Fatal Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome in an alcoholic diabetic patient from México
Abstract
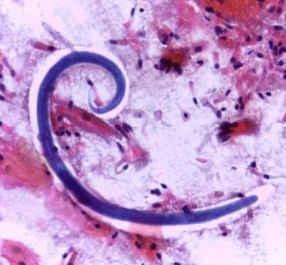
Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome is a medical emergency that requires a high level of suspicion. Immunocompromised patients are at high risk of hyperinfection syndrome; however, malnutrition, alcoholism, and diabetes mellitus also need to be considered as predisposing factors. The diagnosis and treatment of Strongyloides hyperinfection are challenging and patients often have severe complications. Consequently, mortality is overwhelmingly high, with proportions above 60%.
Herein, we report a case of Strongyloides hyperinfection in a 40-year-old alcoholic diabetic patient living in México. Unfortunately, the late diagnosis resulted in his death despite the treatment and supportive measures. Increased awareness is needed to prevent the dire consequences of strongyloidiasis.
Downloads
References
Olsen A, van Lieshout L, Marti H, Polderman T, Polman K, Steinmann P, et al. Strongyloidiasis – the most neglected of the neglected tropical diseases? Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2009;103:967-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trstmh.2009.02.013
Bisoffi Z, Buonfrate D, Montresor A, Requena-Méndez A, Muñoz J, Krolewiecki AJ, et al. Strongyloides stercoralis: A plea for action. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7:7-10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002214
Guarner J, Matilde-Nava T, Villaseñor-Flores R, Sánchez-Mejorada G. Frequency of intestinal parasites in adult cancer patients in México. Arch Med Res. 1997;28:219-22.
Faulkner CT, Borrego-García B, Logan MH, New JC, Patton S. Prevalence of endoparasitic infection in children and its relation with cholera prevention efforts in México. Rev Panam Salud Pública. 2003;14:31-41. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1020-49892003000600006
Carrada-Bravo T. Strongyloides stercoralis: ciclo vital, cuadros clínicos, epidemiología, patología y terapéutica. Revista Latinoamericana de Patología Clínica y Medicina de Laboratorio. 2008;55:88-110.
Viney ME, Lok JB. The biology of Strongyloides spp. Pasadena: WormBook; 2015. p. 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1895/wormbook.1.141.2
Krolewiecki A, Nutman TB. Strongyloidiasis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2019;33:135-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idc.2018.10.006
Teixeira MCA, Pacheco FTF, Souza JN, Silva MLS, Inês EJ, Soares NM. Strongyloides stercoralis infection in alcoholic patients. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:4872473. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4872473
McGuire E, Welch C, Melzer M. Is Strongyloides seropositivity associated with diabetes mellitus? A retrospective case-control study in an East London NHS Trust. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2019;113:189-94. https://doi.org/10.1093/trstmh/try132
Silva MLS, de J. Inês E, da S. Souza AB, dos S. Dias VM, Guimarães CM, Menezes ER, et al. Association between Strongyloides stercoralis infection and cortisol secretion in alcoholic patients. Acta Trop. 2016;154:133-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2015.11.010
Buonfrate D, Requena-Méndez A, Angheben A, Muñoz J, Gobbi F, van Den Ende J, et al. Severe strongyloidiasis: A systematic review of case reports. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:78. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-13-78
Geri G, Rabbat A, Mayaux J, Zafrani L, Chalumeau-Lemoine L, Guidet B, et al. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome: A case series and a review of the literature. Infection. 2015;43:691-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-015-0799-1
Henríquez-Camacho C, Gotuzzo E, Echevarría J, White AC, Terashima A, Samalvides F, et al. Ivermectin versus albendazole or thiabendazole for Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;CD007745. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007745.pub3
Barrett J, Broderick C, Soulsby H, Wade P, Newsholme W. Subcutaneous ivermectin use in the treatment of severe Strongyloides stercoralis infection: Two case reports and a discussion of the literature. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71:220-5. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkv315
Some similar items:
- Leonardo Elías Ordóñez, Esther Sofía Angulo, Efficacy of ivermectin in the treatment of children parasitized by Strongyloides stercoralis. , Biomedica: Vol. 24 No. 1 (2004)
- Jorge Alberto García-Aguilar, Jackeline Alger, Frequency of strongyloidiasis and associated factors: Analysis of 13 years of laboratory results in a tertiary referral hospital in Honduras, 2010-2022 , Biomedica: Vol. 43 No. 4 (2023)
- Nilo Manoel Pereira Vieira Barreto , Marina Morena Brito Farias , Cíntia de Lima Oliveira, Weslei Almeida Costa Araujo , Maria Fernanda Rios Grassi , Joelma Nascimento de Souza , Beatriz Soares Jacobina , Márcia Cristina Aquino Teixeira, Bernardo Galvão-Castro, Neci Matos Soares, Evaluation of Strongyloides stercoralis infection in patients with HTLV-1 , Biomedica: Vol. 42 No. 1 (2022)
- José Alejandro Martínez-Ibarra, Jorge Alejandro Martínez-Grant, Miguel Roberto Verdugo-Cervantes, Rafael Bustos-Saldaña, Benjamín Nogueda-Torres, Monitoring triatomid bug (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) presence by sentinel chicken coops in Southern Jalisco State, México , Biomedica: Vol. 30 No. 1 (2010)
- Gladys Acuña-González, Carlo E. Medina-Solís, Gerardo Maupomé, Mauricio Escoffie-Ramírez, Jesús Hernández-Romano, María de L. Márquez-Corona, Arturo J. Islas-Márquez, Juan J. Villalobos-Rodelo, Family history and socioeconomic risk factors for non-syndromic cleft lip and palate: A matched case-control study in a less developed country , Biomedica: Vol. 31 No. 3 (2011)
- María Isabel Giraldo, Nora Lizeth García, Jhon Carlos Castaño, Prevalence of intestinal helminths in dogs from Quindío Province. , Biomedica: Vol. 25 No. 3 (2005)
- Juan José Villalobos Rodelo, Carlo Eduardo Medina Solís, Nelly Molina Frechero, Ana Alicia Vallejos Sánchez, América Patricia Pontigo Loyola, José Luis Espinoza Beltrán, Dental caries in schoolchildren aged 6-12 years in Navolato, Sinaloa, México: experience, prevalence, severity and treatment needs. , Biomedica: Vol. 26 No. 2 (2006)
- Zinnia J. Molina-Garza, Lucio Galaviz-Silva, Pediculus capitis in schoolchildren of the urban area of Nuevo León, México: Analyses of associated factors , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. 3 (2017)
- Ernesto Pérez-Sánchez, Raúl Montiel-Cruz, Eréndira Romero-Domínguez, Griselda Pascacio-Bermúdez, Arturo Báez-Hernández, Guadalupe Díaz del Castillo-Flores, Fabián Correa-Morales, Gonzalo Vázquez-Prokopec, Pablo Manrique-Saide, Azael Che-Mendoza, Gabriela Meneses-Ruiz , Irma López-Martínez, María Jesús Sánchez, Seroprevalence of Trypanosoma cruzi among children from Veracruz, Mexico: Epidemiological baseline for a control model based on Chagas disease active transmission , Biomedica: Vol. 44 No. 1 (2024)
- Karen López, Lilian Catalina Tartaglino, Ingrid Iris Steinhorst, María Soledad Santini, Oscar Daniel Salomon, Risk factors, representations and practices associated with emerging urban human visceral leishmaniasis in Posadas, Argentina , Biomedica: Vol. 36 (2016): Suplemento 1, Microbiología médica
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























