Combined hyperglycemic crises in adult patients already exist in Latin America.
Abstract
Introduction. Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common diseases worldwide, with a high morbidity and mortality rate. Its prevalence has been increasing, as well as its acute complications, such as hyperglycemic crises. Hyperglycemic crises can present with combined features of diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar state. However, their implications are not fully understood.
Objective. To describe the characteristics, outcomes, and complications of the diabetic population with hyperglycemic crises and to value the combined state in the Latin American population.
Materials and methods. Retrospective observational study of all hyperglycemic crises treated in the intensive care unit of the Fundación Valle del Lili between January 1, 2015, and December 31, 2020. Descriptive analysis and prevalence ratio estimation for deaths were performed using the robust Poisson regression method.
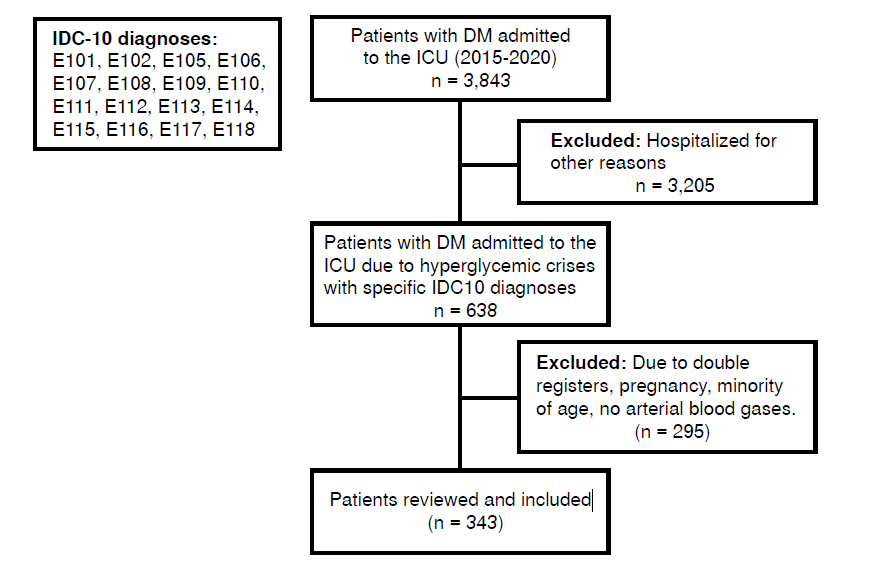
Results. There were 317 patients with confirmed hyperglycemic crises, 43 (13.56%) with diabetic ketoacidosis, 9 (2.83%) in hyperosmolar state, and 265 (83.59%) with combined diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar state. Infection was the most frequent triggering cause (52.52%). Fatalities due to ketoacidosis occurred in four patients (9.30%) and combined diabetic ketoacidosis/hyperosmolar state in 22 patients (8.30%); no patient had a hyperosmolar state. Mechanical ventilation was associated with death occurrence (adjusted PR = 1.15; 95 % CI 95 = 1.06 - 1.24).
Conclusions. The combined state was the most prevalent presentation of the hyperglycemic crisis, with a mortality rate similar to diabetic ketoacidosis. Invasive mechanical ventilation was associated with a higher occurrence of death.
Downloads
References
Stanaway JD, Afshin A, Gakidou E, Lim SS, Abate D, Abate KH, et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioral, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Stu. Lancet. 2018;392:1923-94. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32225-6
Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;128:40-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2017.03.024
Harris S, Aschner P, Mequanint S, Esler J. Use of diabetes registry data for comparing indices of diabetes management: A comparison of 2 urban sites in Canada and Colombia. Can J Diabetes. 2015;39:496-501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcjd.2015.05.010
Vargas-Uricoechea H, Casas-Figueroa LÁ. An epidemiologic analysis of diabetes in Colombia. Ann Glob Health. 2015;81:742-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aogh.2015.11.001
Umpierrez G, Korytkowski M. Diabetic emergencies-ketoacidosis, hyperglycaemic hyperosmolar state and hypoglycaemia. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12):222-32. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2016.15
Domínguez M, Calderón A, Armas R. Características clínico-epidemiológicas de las complicaciones agudas de la diabetes en el servicio de urgencias del Hospital General de Atizapán. Rev Fac Med UNAM. 2013;56:25-36.
Umpierrez GE, Kelly JP, Navarrete JE, Casals MM, Kitabchi AE. Hyperglycemic crises in urban blacks. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157:669-75. https://doi.org/10.1001/ARCHINTE.1997.00440270117011
Xu Y, Bai J, Wang G, Zhong S, Su X, Huang Z, et al. Clinical profile of diabetic ketoacidosis in tertiary hospitals in China: A multicentre, clinic-based study. Diabet Med. 2016;33:261-8. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.12820
Anthanont P, Khawcharoenporn T, Tharavanij T. Incidences and outcomes of hyperglycemic crises: A 5-year study in a tertiary care center in Thailand. J Med Assoc Thai. 2012;95:995-1002.
Wachtel TJ, Tetu-Mouradjian LM, Goldman DL, Ellis SE, O’Sullivan PS. Hyperosmolarity and acidosis in diabetes mellitus - A three-year experience in Rhode Island. J Gen Intern Med. 1991;6:495-502. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02598216
Pasquel FJ, Tsegka K, Wang H, Cardona S, Galindo RJ, Fayfman M, et al. Clinical outcomes in patients with isolated or combined diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state: A retrospective, hospital-based cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2020;43:349-57. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-1168
Fayfman M, Pasquel FJ, Umpierrez GE. Management of hyperglycemic crises: Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Med Clin North Am. 2017;101:587-606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2016.12.011
Samos LF, Roos BA. Diabetes mellitus in older persons. Med Clin North Am. 1998;82:791-803. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-7125(05)70024-9
McCoy RG, Galindo RJ, Swarna KS, van Houten HK, O’Connor PJ, Umpierrez GE, et al. Sociodemographic, clinical, and treatment-related factors associated with hyperglycemic crises among adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes in the US from 2014 to 2020. AMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2123471. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.23471
Builes-Montaño CE, Chavarriaga A, Ballesteros L, Muñoz M, Medina S, Donado-Gómez JH, et al. Characteristics of hyperglycemic crises in an adult population in a teaching hospital in Colombia. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2018;17:143-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-018-0353-7
Chen HF, Wang CY, Lee HY, See TT, Chen MH, Jiang JY, et al. Short-term case fatality rate and associated factors among inpatients with diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state: A hospital-based analysis over a 15-year period. Intern Med. 2010;49:729-37. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.49.2965
Fadini GP, de Kreutzenberg SV, Rigato M, Brocco S, Marchesan M, Tiengo A, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of the hyperglycemic hyperosmolar non-ketotic syndrome in a cohort of 51 consecutive cases at a single center. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;94:172-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DIABRES.2011.06.01
Nishikawa T, Kinoshita H, Ono K, Kodama-Hashimoto S, Kobayashi Y, Nakamura T, et al. Clinical profiles of hyperglycemic crises: A single-center retrospective study from Japan. J Diabetes Investig. 2021;12:1359-66. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.13475
Álvarez LS, Salmon JW, Swartzman D. The Colombian health insurance system and its effect on access to health care. Int J Health Serv. 2011;41:355-70. https://doi.org/10.2190/HS.41.2.i
Gosmanov AR, Gosmanova EO, Kitabchi AE. Hyperglycemic crises: Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, et al., editors. Endotext. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000. Accessed: May 9, 2021. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279052/
Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM, Fisher JN. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:1335-43 https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-9032
Guisado-Vasco P, Cano-Megías M, Carrasco-de la Fuente M, Corres-González J, Matei AM, González-Albarrán O. Clinical features, mortality, hospital admission, and length of stay of a cohort of adult patients with diabetic ketoacidosis attending the emergency room of a tertiary hospital in Spain. Endocrinol Nutr. 2015;62:277-84. https://doi.org 10.1016/j.endonu.2015.02.003
Dhatariya KK, Nunney I, Higgins K, Sampson MJ, Iceton G. National survey of the management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) in the UK in 2014. Diabet Med. 2016;33:252-60. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.12875
Some similar items:
- Luis Eduardo Echeverría, Clara Saldarriaga, Sebastián Campbell-Quintero, Lisbeth Natalia Morales-Rodríguez, Juan David López-Ponce de León, Andrés Felipe Buitrago, Erika Martínez-Carreño, Jorge Alberto Sandoval-Luna, Alexis Llamas, Gustavo Adolfo Moreno-Silgado, Julián Vanegas-Eljach, Nelson Eduardo Murillo-Benítez, Ricardo Gómez-Paláu, Alex Arnulfo Rivera-Toquica, Juan Esteban Gómez-Mesa, RECOLFACA research group, Diabetes mellitus in patients with heart failure and effect modification of risk factors for short-term mortality: An observational study from the Registro Colombiano de Falla Cardíaca (RECOLFACA) , Biomedica: Vol. 44 No. Sp. 1 (2024): Enfermedades crónicas no transmisibles
- Karen Feriz, Maria B. Iriarte, Oscar Giraldo, Luis G. Parra -Lara, Veline Martinez, Maria A. Urbano, Guillermo Guzman, Clinical outcomes in patients with diabetes and stress hyperglycemia that developed SARS-CoV-2 infection , Biomedica: Vol. 44 No. Sp. 1 (2024): Enfermedades crónicas no transmisibles
- Julio César Velasco, Ledmar Jovanny Vargas , Lorena García, Iván José Torres, Iván Camilo González , Oral mucormycosis associated with COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: Case report and literature review , Biomedica: Vol. 44 No. 1 (2024)
- Karen Melissa Ordóñez, Odismar Andrea Hernández, Jorge Alberto Cortés, María José López, Gladys Alfonso, Alejandro Junca, Left-sided infective endocarditis caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa treated medically , Biomedica: Vol. 30 No. 2 (2010)
- Jairo Lizarazo, Melva Linares, Catalina de Bedout, Ángela Restrepo, Clara Inés Agudelo, Elizabeth Castañeda, Grupo Colombiano para el Estudio de la Criptococosis, Results of nine years of the clinical and epidemiological survey on cryptococcosis in Colombia, 1997-2005 , Biomedica: Vol. 27 No. 1 (2007)
- Sandra Paola Ochoa, Carlos Andrés Ospina, Kelly Johana Colorado, Yenny Paola Montoya, Andrés Fernando Saldarriaga, Marisol Miranda, Natalia Muñoz, María Eugenia Gómez, Fanny Lucía Yepes, Javier Enrique Botero, Periodontal condition and tooth loss in diabetic patients , Biomedica: Vol. 32 No. 1 (2012)
- Luz E. Botero, Andrés E. Toro, Alber J. Patiño, Guillermo Salazar, Juan C. Rodríguez, Juan C. Suárez-Escudero, Gustavo A. Alarcón, Ana Corcimaru, Cristina Osorio, Joseph S. Y. Jeong, Oscar Alzate, Diabetes mellitus in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: clinical description and correlation with the APOE genotype in a sample population from the province of Antioquia, Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 32 No. 2 (2012)
- Álvaro J. Ruiz, Pablo J. Aschner, María Fernanda Puerta, Rafael Alfonso-Cristancho, IDEA Study (International Day for the Evaluation of Abdominal Obesity): Primary care study of the prevalence of abdominal obesity and associated risk factors in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 32 No. 4 (2012)
- Andrés Leonardo González, Aura Lucía Leal, Jorge Alberto Cortés, Ricardo Sánchez, Liliana Isabel Barrero, Juan Sebastián Castillo, Carlos Arturo Álvarez, Effect of adequate initial antimicrobial therapy on mortality in critical patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia , Biomedica: Vol. 34 (2014): Abril, Suplemento 1, Resistencia bacteriana
- Ricardo Pineda-Tamayo, Giovanna Arcila, Patricia Restrepo, Juan Manuel Anaya, Impact of cardiovascular illness on hospitalization costs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. , Biomedica: Vol. 24 No. 4 (2004)
Copyright (c) 2024 Biomedica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























