Urticaria inducible: serie de casos y revisión de la literatura
Resumen
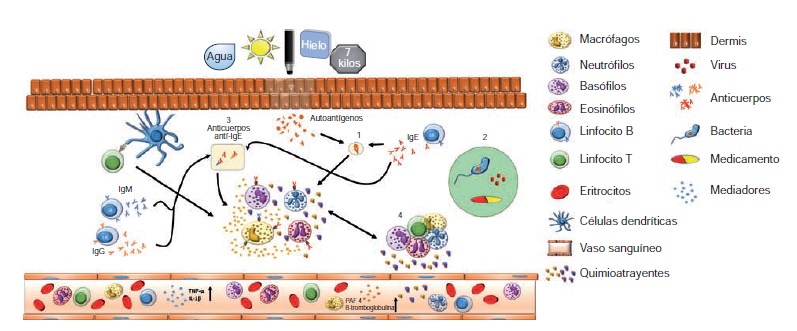
Las urticarias inducibles constituyen un grupo heterogéneo de trastornos cutáneos caracterizados por la aparición de habones, prurito o angioedema, que en ocasiones se acompañan de síntomas sistémicos causados por estímulos inocuos para la mayoría de la población, como el frío, el calor, la presión, etc., y que comprometen la calidad de vida de los pacientes. La mayor parte de la literatura médica pertinente proviene de reportes y series de casos, ya que su epidemiología se ha estudiado poco.
El objetivo de esta revisión es ofrecer una visión actualizada de la información disponible sobre varios tipos de urticaria inducida, mediante la presentación de un caso clínico ilustrativo y la descripción de los mecanismos fisiopatológicos, las manifestaciones clínicas y el tratamiento de cada condición.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Zuberbier T, Aberer W, Asero R, Bindslev-Jensen C, Brzoza Z, Canonica GW, et al . The EAACI/GA(2)LEN/EDF/WAO Guideline for the definition, classification, diagnosis, and management of urticaria: The 2013 revision and update. Allergy. 2014;69:868-87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/all.12313
Bernstein JA, Lang DM, Khan DA, Craig T, Dreyfus D, Hsieh F, et al . The diagnosis and management of acute and chronic urticaria: 2014 update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:1270-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2014
Abajian M, Schoepke N, Altrichter S, Zuberbier T, Zuberbier HC, Maurer M. Physical urticarias and cholinergic urticaria. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2014;34:73-88. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.iac.2013.09.010
Magerl M, Borzova E, Giménez-Arnau A, Grattan CE, Lawlor F, Mathelier-Fusade P, et al . The definition and diagnostic testing of physical and cholinergic urticarias--EAACI/GA2LEN/EDF/UNEV consensus panel recommendations. Allergy. 2009;64:1715-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.02177.x
Mlynek A, Vieira dos Santos R, Ardelean E, Weller K, Magerl M, Church MK, et al . A novel, simple, validated and reproducible instrument for assessing provocation threshold levels in patients with symptomatic dermographism. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38:360-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/ced.12107
Heinzerling L, Mari A, Bergmann KC, Bresciani M, Burbach G, Darsow U, et al . The skin prick test - European standards. Clin Transl Allergy. 2013;3:3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/2045-7022-3-3
Bousquet J, Heinzerling L, Bachert C, Papadopoulos NG, Bousquet PJ, Burney PG, et al . Practical guide to skin prick tests in allergy to aeroallergens. Allergy. 2012;67:18-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02728.x
Herman-Kideckel SM, Cadesky K, Sussman D, Maclachlan S, Sussman G. Association of dermographic urticaria with the use of progesterone in cottonseed oil. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011;106:439-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2011.01.009
Murphy GM, Greaves MW, Zollman PE, Winkelmann RK. Cholinergic urticaria, passive transfer experiments from human to monkey. Dermatologica. 1988;177:338-40.
Garafalo J, Kaplan AP. Histamine release and therapy of severe dermatographism. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981;68:103-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0091-6749(81)90166-4
Metz M, Altrichter S, Ardelean E, Kessler B, Krause K, Magerl M, et al . Anti-immunoglobulin E treatment of patients with recalcitrant physical urticaria. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011;154:177-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000320233
Poon E, Seed PT, Greaves MW, Kobza-Black A. The extent and nature of disability in different urticarial conditions. Br J Dermatol. 1999;140: 667-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2133.1999.02767.x
Barlow RJ, Warburton F, Watson K, Black AK, Greaves MW. Diagnosis and incidence of delayed pressure urticaria in patients with chronic urticaria. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29:954-8.
Dover JS, Black AK, Ward AM, Greaves MW. Delayed pressure urticaria. Clinical features, laboratory investigations, and response to therapy of 44 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988;18:1289-98.
Cassano N, Mastrandrea V, Vestita M, Vena GA. An overview of delayed pressure urticaria with special emphasis on pathogenesis and treatment. Dermatol Ther. 2009;22(Suppl.1):S22-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8019.2009.01268.x
Plager DA, Davis MD, Andrews AG, Coenen MJ, George TJ, Gleich GJ, et al . Eosinophil ribonucleases and their cutaneous lesion-forming activity. J Immunol. 2009;183:4013-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0900055
Plager DA, Weiss EA, Kephart GM, Mocharla RM, Matsumoto R, Checkel JL, et al . Identification of basophils by a mAb directed against pro-major basic protein 1. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:626-34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2005.10.023
Nettis E, Colanardi MC, Soccio AL, Ferrannini A, Vacca A. Desloratadine in combination with montelukast suppresses the dermographometer challenge test papule, and is effective in the treatment of delayed pressure urticaria: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155:1279-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07533.x
Dawn G, Urcelay M, Ah-Weng A, O´Neill SM, Douglas WS. Effect of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in delayed pressure urticaria. Br J Dermatol. 2003;149:836-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05486.x
Magerl M, Philipp S, Manasterski M, Friedrich M, Maurer M. Successful treatment of delayed pressure urticaria with anti-TNF-alpha. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:752-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2006.12.658
Rodríguez-Rodríguez M, Antolin-Amerigo D, Barbarroja-Escudero J, Sánchez-González MJ, Álvarez-Mon M. Successful treatment of severe delayed pressure angio- oedema with omalizumab. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2014;42:78-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aller.2012.11.001
Shelley WB, Rawnsley HM. Aquagenic urticaria. Contact sensitivity to water. JAMA. 1964;189:895-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.1964.03070120017003
Treudler R, Tebbe B, Steinhoff M, Orfanos CE. Familial aquagenic urticaria associated with familial lactose intolerance. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:611-3.
Tkach JR. Aquagenic urticaria. Cutis. 1981;28:454-63.
Chalamidas SL, Charles CR. Aquagenic urticaria. Arch Dermatol. 1971;104:541-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archderm.1971.04000230083015.
Czarnetzki BM, Breetholt KH, Traupe H. Evidence that water acts as a carrier for an epidermal antigen in aquagenic urticaria. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;15 623-7.
Park H, Kim HS, Yoo DS, Kim JW, Kim CW, Kim SS, et al . Aquagenic urticaria: A report of two cases. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:S371-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.S3.S371.
Nosbaum A, Pecquet C, Bayrou O, Amsler E, Nicolas JF, Bérard F, et al . Treatment with propranolol of 6 patients with idiopathic aquagenic pruritus. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:1113. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2011.05.001
Martínez-Escribano JA, Quecedo E, De la Cuadra J, Frías J, Sánchez-Pedreño P, Aliaga A. Treatment of aquagenic urticaria with PUVA and astemizole. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36:118-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0190-9622(97)70344-X
Mathelier-Fusade P, Leynadier F. Cold urticaria. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1994;121:429-33.
Wanderer AA. Cold urticaria syndromes: Historical background, diagnostic classification, clinical and laboratory characteristics, pathogenesis, and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990;85:65-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0091-6749(90)90037-5
Alangari AA, Twarog FJ, Shih MC, Schneider LC. Clinical features and anaphylaxis in children with cold urticaria. Pediatrics. 2004;113:e313-7.
Siebenhaar F, Weller K, Mlynek A, Magerl M, Altrichter S, Vieira Dos Santos R, et al . Acquired cold urticaria: Clinical picture and update on diagnosis and treatment. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2007;32:241-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2230.2007.02376.x
Sánchez JM, Ramírez RH, Tamayo LM, Chinchilla CF, Cardona R. Urticaria por frío: serie de casos y revisión del tema. Biomédica. 2011;31:168-77. http://dx.doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.v31i2.298
Nakamura Y, Kambe N, Saito M, Nishikomori R, Nishikomiri R, Kim YG, et al . Mast cells mediate neutrophil recruitment and vascular leakage through the NLRP3 inflammasome in histamine-independent urticaria. J Exp Med. 2009;206:1037-46. http://dx.doi.org/10.1084/jem.20082179
Lachmann HJ, Kone-Paut I, Kuemmerle-Deschner JB, Leslie KS, Hachulla E, Quartier P, et al . Use of canakinumab in the cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:2416-25. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0810787
Hermes B, Prochazka AK, Haas N, Jurgovsky K, Sticherling M, Henz BM. Upregulation of TNF-alpha and IL-3 expression in lesional and uninvolved skin in different types of urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;103:307-14.
Weinstein ME, Wolff AH, Bielory L. Efficacy and tolerability of second- and third-generation antihistamines in the treatment of acquired cold urticaria: A meta-analysis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010;104:518-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2010.04.002
Boyce JA. Successful treatment of cold-induced urticaria/ anaphylaxis with anti-IgE. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:1415-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2006.04.003
Brodská P, Schmid-Grendelmeier P. Treatment of severe cold contact urticaria with omalizumab: Case reports. Case Rep Dermatol. 2012;4:275-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000346284
Bodar EJ, Simon A, de Visser M, van der Meer JW. Complete remission of severe idiopathic cold urticaria on interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (anakinra). Neth J Med. 2009;67:302-5.
Gualdi G, Monari P, Rossi MT, Crotti S, Calzavara-Pinton PG. Successful treatment of systemic cold contact urticaria with etanercept in a patient with psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1373-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10797.x
Lang DM, Hsieh FH, Bernstein JA. Contemporary approaches to the diagnosis and management of physical urticaria. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013;111:235-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2013.07.031
Zuberbier T, Althaus C, Chantraine-Hess S, Czarnetzki BM. Prevalence of cholinergic urticaria in young adults. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31:978-81.
Godse K, Farooqui S, Nadkarni N, Patil S. Prevalence of cholinergic urticaria in Indian adults. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2013;4:62-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/2229-5178.105493
Bito T, Sawada Y, Tokura Y. Pathogenesis of cholinergic urticaria in relation to sweating. Allergol Int. 2012;61:539-44. http://dx.doi.org/10.2332/allergolint.12-RAI-0485
Takahagi S, Tanaka T, Ishii K, Suzuki H, Kameyoshi Y, Shindo H, et al . Sweat antigen induces histamine release from basophils of patients with cholinergic urticaria asso- ciated with atopic diathesis. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:426-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08862.x
Kobayashi H, Aiba S, Yamagishi T, Tanita M, Hara M, Saito H, et al . Cholinergic urticaria, a new pathogenic concept: Hypohidrosis due to interference with the delivery of sweat to the skin surface. Dermatology. 2002;204:173-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000057877
Sánchez-Borges M, Caballero-Fonseca F, Capriles- Hulett A. Treatment of recalcitrant chronic urticaria with nonsedating antihistamines: Is there evidence for updosing? J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2013;23:141-4.
La Shell MS, England RW. Severe refractory cholinergic urticaria treated with danazol. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006; 5:664-7.
Sabroe RA. Failure of omalizumab in cholinergic urticaria. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35:e127-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2230.2009.03748.x
Metz M, Ohanyan T, Church MK, Maurer M. Retreatment with omalizumab results in rapid remission in chronic spontaneous and inducible urticaria. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:288-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.8705
Patterson R, Mellies CJ, Blankenship ML, Pruzansky JJ. Vibratory angioedema: A hereditary type of physical hypersensitivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1972;50:174-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0091-6749(72)90048-6
Keahey TM, Indrisano J, Lavker RM, Kaliner MA. Delayed vibratory angioedema: Insights into pathophysiologic mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1987;80:831-8.
Mathelier-Fusade P, Vermeulen C, Leynadier F. Vibratory angioedema. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2001;128:750-2.
Pressler A, Grosber M, Halle M, Ring J, Brockow K. Failure of omalizumab and successful control with ketotifen in a patient with vibratory angio-oedema. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38:151-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2230.2012.04430.x
Lawlor F, Black AK, Breathnach AS, Greaves MW. Vibratory angioedema: Lesion induction, clinical features, laboratory and ultrastructural findings and response to therapy. Br J Dermatol. 1989;120:93-9.
Algunos artículos similares:
- Jorge Mario Sánchez, Ruth Helena Ramírez, Liliana María Tamayo, Carlos Fernando Chinchilla, Ricardo Cardona, Urticaria por frío: serie de casos y revisión del tema , Biomédica: Vol. 31 Núm. 2 (2011)
- Elizabeth García, Silvia Duarte, Camila Calderón, John Mario González, Adriana Cuéllar, Alberto Gómez, Evelyne Halpert, Adriana Rodríguez, Expresión de IL-10, IL-4 e IFN-γ en lesiones activas de piel en niños con urticaria papular por picadura de pulga , Biomédica: Vol. 31 Núm. 4 (2011)
- Libia Susana Diez, Liliana María Tamayo, Ricardo Cardona, Omalizumab: opción terapéutica para la urticaria crónica espontánea de difícil control con vasculitis asociada, reporte de tres casos , Biomédica: Vol. 33 Núm. 4 (2013)
- Ana Milena Lozano, Juan Felipe López, Josefina Zakzuk, Elizabeth García, Urticaria papular y sus agentes causales en Colombia , Biomédica: Vol. 36 Núm. 4 (2016)
- Teddy Angarita-Sierra, Alejandro Montañez-Méndez , Tatiana Toro-Sánchez , Ariadna Rodríguez-Vargas , Un caso de envenenamiento por mordedura de una serpiente falsa cabeza de lanza, Leptodeira annulata (Linnaeus, 1758), en el departamento de La Guajira, Colombia , Biomédica: Vol. 40 Núm. 1 (2020)
| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |

























