Classical HLA alleles tag SNP in families from Antioquia with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Introduction: The HLA region strongly associates with autoimmune diseases, such as type 1 diabetes. An alternative way to test classical HLA alleles is by using tag SNP. A set of tag SNP for several classical HLA alleles has been reported as associated with susceptibility or resistance to this disease in Europeans.
Objective: We aimed at validating the methodology based on tag SNP focused on the inference of classical HLA alleles, and at evaluating their association with type 1 diabetes mellitus in a sample of 200 families from Antioquia.
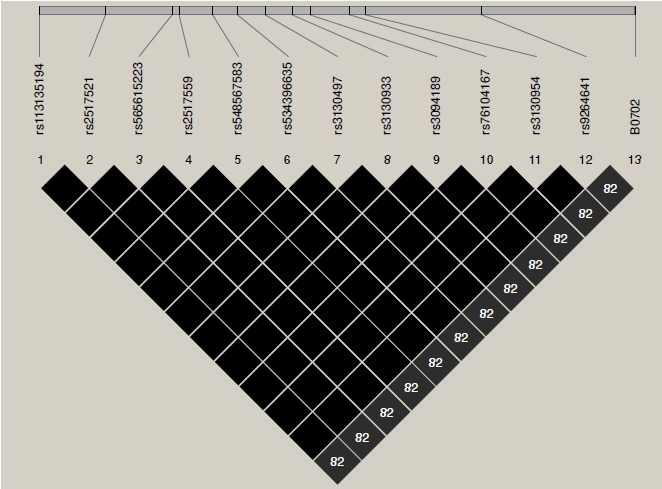
Materials and methods: We studied a sample of 200 families from Antioquia. Each family had one or two children with T1D. We genotyped 13 SNPs using tetra-primer ARMS-PCR or PCRRFLP. In addition, we tested the validity of the tag SNP reported for Europeans in 60 individuals from a population of Colombians living in Medellín (CLM) from the 1000 Genomes Project database. Statistical analyses included the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the transmission disequilibrium and the linkage disequilibrium tests.
Results: The linkage disequilibrium was low in reported tag SNP and classical HLA alleles in this CLM population. Association analyses revealed both risk and protection factors to develop type 1 diabetes mellitus. Appropriate tag SNPs for the CLM population were determined by using the genotype information available in the 1000 Genome Project database.
Conclusions: Although linkage disequilibrium patterns in this CLM population were different from those reported in Europeans, we did find strong evidence of the role of HLA in the development of type 1 diabetes mellitus in the study population.
Downloads
References
Kim MS, Polychronakos C. Immunogenetics of type 1 diabetes. Horm Res. 2005;64:180-8. https://doi.org/10.1159/000089190
Černá M. Genetics of autoimmune diabetes mellitus. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2008;158:2-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10354-007-0448-0
Concannon P, Rich SS, Nepom GT. Genetics of type 1A diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1646-54. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra0808284
Al-Mutairi HF, Mohsen AM, Al-Mazidi ZM. Genetics of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Kuwait Med J. 2007;39:107-15.
Sia C, Weinem M. The role of HLA class I gene variation in autoimmune diabetes. Rev Diabet Stud. 2005;2:97-109.https://doi.org/10.1900/RDS.2005.2.97
Noble JA, Valdés AM, Varney MD, Carlson JA, Moonsamy P, Fear AL, et al. HLA class I and genetic susceptibility to type 1 diabetes: Results from the Type 1 Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Diabetes. 2010;59:2972-9. https://doi.org/10.2337/db10-0699
Cruz-Tapias P, Pérez-Fernández OM, Rojas-Villarraga A, Rodríguez-Rodríguez A, Arango M-T, Anaya JM. Shared HLA class II in six autoimmune diseases in Latin America: A meta-analysis. Autoimmune Dis. 2012;2012:569728. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/569728
Montoya F, Bedoya CI, Restrepo MC, Villegas A, Posada SC, García HI, et al. Determinación de marcadores genéticos en pacientes con diabetes tipo I y población sana. Acta Médica Colombiana. 1996;21:10-6.
de Bakker PI, McVean G, Sabeti PC, Miretti MM, Green T, Marchini J, et al. A high-resolution HLA and SNP haplotype map for disease association studies in the extended human MHC. Nat Genet. 2006;38:1166-72. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1885
Halperin E, Kimmel G, Shamir R. Tag SNP selection in genotype data for maximizing SNP prediction accuracy. Bioinformatics. 2005;21(Suppl.1):i195-203. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti1021
Barker JM, Triolo TM, Aly TA, Baschal EE, Babu SR, Kretowski A, et al. Two single nucleotide polymorphisms identify the highest-risk diabetes HLA genotype potential for rapid screening. Diabetes. 2008;57:3152-5. https://doi.org/10.2337/db08-0605
American Diabetes Association. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(Supl.1):S13-22. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc16-er09
Ye S, Dhillon S, Ke X, Collins AR, Day IN. An efficient procedure for genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:E88-8.
Vincze T, Posfai J, Roberts R. NEBcutter: A program to cleave DNA with restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3688-91.
Durbin RM, Altshuler DL, Abecasis GR, Bentley DR, Chakravarti A, Clark AG, et al. A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature. 2010;467:1061-73. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09534
Gourraud PA, Khankhanian P, Cereb N, Yang SY, Feolo M, Maiers M, et al. HLA diversity in the 1000 genomes dataset. PLoS One. 2014;9:e97282. https://doi.org/1010.
/journal.pone.0097282
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:263-5. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bth457
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;81:559-75. https://doi.org/10.1086/519795
Spielman RS, Ewens WJ. The TDT and other family-based tests for linkage disequilibrium and association. Am J Hum Genet. 1996;59:983-9.
Dudbridge F. Likelihood-based association analysis for nuclear families and unrelated subjects with missing genotype data. Hum Hered. 2008;66:87-98. https://doi.org/10.1159/000119108
Li Q, Fallin MD, Louis TA, Lasseter VK, McGrath JA, Avramopoulos D, et al. Trio logic regression - detection of SNP-SNP interactions in case-parent trios. Genet Epidemiol. 2010;34:396-406. https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.20488
Rodríguez A, Alfaro JM, Balthazar V, Pineda-Trujillo N. Association analysis of PTPN22, CTLA4 and IFIH1 genes with type 1 diabetes in Colombian families. J Diabetes. 2015;7:402-10. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-0407.12192
Slatkin M. Linkage disequilibrium — understanding the evolutionary past and mapping the medical future. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:477-85. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2361
Bedoya G, Montoya P, García J, Soto I, Bourgeois S, Carvajal L, et al. Admixture dynamics in Hispanics: A shift in the nuclear genetic ancestry of a South American population isolate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:7234-9. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0508716103
Gravel S, Zakharia F, Moreno-Estrada A, Byrnes JK, Muzzio M, Rodríguez-Flores JL, et al. Reconstructing Native American migrations from whole-genome and wholeexome data. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1004023. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004023
Stephens JC, Schneider JA, Tanguay DA, Choi J, Acharya T, Stanley SE, et al. Haplotype variation and linkage disequilibrium in 313 human genes. Science. 2001;293:489-93. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1059431
Federal Research Division Library of Congress. Colombia: A country study. 5th ed. Washington, D.C.; U.S. Government Printing Office Official Editions; 2010. p. 541.
Miretti MM, Walsh EC, Ke X, Delgado M, Griffiths M, Hunt S, et al. A high-resolution linkage-disequilibrium map of the human major histocompatibility complex and first generation of tag single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;76:634-46. https://doi.org/10.1086/429393
Rani R, Sood A, Goswami R. Molecular basis of predisposition to develop type 1 diabetes mellitus in North Indians. Tissue Antigens. 2004;64:145-55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0039.2004.00246.x
Aly TA, Ide A, Jahromi MM, Barker JM, Fernando MS, Babu SR, et al. Extreme genetic risk for type 1A diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:14074-9. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0606349103
Noble JA, Martin A, Valdés AM, Lane JA, Galgani A, Petrone A, et al. Type 1 diabetes risk for HLA-DR3 haplotypes depends on genotypic context: Association of DPB1 and HLA class I loci among DR3 and DR4 matched Italian patients and controls. Hum Immunol. 2008;69:291-300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2008.02.003
Mbunwe E, van der Auwera BJ, Weets I, van Crombrugge P, Crenier L, Coeckelberghs M, et al. In antibody-positive first-degree relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes, HLA-A*24 and HLA-B*18, but not HLA-B*39, are predictors of impending diabetes with distinct HLA-DQ interactions. Diabetologia. 2013;56:1964-70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-013-2951-8
Some similar items:
- Sandra Paola Ochoa, Carlos Andrés Ospina, Kelly Johana Colorado, Yenny Paola Montoya, Andrés Fernando Saldarriaga, Marisol Miranda, Natalia Muñoz, María Eugenia Gómez, Fanny Lucía Yepes, Javier Enrique Botero, Periodontal condition and tooth loss in diabetic patients , Biomedica: Vol. 32 No. 1 (2012)
- Luz E. Botero, Andrés E. Toro, Alber J. Patiño, Guillermo Salazar, Juan C. Rodríguez, Juan C. Suárez-Escudero, Gustavo A. Alarcón, Ana Corcimaru, Cristina Osorio, Joseph S. Y. Jeong, Oscar Alzate, Diabetes mellitus in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: clinical description and correlation with the APOE genotype in a sample population from the province of Antioquia, Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 32 No. 2 (2012)
- Silvana Marisa Montenegro, María Cristina Tarrés, Juan Carlos Picena, Stella Maris Martínez, Feeding behavior and glycemic profile in two lines of rats with genetic diabetes. , Biomedica: Vol. 25 No. 4 (2005)
- Argemiro Fragozo, María Fernanda Puerta, Juan Diego Misas, Comparative analysis of insulin glargine vs. insulin detemir: A cost-minimization study applicable to Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 35 No. 2 (2015)
- Henry A. Vargas, Martín Rondón, Rodolfo Dennis, Pharmacological treatment and impairment of pulmonary function in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study , Biomedica: Vol. 36 No. 2 (2016)
- Leticia Bequer, Tahiry Gómez, José Luis Molina, Daniel Artiles, Rosa Bermúdez, Sonia Clapés, Streptozotocin diabetogenic action in an experimental neonatal induction model , Biomedica: Vol. 36 No. 2 (2016)
- Gloria Garavito, Eduardo Egea, Luis Fang, Clara Malagón, Carlos Olmos, Luz González, Pilar Guarnizo, Gustavo Aroca, Guillermo López, Antonio Iglesias, Association of polymorphic variants of PTPN22, TNF and VDR genes in children with lupus nephritis: A study in Colombian family triads , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. 2 (2017)
- Laura Cristina Nocua-Báez, Jorge Alberto Cortés, Aura Lucía Leal, Gerson Fitzgerald Arias, María Victoria Ovalle-Guerro, Sandra Yamile Saavedra-Rojas, Giancarlo Buitrago, Javier Antonio Escobar-Pérez, Betsy Castro-Cardozo, Antimicrobial susceptibility profile in urinary pathogens causing community-acquired infections in diabetic patients in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. 3 (2017)
- Ana Yibby Forero, Jenny Alexandra Hernández, Sandra Milena Rodríguez, Jhon Jairo Romero, Gina Emely Morales, Gabriel Ángel Ramírez, Feeding in adults with type II diabetes mellitus in three public hospitals in Cundinamarca, Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 38 No. 3 (2018)
- Ana María Gómez, Luis G. Chica, Álvaro F. Burbano, Esdras M. Vásquez, Jorge A. Escobar, Paola M. Arias, Dora I. Molina, Survey on hypoglycemia among insulin-treated patients with diabetes: The Colombian International Operations Hypoglycemia Assessment Tool population , Biomedica: Vol. 39 No. 3 (2019)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























