha therapy. Swiss Med Wkly. 2007;137:620-2.
Diel R, Hauer B, Loddenkemper R, Manger B, Krüger K. Recommendations for tuberculosis screening before initiation of TNF-alpha-inhibitor treatment in rheumatic disease. Pneumologie. 2009;63:329-34. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1214673
Hur Y-G, Kang YA, Jang S-H, Hong JY, Kim A, Lee SA, et al. Adjunctive biomarkers for improving diagnosis of tuberculosis and monitoring therapeutic effects. J Infect. 2015;70:346-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2014.10.019
Brock I, Ruhwald M, Lundgren B, Westh H, Mathiesen LR, Ravn P. Latent tuberculosis in HIV positive, diagnosed by the M. tuberculosis specific interferon-gamma test. Respir Res. 2006;7:56. https://doi.org/10.1186/1465-9921-7-56
Sester M, van Leth F, Bruchfeld J, Bumbacea D, Cirillo DM, Dilektasli AG, et al. Risk assessment of tuberculosis in immunocompromised patients. A TBNET Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;190:1168-76. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201405-0967OC
Quintana-López G, Grillo-Ardila C, Méndez P, Vallejo M, Guevara O, Velásquez C, et al. Guía de práctica clínica para la detección temprana, diagnóstico y tratamiento de la artritis reumatoide. Primera edición. Bogotá, D.C.: Ministerio de Salud y Protección Social; 2014.
Debeuckelaere C, De Munter P, van Bleyenbergh P, De Wever W, van Assche G, Rutgeerts P, et al. Tuberculosis infection following anti-TNF therapy in inflammatory bowel disease, despite negative screening. J Crohns Colitis. 2014;8:550-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crohns.2013.11.008
Çekiç C, Aslan F, Vatansever S, Topal F, Yüksel ES, Alper E, et al. Latent tuberculosis screening tests and active tuberculosis infection rates in Turkish inflammatory bowel disease patients under anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Ann Gastroenterol. 2015;28:241-6.
Bernal JA, Andrés M, Jovaní V, García-Sevila R, Begazo A, Vela P. Primary tuberculosis infection in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists and a negative initial screening. Reumatol Clin. 2016;12:81-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reuma.2015.04.001
Smith MY, Attig B, McNamee L, Eagle T. Tuberculosis screening in prescribers of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in the European Union. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2012;16:1168-73. https://doi.org/10.5588/ijtld.12.0029
Ferreira BA, Ribeiro S, Meireles J, Correia A, Duarte R. Tuberculosis screening and compliance rate with guidelines among northern Portuguese hospitals prescribers of anti-TNF therapy. Rev Port Pneumol. 2014;21:99-101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rppnen.2014.09.008
Some similar items:
- Leandro Galvis, Ángel Y. Sánchez, Leonardo F. Jurado, Martha I. Murcia, Tuberculosis associated with tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists, case description and analysis of reported cases in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 38 No. 1 (2018)
- Jorge Machado, Juan Carlos Moncada, Ricardo Pineda, Profile of use of anti tumor necrosis factor in Colombian patients , Biomedica: Vol. 31 No. 2 (2011)
- Claudia Llerena, Santiago Elías Fadul, María Consuelo Garzón, Graciela Mejía, Dora Leticia Orjuela, Luz Mary García, Hilda Beatriz Álvarez, Fernando Javier Ruiz, Drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in children under 15 years , Biomedica: Vol. 30 No. 3 (2010)
- Claudia Llerena, Angie Zabaleta, Angélica Valbuena, Martha Murcia, Prevalence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistance to quinolones and injectables in Colombia, 2012-2013 , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. 1 (2017)
- Julio César Martínez, Claudia Llerena, Yanely Angélica Valbuena, The Importance of investigating Mycobacterium bovis in clinical samples of human origin , Biomedica: Vol. 39 No. Sp. 1 (2019): Suplemento 1, Microbiología médica, mayo
- Juan Gabriel Bueno-Sánchez, Jairo René Martínez-Morales, Elena E. Stashenko, Wellman Ribón, Anti-tubercular activity of eleven aromatic and medicinal plants occurring in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 1 (2009)
- Gerardo Quintana, Claudia Mora, Andrés González, Jorge Díaz Díaz, Financial cost of early rheumatoid arthritis in the first year medical attention: three clinical scenarios. , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 1 (2009)
- Diego Chaves, Andrea Sandoval, Luis Rodríguez, Juan C. García, Silvia Restrepo, María Mercedes Zambrano, Comparative analysis of six Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex genomes , Biomedica: Vol. 30 No. 1 (2010)
- Olga María Moreno, Clara Isabel González, Diego Luis Saaibi, William Otero, Reynaldo Badillo, Javier Martín, Gerardo Ramírez, Polymorphisms of IL-10 gene promoter and rheumatoid arthritis in a Colombian population , Biomedica: Vol. 27 No. 1 (2007)
- Adriana Rojas-Villarraga, Carlos Andrés Agudelo, Ricardo Pineda-Tamayo, Alvaro Porras, Gustavo Matute, Juan Manuel Anaya, Tuberculosis in patientes treated with tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonists living in an endemic area. Is the risk worthwhile? , Biomedica: Vol. 27 No. 2 (2007)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























