Los patrones electroforéticos de proteínas salivales permiten diferenciar los grupos transandino y cisandino de las especies de Rhodnius de Colombia
Resumen
Introducción. Las especies Rhodnius (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae) están conformadas por insectos hematófagos vectores de Trypanosoma cruzi, agente etiológico de la enfermedad de Chagas, y T. rangeli, parásito infectivo pero no patógeno para el vertebrado. El estudio de la diversidad proteica de la saliva de estos insectos permite la obtención de perfiles electroforéticos unidimensionales característicos de algunas especies de triatominos. Sin embargo, el reporte de los patrones electroforéticos de proteínas salivales de las especies de Rhodnius ha sido escaso.
Objetivo. Hacer un análisis comparativo de los perfiles electroforéticos unidimensionales de las proteínas salivales de R. colombiensis, R. pallescens, R. pictipes, R. prolixus y R. robustus.
Materiales y métodos. Se obtuvieron los perfiles electroforéticos de la saliva de las especies en estudio mediante electroforesis en gel de poliacrilamida con dodecilsulfatosódico (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis, SDS-PAGE) y se construyó un fenograma mediante el método UPGMA (Unweighted Pair Group Method Using Arithmetic Averages).
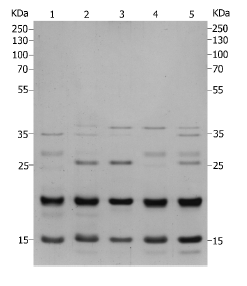
Resultados. Los perfiles electroforéticos de las proteínas solubles de saliva presentaron bandas en un rango de masa aproximado de 15 a 45 kDa, los cuales permitieron diferenciar las cinco especies estudiadas. El fenograma reveló la existencia de dos grupos principales: uno conformado por los grupos cisandinos Pictipes y Prolixus y otro constituido por el grupo transandino Pallescens.
Conclusiones. Existen diferencias en los perfiles electroforéticos de las proteínas salivales entre R. colombiensis, R. pallescens, R. pictipes, R. prolixus y R. robustus, cuya variabilidad permitió construir un fenograma congruente con los grupos del género Rhodnius.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Justi S, Galvão C, Schrago G. Geological changes of the Americas and their influence on the diversification of the neotropical kissing bugs (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae). PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10:e0004527. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0004527
Da Rosa J, Justino H, Nascimento J, Mendonça V, Rocha C, de Carvalho D, et al. A new species of Rhodnius from Brazil (Hemiptera, Reduviidae, Triatominae). ZooKeys. 2017;675:1-25. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.675.12024
Cuba-Cuba C. Revisión de los aspectos biológicos y diagnósticos del Trypanosoma (Herpetosoma) rangeli. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 1998;31:207-20. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0037-86821998000200007
Vallejo G, Suárez Y, Olaya J, Gutiérrez S, Carranza J. Trypanosoma rangeli: un protozoo infectivo y no patógeno para el humano que contribuye al entendimiento de la transmisión vectorial y la infección por Trypanosoma cruzi, agente causal de la enfermedad de Chagas. Revista de la Academia Colombiana de Ciencias Exactas Físicas y Naturales. 2015;39:111-22.
Abad-Franch F, Monteiro F, Gurgel-Golçalves R, Dias F, Diotaiuti L. Ecology, evolution, and the long-term surveillance of vector-borne Chagas disease: A multi-scale appraisal of the tribe Rhodniini (Triatominae). Acta Trop. 2009;110:159-77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2008.06.005
Díaz S, Panzera F, Jaramillo-O N, Pérez R, Fernández R, Vallejo G, et al. Genetic, cytogenetic and morphological trends in the evolution of the Rhodnius (Triatominae: Rhodniini) Trans-Andean group. PLoS One. 2014;9:e87493. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087493
Galvão C, Justi S. The evolutionary origin of diversity in Chagas disease vectors. Trends Parasitol. 2017;33:42-52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2016.11.002
Schofield C, Dujardin J. Theories on the evolution of Rhodnius. Actualidades Biológicas. 1999;21:183-97.
Schofield C, Galvão C. Classification, evolution and species groups within the Triatominae. Acta Trop. 2009;110:88-100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2009.01.010
Arévalo A, Carranza JC, Guhl F, Vallejo GA. Patrones electroforéticos de hemoproteínas salivares (nitroforinas) de Rhodnius colombiensis y Rhodnius prolixus (Hemiptera, Reduviidae, Triatominae). Biomédica. 2007;27(Suppl.1):137-42. https://doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.v27i1.257
Soares R, Gontijo N, Romanha A, Diotaiuti L, Pereira M. Salivary heme proteins distinguish Rhodnius prolixus from Rhodnius robustus (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae). Acta Trop. 1998;71:285-91. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-706X(98)00065-5
Soares R, Sant’Anna M, Gontijo N, Romanha A, Diotaiuti L, Pereira M. Identification of morphologically similar Rhodnius species (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae) by electrophoresis of salivary heme proteins. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000;62:157-61.
Barbosa S, Diotaiuti L, Braga E, Pereira M. Variability of the salivary proteins of 20 Brazilian populations of Panstrongylus megistus (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae). Acta Trop. 2004;92:25-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2004.05.012
Flórez M, Niño R, Gonzalo R, Muñoz G, Angulo V. Perfil electroforético de proteínas presentes en la saliva de Triatoma dimidiata (Hemiptera: Reduviidae:Triatominae). Salud UIS. 2009;41:121-7.
Pineda S, Melgar S, Dorn P, Agreda E, Rodas A, Monroy C. Salivary protein profiles distinguish triatomine species and populations of Triatoma dimidiata (Hemiptera: Reduviidae). J Med Entomol. 2008;45:52-8. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/45.1.52
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248-54. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Blum H, Beier H, Gross HJ. Improved silver staining of plant proteins, RNA and DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis. 1987;8:93-9.
Shevchenko A, Wilm M, Vorm O, Mann M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins silverstained polyacrylamide gels. Anal Chem. 1996;68:850-8. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac950914h
Dice L. Measures of the amount of ecological association between species. Ecology. 1945;26:297-302. https://doi.org/10.2307/1932409
Ribeiro J, Andersen J, Silva-Neto M, Pham V, Garfield M, Valenzuela J. Exploring the sialome of the blood-sucking bug Rhodnius prolixus. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2004;34:61-79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2003.09.004
Andersen J, Gudderra N, Francischetti I, Ribeiro J. The role of salivary lipocalins in blood feeding by Rhodnius prolixus. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2005;58:97-105. https://doi.org/10.1002/arch.20032
Francischetti I, Ribeiro J, Champagne D, Andersen J. Purification, cloning, expression, and mechanism of action of a novel platelet aggregation inhibitor from the salivary gland of the blood-sucking bug, Rhodnius prolixus. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:12639-50. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.17.12639
Sun J, Yuda M, Miura K, Chinzei Y. Characterization and cDNA cloning of a hemoprotein in the salivary glands of the blood-sucking insect, Rhodnius prolixus. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1998;29:191-200. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0965-1748(97)00115-X
Costa C, Sousa M, Ricart C, Santana J, Teixeira A, Roepstorff P, et al. 2-DE-based proteomic investigation of the saliva of the Amazonian triatomine vectors of Chagas disease: Rhodnius brethesi and Rhodnius robustus. J Proteomics. 2011;74:1652-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2011.02.022
Montandon C, Barros E, Vidigal P, Mendes M, Anhê A, de Oliveira H, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of the saliva of the Rhodnius prolixus, Triatoma lecticularia and Panstrongylus herreri triatomines reveals a high interespecific functional biodiversity. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2016;71:83-90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2016.02.009
Santiago P, Assumpção T, Araújo C, Bastos I, Neves D, Silva I, et al. A deep insight into the sialome of Rhodnius neglectus, a vector of Chagas disease. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10:e0004581. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0004581
Andrade B, Teixeira R, Barral A, Barral-Netto M. Haematophagous arthropod saliva and host defense system: A tale of tear and blood. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências. 2005;77:665-93. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0001-37652005000400008
Fontaine A, Diouf I, Bakkali N, Missé D, Pagès F, Fusai F, et al. Implication of haematophagous arthropod salivary proteins in host-vector interactions. Parasit Vectors. 2011;187:1-17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-4-187
Bargues M, Schofield C, Dujardin J. Classification and phylogeny of the Triatominae. En: Telleria J, Tibayrenc M, editors. American Trypanosomiasis, Chagas Disease One Hundred Years of Research. Montpellier: Elsevier; 2010. p.117-47. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-384876-5.00006-X
Lyman D, Monteiro F, Escalante A, Cordon-Rosales C, Wesson D, Dujardin JP, et al. Mitochondrial DNA sequence variation among triatomine vectors of Chagas’ disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;60:377-86. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.1999.60.377
Monteiro F, Wesson D, Dotson E, Schofield C, Beard C. Phylogeny and molecular taxonomy of the Rhodniini derived from mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000;62:460-5.
Hypsa V, Tietz D, Zrzavy J, Rego R, Galvão C, Jurberg J. Phylogeny and biogeography of Triatominae (Hemiptera Reduviidae): Molecular evidence of a New World origin of the Asiatic clade. Mol Phylogen Evol. 2002;23:447-57. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1055-7903(02)00023-4
Justi S, Russo C, Dos Santos J, Takashi M, Galvão C. Molecular phylogeny of Triatomini (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae). Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:149-61. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-7-149
Barreto-Santana D, Santos-Schuenker L, da Fonseca A, Gurgel-Gonçalves R, Cuba-Cuba
A. Susceptibility of different Rhodnius species (Hemiptera, Reduviidae, Triatominae) to a Brazilian strain of Trypanosoma rangeli (SC58/KP1-). Biomédica. 2015;35:81-9. https://doi.org/10.7705/biomedica.v35i1.2213
Algunos artículos similares:
- Diana Carolina López, Carlos Jaramillo, Felipe Guhl, Estructura poblacional y variabilidad genética de Rhodnius prolixus (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) procedente de diferentes áreas geográficas de Colombia , Biomédica: Vol. 27 Núm. 1esp (2007): Enfermedad de Chagas
- Gustavo Adolfo Vallejo, Felipe Guhl, Julio César Carranza, Omar Triana, Gerardo Pérez, Paola Andrea Ortiz, Dairo Humberto Marín, Lina Marcela Villa, Jazmín Suárez, Isaura Pilar Sánchez, Ximena Pulido, Ingrid Bibiana Rodríguez, Leyder Elena Lozano, Daniel Alfonso Urrea, Fredy Arvey Rivera, César Cuba-Cuba, Jairo Alfonso Clavijo, Interacción tripanosoma-vector-vertebrado y su relación con la sistemática y la epidemiología de la tripanosomiasis americana , Biomédica: Vol. 27 Núm. 1esp (2007): Enfermedad de Chagas
- Andrea Arévalo, Julio César Carranza, Felipe Guhl, Jairo Alfonso Clavijo, Gustavo Adolfo Vallejo, Comparación del ciclo de vida de Rhodnius colombiensis Moreno, Jurberg & Galvão, 1999 y Rhodnius prolixus Stal, 1872(Hemiptera, Reduviidae, Triatominae) en condiciones de laboratorio , Biomédica: Vol. 27 Núm. 1esp (2007): Enfermedad de Chagas
- Andrea Arévalo, Julio César Carranza, Felipe Guhl, Gustavo Adolfo Vallejo, Patrones electroforéticos de hemoproteínas salivares (nitroforinas) de Rhodnius colombiensis y Rhodnius prolixus (Hemiptera, Reduviidae, Triatominae) , Biomédica: Vol. 27 Núm. 1esp (2007): Enfermedad de Chagas
- Elsa Nieves, Neudo Buelvas, Maritza Rondón, Néstor González, Las glándulas salivales de dos flebotominos vectores de Leishmania: Lutzomyia migonei (França) y Lutzomyia ovallesi (Ortiz) (Diptera: Psychodidae) , Biomédica: Vol. 30 Núm. 3 (2010)
- Lorenzo Cáceres, José R. Rovira, José Calzada, Azael Saldaña, Evaluación de la actividad tóxica de los insecticidas piretroides deltametrina y lambdacihalotrina en dos poblaciones de campo de Rhodnius pallescens (Hemíptera: Reduviidae) de Panamá , Biomédica: Vol. 31 Núm. 1 (2011)
- Víctor Manuel Angulo, Lyda Esteban, Katherine Paola Luna, Attalea butyracea próximas a las viviendas como posible fuente de infestación domiciliaria por Rhodnius prolixus (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) en los Llanos Orientales de Colombia , Biomédica: Vol. 32 Núm. 2 (2012)
- Camilo Rubio, Ligia Inés Moncada, Marco Andrés Rojas, Alexander García, Comportamiento de Rhodnius robustus Larousse, 1927 (Hemiptera, Reduviidae) durante su alimentación en condiciones de laboratorio , Biomédica: Vol. 33 Núm. 2 (2013)
- Víctor Manuel Angulo, Lyda Esteban, Plutarco Urbano, Eduwin Hincapié, Luis Alberto Núñez, Comparación de métodos para la captura de triatominos (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) en palmas Attalea butyracea en los Llanos Orientales de Colombia , Biomédica: Vol. 33 Núm. 4 (2013)
- Carmen Vásquez, Sara Robledo, Jaime Calle, Omar Triana, Identificación de nuevos escenarios epidemiológicos para la enfermedad de Chagas en la región momposina, norte de Colombia , Biomédica: Vol. 33 Núm. 4 (2013)
| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |

























