Tuberculosis associated with tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists, case description and analysis of reported cases in Colombia
Abstract
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is an important fundamental cytokine during the immune response against cancer and infections such as tuberculosis. This molecule also plays a key pathogenic role in complex and difficult-to-treat diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease, psoriasis and ulcerative colitis. The treatment of these diseases frequently needs TNF-α antagonists, which has been related to an increased risk of developing tuberculosis, mycoses, and other severe infections.
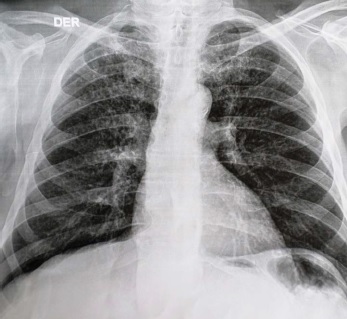
We report the case of a 68-year-old man with Crohn’s disease, who developed disseminated tuberculosis due to anti-TNF-α immunosuppressive therapy. The diagnosis was based on the histopathological findings and molecular biology assays.
We discuss the clinical presentation and workup of this case, and we present a comparative analysis of tuberculosis cases associated with anti-TNF-α reported in Colombia during the last 10 years emphasizing on the diagnosis and treatment of latent tuberculosis.
Downloads
References
Xie X, Li F, Chen JW, Wang J. Risk of tuberculosis infection in anti-TNF-α biological therapy: From bench to bedside. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2014;47:268-74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2013.03.005
Unlu M, Cimen P, Ayranci A, Akarca T, Karaman O, Dereli MS. Disseminated tuberculosis infection and paradoxical reaction during antimycobacterial treatment related to TNFalpha blocker agent Infliximab. Respir Med Case Rep. 2014;13:43-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmcr.2014.09.005
Andrews JR, Noubary F, Walensky RP. Risk of progression to active tuberculosis following reinfection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:784-91. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cir951
World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2015. Geneva. Fecha de consulta: 3 de marzo de 2016. Disponible en: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/191102/1/9789241565059_eng.pdf
Instituto Nacional de Salud. Boletín epidemiológico semana 53, 2015. Fecha de consulta: 3 de marzo de 2016. Disponible en: http://www.ins.gov.co/boletin-epidemiologico/Boletn%20Epidemiolgico/2015%20Boletin%20epidemiologico%20Semana%2052.pdf
Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ. Crohn’s disease. Lancet. 2012;380:1590-605. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60026-9
Pérez-Perdomo R, Pérez-Cardona CM. An epidemiological review of tuberculosis in the Puerto Rican population. PR Health Sci J. 1999;18:117-22.
Molodecky N, Soon I, Rabi D, Ghali W, Ferris M, Chernoff G, et al. Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:46-54. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.10.001
Martínez JV, Medina Y, Parga R, Restrepo JF, Iglesias-Gamarra A, Rondón F. Reactivación de tuberculosis pulmonar (TBC) con el uso de antagonistas del factor de necrosis tumoral alfa (FNTα) en artritis reumatoide. A propósito de un caso. Rev Colomb Reumatol. 2005;12:54-61.
Caballero C, Pinzón L. Artritis reumatoide tratada con inhibidores del factor de necrosis tumoral α (Anti-TNF-α) y tuberculosis pulmonar. Salud Uninorte. 2006;22:29-39.
Rojas-Villarraga A, Agudelo C, Pineda R, Porras A, Matute G, Anaya JM. Tuberculosis in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists living in an endemic area. Is the risk worthwhile? Biomédica. 2007;27:159-71. https://doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.v27i2.212
Hidalgo P, Echeverri J, Gutiérrez J. Tuberculosis pleural asociada con adalimumab en un paciente con artritis reumatoide. Infectio. 2010;14:47-54. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0123-9392(10)70092-8
Cano D, Rodríguez J, Torres C. Terapias biológicas y tuberculosis. Un riesgo manejable. Perspectiva Neumológica. 2014;16. http://www.neumologica.org/sites/default/
files/pdf/perspectiva_neumologica/PN-VOL-16-1-05-2014%20Terapiabiologica.pdf
Insuasty J, Bolívar A, Calvo L, Roberto S. Tuberculosis peritoneal simulando cáncer de ovario. Acta Med Colomb. 2014;39:383-7.
Salgado E, Gómez-Reino JJ. The risk of tuberculosis in patients treated with TNF antagonists. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2011;7:329-40. https://doi.org/10.1586/eci.11.6
O’Garra A, Redford P, McNab F, Bloom C, Wilkinson RJ, Berry M. The immune response in tuberculosis. Annu Rev Immunol. 2013;31:475-527. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-095939
Maini R, St Clair EW, Breedveld F, Furst D, Kalden J, Weisman M, et al. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: A randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet. 1999;354:1932-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(99)05246-0
Keane J, Gershon S, Wise RP, Mirabile-Levens E, Kasznica J, Schwieterman WD, et al. Tuberculosis associated with infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor alphaneutralizing agent. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1098-104. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa011110
Lorenzetti R, Zullo A, Ridola L, Diamanti AP, Laganà B, Gatta L, et al. Higher risk of tuberculosis reactivation when anti-TNF is combined with immunosuppressive agents: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Ann Med. 2014;46:547-54. https://doi.org/10.3109/07853890.2014.941919
Wallis RS, Broder MS, Wong JY, Hanson ME, Beenhouwer DO. Granulomatous infectious diseases associated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:1261-5. https://doi.org/10.1086/383317
Gómez-Reino JJ, Carmona L, Valverde VR, Mola EM, Montero MD, BIOBADASER Group. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors may predispose to significant increase in tuberculosis risk: A multicenter active-surveillance report. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:2122-7. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.11137
Gardam MA, Keystone EC, Menzies R, Manners S, Skamene E, Long R, et al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor agents and tuberculosis risk: Mechanism of action and clinical management. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003;3:148-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(03)00545-0
Tubach F, Salmon D, Ravaud P, Allanore Y, Goupille P, Bréban M, et al. Risk of tuberculosis is higher with antitumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody therapy than with soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor therapy: The three-year prospective French Research Axed on Tolerance of Biotherapies registry. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:1884-94. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24632
Dixon WG, Hyrich KL, Watson KD, Lunt M, Galloway J, Ustianowski A, et al. Drug-specific risk of tuberculosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF therapy: Results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register (BSRBR). Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:522-8. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.118935
Getahun H, Matteelli A, Chaisson RE, Raviglione M. Latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. N Engl J Med 2015;372:2127-35. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1405427
Pai M, Denkinger CM, Kik SV, Rangaka MX, Zwerling A, Oxlade O, et al. Gamma interferon release assays for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014;27:3-20. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00034-13
Jurado LF, Murcia MI, Hidalgo P, Leguizamón JE, González LR. Diagnóstico genotípico y fenotípico de tuberculosis ósea y miliar en un paciente VIH positivo en Bogotá, Colombia. Biomédica. 2015;35:8-15. https://doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.v35i1.2275
Jurado LF, Palacios DM, Álvarez J, Baldión M, Campos G. Diagnóstico patológico y molecular de un caso de tuberculosis laríngea primaria en un médico. Biomédica. 2014;34:15-
https://doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.v34i1.1624
Landry J, Menzies D. Preventive chemotherapy. Where has it got us? Where to go next? Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2008;12:1352-64.
Akolo C, Adetifa I, Shepperd S, Volmink J. Treatment of latent tuberculosis infection in HIV infected persons. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;20:CD000171. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD000171.pub3
Sichletidis L, Settas L, Spyratos D, Chloros D, Patakas D. Tuberculosis in patients receiving anti-TNF agents despite chemoprophylaxis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2006;10:1127-32.
Muñoz OM, Hurtado-Uriarte M, Fernández-Ávila D, Hidalgo P, Gutiérrez-Dávila JM. Conversión de tuberculosis latente en un grupo de pacientes tratados con terapia biológica en una unidad de reumatología. Revista Colombiana de Neumología. 2014;26:116-22.
Furst DE, Keystone EC, So AK, Braun J, Breedveld FC, Burmester GR. Updated consensus statement on biological agents for the treatment of rheumatic diseases 2012. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72:ii2-34. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203348
Mir-Viladrich I, Daudén-Tello E, Solano-López G, López- Longo FJ, Taxonera-Samso C, Sánchez-Martínez P, et al. Documento de consenso sobre la prevención y el tratamiento de la tuberculosis en pacientes candidatos a tratamiento biológico. Arch Bronconeumol. 2016;52:36-45.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arbres.2015.04.016
Juliao F, Agudelo Y, Yepes, Delgado C. Variación en el cuidado de pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII): resultado de una encuesta. Rev Col Gastroenterol. 2014;29:11-8.
Chang B, Park HY, Jeon K, Ahn JK, Cha HS, Koh EM, et al. Interferon-gamma release assay in the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection in arthritis patients treated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists in Korea. Clin Rheumatol. 2011;30:1535-41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-011-1771-9
Winthrop KL, Weinblatt ME, Daley CL. You can’t always get what you want, but if you try sometimes (with two tests-TST and IGRA-for tuberculosis) you get what you need.
Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:1757-60. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201979
Menzies D, Gardiner G, Farhat M, Greenaway C, Pai M. Thinking in three dimensions: A web-based algorithm to aid the interpretation of tuberculin skin test results. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2008;12:498-505.
Some similar items:
- Angie Paola Zabaleta, Claudia Llerena, Angélica Valbuena, Resistant tuberculosis in children under 15 years of age, Colombia 2010-2015 , Biomedica: Vol. 39 No. 2 (2019)
- Julio César Martínez, Claudia Llerena, Yanely Angélica Valbuena, The Importance of investigating Mycobacterium bovis in clinical samples of human origin , Biomedica: Vol. 39 No. Sp. 1 (2019): Suplemento 1, Microbiología médica, mayo
- John-Leonardo Torres-Castiblanco, Jorge Alberto Carrillo, Daniel Hincapié-Urrego, Adriana Rojas-Villarraga, Tuberculosis in the era of anti-TNF-alpha therapy: Why does the risk still exist? , Biomedica: Vol. 38 No. 1 (2018)
- Angie Zabaleta, Claudia Llerena, Extensively resistant tuberculosis, Colombia, 2006-2016 , Biomedica: Vol. 39 No. 4 (2019)
- Claudia Llerena, Angie Zabaleta, Angélica Valbuena, Martha Murcia, Prevalence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistance to quinolones and injectables in Colombia, 2012-2013 , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. 1 (2017)
- Juan Gabriel Bueno-Sánchez, Jairo René Martínez-Morales, Elena E. Stashenko, Wellman Ribón, Anti-tubercular activity of eleven aromatic and medicinal plants occurring in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 1 (2009)
- Raúl Murillo, Ricardo Cendales, Carolina Wiesner, Marion Piñeros, Sandra Tovar, Effectiveness of cytology-based cervical cancer screening in the Colombian health system , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
- Jaime E. Bernal, Martha Lucía Tamayo , Ignacio Briceño , Escilda Benavides , Newborn screening in Colombia: The experience of a private program in Bogotá , Biomedica: Vol. 44 No. 1 (2024)
- Andrés Páez, Gloria Rey, Carlos Agudelo, Alvaro Dulce, Edgar Parra, Hernando Díaz-Granados, Damaris Heredia, Luis Polo, Outbreak of urban rabies transmitted by dogs in Santa Marta, northern Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
- Patricia Escobar, Katherine Paola Luna, Indira Paola Hernández, César Mauricio Rueda, María Magdalena Zorro, Simon L. Croft, In vitro susceptibility of Trypanosoma cruzi strains from Santander, Colombia, to hexadecylphosphocholine (miltefosine), nifurtimox and benznidazole , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























