Meningeal cryptococcosis and SARS-CoV-2 infection in people living with HIV/AIDS
Abstract
Introduction. Fungal infections in patients with COVID-19 was one of the most debated topics during the pandemic.
Objectives. To analyze the clinical characteristics and evolution of people living with HIV/AIDS and coinfection with cryptococcus and COVID-19 (group A) or without it (group B).
Materials and methods. This is an analytical and retrospective study. We reviewed medical records of patients with meningeal cryptococcosis between April 2020 and May 2021.
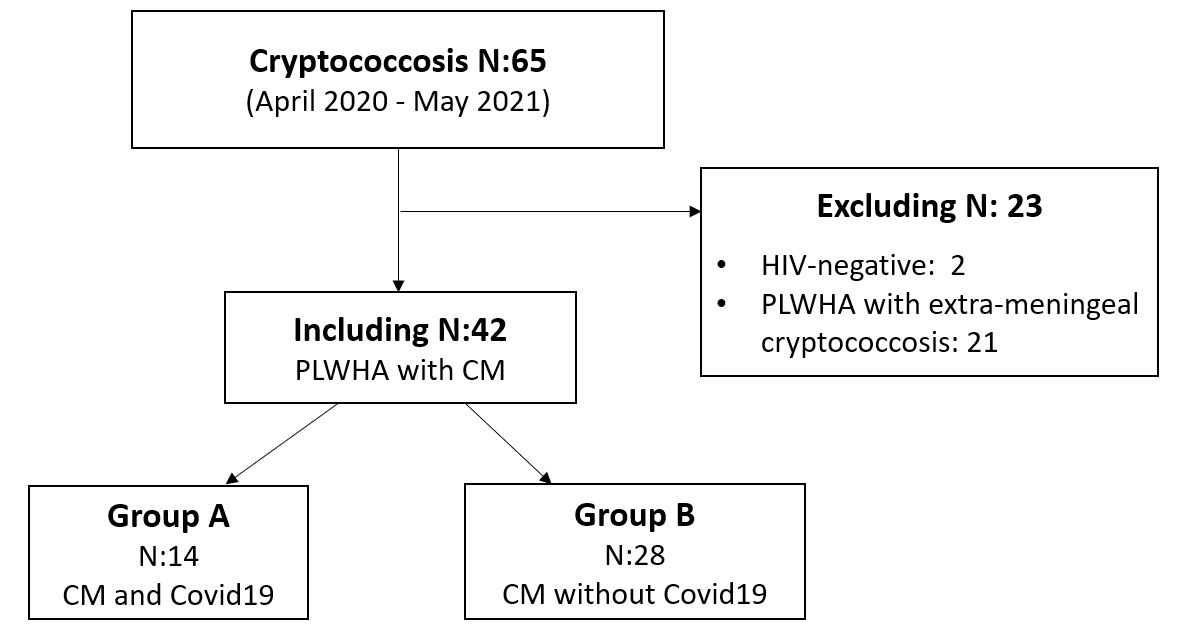
Results. We studied 65 people living with HIV/AIDS and with cryptococcosis infection diagnosed from April 2020 to May 2021. Fifteen patients with HIV/AIDS suffered from cryptococcosis and COVID-19, and out of these, 14 presented meningitis (group A), while 28 suffered from meningeal cryptococcosis, but did not have COVID-19 (group B).
Conclusions. No statistically significant differences were observed between the two groups (A and B) considering: intracranial hypertension, presence of Cryptococcus antigens in cerebrospinal fluid, sensorium deterioration or mortality.
The detection of Cryptococcus antigens in serum by lateral flow assay was highly effective to rapidly diagnose cryptococcosis in patients with HIV/AIDS who also developed COVID-19. Patients of both groups consulted for cryptoccocosis sometime after, in comparison with the pre-pandemic cases related to this infection.
Downloads
References
Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:727-33. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497-506. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Cucinotta D, Vanelli M. WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020;91:157-60. https://doi.org/10.23750 /abm.v91i1.9397
Zhang H, Wu T. CD4+T, CD8+T counts and severe COVID-19: A meta-analysis. J Infect. 2020;81:e82-e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2020.06.036
Ho HE, Peluso MJ, Margus C, Matias Lopes JP, He C, Gaisa MM, et al. Clinical outcomes and immunologic characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in people with human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 2021;223:4038. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa380
Lee KW, Yap SF, Ngeow YF, Lye MS. COVID-19 in people living with HIV: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:3554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073554
Pal R, Singh B, Bhadada SK, Banerjee M, Bhogal RS, Hage N, et al. COVID-19-associated mucormycosis: An updated systematic review of literature. Mycoses. 2021;64:1452-9. https://doi.org/10.1111/myc.13338
Kariyawasam RM, Dingle TC, Kula BE, Vandermeer B, Sligl WI, Schwartz IS. Defining COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2022;28:920-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2022.01.027
Messina F, Marin E, Valerga M, Depardo R, Chediak V, Romero M et al. Updates on AIDS and infectology. Actualizaciones en Sida e Infectología. 2021;29:6-16. https://doi.org/10.52226/revista.v29i105.49
Khatib MY, Ahmed AA, Shaat SB, Mohamed AS, Nashwan AJ. Cryptococcemia in a patient with COVID-19: A case report. Clin Case Rep. 2020;9:853-5. https://doi.org/10.1002/ccr3.3668
Woldie IL, Brown IG, Nwadiaro NF, Patel A, Jarrar M, Quint E, et al. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia in a 24-year-old patient with COVID-19 complicated by secondary cryptococcemia and acute necrotizing encephalitis: A case report and review of literature. J Med Cases. 2020;11:362-5. https://doi.org/10.14740/jmc3575
Frías-De-León MG, Pinto-Almazán R, Hernández-Castro R, GarcíaSalazar E, Meza-Meneses P, Rodríguez-Cerdeira C, et al. Epidemiology of systemic mycoses in the COVID-19 pandemic. J Fungi (Basel). 2021;7:556. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7070556
Arechavala A, Negroni R, Messina F, Romero M, Marín E, Depardo R, et al. Cryptococcosis in an infectious diseases hospital of Buenos Aires, Argentina. Revision of 2041 cases: Diagnosis, clinical features and therapeutics. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2018;35:1-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riam.2017.04.003
Firacative C, Meyer W, Castañeda E. Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gatti species complexes in Latin America: A map of molecular types, genotypic diversity, and antifungal susceptibility as reported by the Latin American Cryptococcal Study Group. J Fungi (Basel). 2021;7:282. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7040282
Rajasingham R, Govender NP, Jordan A, Loyse A, Shroufi A, Denning DW, et al. The global burden of HIV-associated cryptococcal infection in adults in 2020: a modelling analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022;22:1748-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00499-6
Guelfand L, Cataldi S, Arechavala A, Perrone M. Manual práctico de micología médica. Acta Bioquim Clin Latinoam. 2015; Supl. 1.
Arechavala AI, Robles AM, Negroni R, Bianchi MH, Taborda A. Value of direct and indirect diagnostic methods in systemic mycoses associated with AIDS. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1993;35:163-9. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0036-46651993000200008
Huang HR, Fan LC, Rajbanshi B, Xu JF. Evaluation of a new cryptococcal antigen lateral flow immunoassay in serum, cerebrospinal fluid and urine for the diagnosis of cryptococcosis: A meta-analysis and systematic review. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0127117. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127117
IMMY. Immy CrAg lateral flow assay REF CR2003. Fecha de consulta: 05 de agosto del 2020. Disponible en: www.immy.com
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Cryptococcal screening a new strategy for saving lives among people with HIV/AIDS 11-10-2021. Fecha de consulta: 12 de octubre del 2020: Disponible en: https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/pdf/crypto-screen-strategy-508c.pdf
Hu B, Guo H, Zhou P, Shi ZL. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19:141-54. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7. Erratum in: Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022 May;20:315.
Messina FA, Maiolo E, Negroni R, Arechavala A, Santiso G, Bianchi M. Alternativas terapéuticas de la criptococosis meníngea. ASEI. 2015;23:2532.
Liu J, Li H, Luo M, Liu J, Wu L, Lin X, et al. Lymphopenia predicted illness severity and recovery in patients with COVID-19: A single-center, retrospective study. PLoS One. 2020;15:e0241659. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0241659
Toori KU, Qureshi MA, Chaudhry A. Lymphopenia: A useful predictor of COVID-19 disease severity and mortality. Pak J Med Sci. 2021;37:1984-8. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.37.7.4085
Sayah W, Berkane I, Guermache I, Sabri M, Lakhal FZ, Yasmine Rahali S, et al. Interleukin-6, procalcitonin and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: Potential immuneinflammatory parameters to identify severe and fatal forms of COVID-19. Cytokine. 2021;141:155428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155428
Regalla D, VanNatta M, Alam M, Malek AE. COVID-19-associated Cryptococcus infection (CACI): a review of literature and clinical pearls Infection. 2022;50:1-6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-022-01805-y
Some similar items:
- Lida Carolina Lesmes-Rodríguez, Luz Natalia Pedraza-Castillo, Dumar Alexander Jaramillo-Hernández, HCoV-NL63 and HCoV-HKU1 seroprevalence and its relationship with the clinical features of COVID-19 patients from Villavicencio, Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 44 No. 3 (2024): Publicación anticipada, septiembre
- Karen Feriz, Maria B. Iriarte, Oscar Giraldo, Luis G. Parra -Lara, Veline Martinez, Maria A. Urbano, Guillermo Guzman, Clinical outcomes in patients with diabetes and stress hyperglycemia that developed SARS-CoV-2 infection , Biomedica: Vol. 44 No. Sp. 1 (2024): Publicación anticipada, Enfermedades crónicas no transmisibles
- María-Cristina Navas , Juan D. Cerón, Wbeimar Aguilar-Jiménez , María T. Rugeles, Francisco J. Díaz , Outbreak report of SARS-CoV-2 infection by airborne transmission: Epidemiologic and molecular evidence , Biomedica: Vol. 43 No. 1 (2023)
- Cristian Arbey Velarde, Uriel Hurtado, Andres Fernando Cardona Rios, Celeny Ortiz , Idabely Betancur, Genomic epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 δ sublineages of the second wave of 2021 in Antioquia, Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 44 No. 1 (2024)
- Patricia Escandón, Elizabeth Quintero, Diana Granados, Sandra Huérfano, Alejandro Ruiz, Elizabeth Castañeda, Isolation of Cryptococcus gattii serotype B from detritus of Eucalyptus trees in Colombia. , Biomedica: Vol. 25 No. 3 (2005)
- José Roberto Támara-Ramírez, Carlos Arturo Álvarez, Jesús Rodríguez, Loss of follow-up and associated factors in patients enrolled in the HIV/AIDS program of the Hospital Universitario San Ignacio, Colombia, 2012-2013 , Biomedica: Vol. 36 No. 2 (2016)
- Dioselina Peláez, Daniel Martínez-Vargas, Martha Escalante-Mora, Mariel Palacios-Vivero, Lady Contreras-Gómez, Coinfection of hepatitis E virus and other hepatitis virus in Colombia and its genotypic characterization , Biomedica: Vol. 36 (2016): Suplemento 2, Enfermedades virales
- Eliana Patricia Calvo, Carolina Coronel-Ruiz, Syrley Velazco, Myriam Velandia-Romero, Jaime E. Castellanos, Dengue and Chikungunya differential diagnosis in pediatric patients , Biomedica: Vol. 36 (2016): Suplemento 2, Enfermedades virales
- Julián A. Fernández-Niño, Claudia I. Astudillo-García, Laura María Segura, Natalia Gómez, Ángela Skantria Salazar, Juan Hember Tabares, Cristian Andrés Restrepo, Miguel Ángel Ruiz, Myriam Consuelo López, Patricia Reyes, Profiles of intestinal polyparasitism in a community of the Colombian Amazon region , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. 3 (2017)
- Claudia Llerena, Angélica Valbuena, Angie Paola Zabaleta, Mycobacterioses identified in the National Reference Laboratory of Colombia from 2012 to 2016 , Biomedica: Vol. 38 No. Sup. 2 (2018): Suplemento 2, Medicina tropical
Copyright (c) 2023 Biomedica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























