Bacteremia after Bacillus clausii administration for the treatment of acute diarrhea: A case report
Abstract
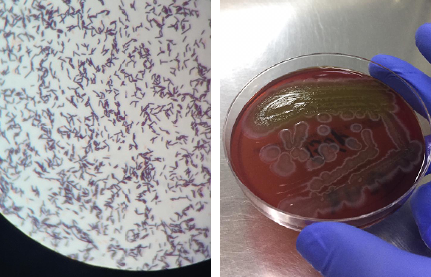
Bacillus clausii is a gram-positive rod used as a probiotic to treat diarrhea and the side effects of antibiotics such as pseudomembranous colitis. We report a case of B. clausii bacteremia in a non-immunocompromised patient with active peptic ulcer disease and acute diarrhea. The probiotic was administered during the patient´s hospitalization due to diarrhea of infectious origin. B. clausii was identified in the bloodstream of the patient through Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight (MALDI-TOF) days after her discharge.
Given the wide use of probiotics, we alert clinicians to consider this microorganism as a causative agent when signs of systemic infection, metabolic compromise, and hemodynamic instability establish after its administration and no pathogens have been identified that could explain the clinical course.
Downloads
References
Duc LH, Hong HA, Barbosa TM, Henriques AO, Cutting SM. Characterization of Bacillus probiotics available for human use. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004;70:2161-71. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.4.2161
Jayanthi N, Ratna MS. Bacillus clausii - The probiotic of choice in the treatment of diarrhoea. J Yoga Phys Ther. 2015;5:1-4. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7595.1000211
Guarino A, Guandalini S, Lo Vecchio A. Probiotics for prevention and treatment of diarrhea. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2015;49(Suppl.1):S37-45. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0000000000000349
Lakshmi SG, Jayanthi N, Saravanan M, Ratna MS. Safety assesment of Bacillus clausii UBBC07, a spore forming probiotic. Toxicol Rep. 2017;4:62-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2016.12.004
Upadrasta A, Pitta S, Madempudi RS. Draft genome sequence of Bacillus clausii UBBC07, a spore-forming probiotic strain. Genome Announc. 2016;4:4-5. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00235-16
Sudha MR, Bhonagiri S, Kumar MA. Efficacy of Bacillus clausii strain UBBC-07 in the treatment of patients suffering from acute diarrhoea. Benef Microbes. 2013;4:211-6. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2012.0034
Ianiro G, Rizzatti G, Plomer M, Lopetuso L, Scaldaferri F, Franceschi F, et al. Bacillus clausii for the treatment of acute diarrhea in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients. 2018;10:1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10081074
Drugs.com. Bacillus clausii. Wolters Kluwer Health; 2018. Consulted: Accessed on June 10, 2021. Available from: https://www.drugs.com/npp/bacillus-clausii.html
Doron S, Snydman DR. Risk and safety of probiotics. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;60 (Suppl. 2):S129-34. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/civ085
Bennet J, Dolin R, Blaser M. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th edition. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2020. p. 2571-3.
Oggioni M, Pozzi G, Valensin P, Galieni P, Bigazzi C. Recurrent septicemia in an immunocompromised patient due to probiotic strains of Bacillus subtilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:325-6. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.36.1.325-326.1998
Gargar JD, Divinagracia RM. When good things go bad: A case series of bacteremia from probiotics. Chest. 2019;155:92A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2019.02.091
Princess I, Natarajan T, Ghosh S. When good bacteria behave badly: A case report of Bacillus clausii sepsis in an immunocompetent adult. Access Microbiol. 2020;2:1-3. https://doi.org/10.1099/acmi.0.000097
Sangeeta J, Soonu U, Supratim S, Suverna K, Anjali S. Bacillus clausii septicemia in a pediatric patient after treatment with probiotics. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2019;38:228-30. https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.0000000000002350
Brunser O. Inocuidad, prevención y riesgos de los probióticos. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2017;88:534-40. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0370-41062017000400015
Castro J de, Kesavelu D, Lahiri KR, Chaijitraruch N, Chongsrisawat V, Jog PP, et al. Recommendations for the adjuvant use of the poly-antibiotic – resistant probiotic Bacillus clausii (O/C, SIN, N/R, T) in acute, chronic, and antibiotic-associated diarrhea in children: Consensus from Asian experts. Trop Dis Travel Med Vaccines. 2020;4:1-15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40794-020-00120-4
Paik NLWKH. Bacillus strains as human probiotics: Characterization, safety, microbiome, and probiotic carrier. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2019;28:1297-305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00691-9
Some similar items:
- María Fernanda Gutiérrez, Sandra Moreno, Mónica Viviana Alvarado, Andrea Bermúdez, DNA sequence analysis indicates human origin of rotavirus and hepatitis A virus strains from western Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 2 (2009)
- Martine Bonnaure-Mallet, Paula Juliana Pérez-Chaparro, Patrice Gracieux, Vincent Meuric, Zohreh Tamanai-Shacoori, Jaime Eduardo Castellanos, Distribution of Porphyromonas gingivalis fimA genotypes in isolates from subgingival plaque and blood sample during bacteremia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 2 (2009)
- Ana Luz Galván, Katherine Bedoya, Martha Nelly Montoya, Jorge Botero, Isolate of Encephalitozoon intestinalis from stools of a Colombian patient with AIDS , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 3 (2008)
- Nélida Muñoz, María Elena Realpe, Elizabeth Castañeda, Clara Inés Agudelo, Characterization by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of Salmonella Typhimurium isolates recovered in the acute diarrheal disease surveillance program in Colombia, 1997-2004 , Biomedica: Vol. 26 No. 3 (2006)
- Iván Darío Flórez, Esteban Ramos, Carlos Bernal, Olga Juliana Cuéllar, José William Cornejo, Intravenous rehydration for diarrheal dehydration of eutrophic children: survey of protocols provided at Colombian medical schools , Biomedica: Vol. 31 No. 3 (2011)
- Andrés F. Henao-Martínez, Guido R. González-Fontal, Steven Johnson, A case of community-acquired Acinetobacter junii-johnsonii cellulitis , Biomedica: Vol. 32 No. 2 (2012)
- Andrés Leonardo González, Aura Lucía Leal, Jorge Alberto Cortés, Ricardo Sánchez, Liliana Isabel Barrero, Juan Sebastián Castillo, Carlos Arturo Álvarez, Effect of adequate initial antimicrobial therapy on mortality in critical patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia , Biomedica: Vol. 34 (2014): Abril, Suplemento 1, Resistencia bacteriana
- Ángela Liliana Londoño-Franco, Juliana Loaiza-Herrera, Fabiana María Lora-Suárez, Jorge Enrique Gómez-Marín, Blastocystis sp. frequency and sources among children from 0 to 5 years of age attending public day care centers in Calarcá, Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 34 No. 2 (2014)
- Carlos Bernal, Claudia Velásquez, Guillermo García, Gustavo Uribe, Carlos Mauricio Palacio, Oral hydratation with a low osmolality solution in dehydrated children with diarrheic diseases: controlled clinical trial. , Biomedica: Vol. 23 No. 1 (2003)
- Victoria Eugenia Ángel, Liliana Franco, Juan Carlos Jaramillo, Luis Alfonso Medina, Francisco Luis Ochoa, Ana María Vélez, David Botero, Inés Helena Vásquez, Cryptosporidiosis en Medellín. Prevalencia de cryptosporidium en muestras fecales diarréicas en 6 laboratorios de Medellín, estudio de 10 casos , Biomedica: Vol. 5 No. 3-4 (1985)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























