Medication errors in outpatient care in Colombia, 2005-2013
Abstract
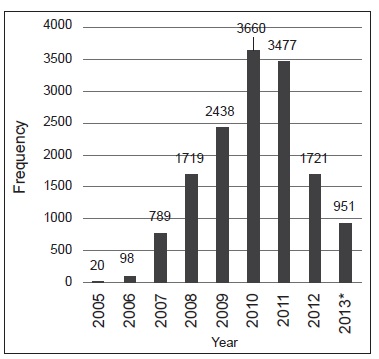
Introduction: Medication errors outside the hospital have been poorly studied despite representing an important threat to patient safety. Objective: To describe the characteristics of medication errors in outpatient dispensing pharmacists reported in a pharmaco-surveillance system between 2005 and 2013 in Colombia. Materials and methods: We conducted a descriptive study by reviewing and categorizing medication error reports from outpatient pharmacy services to a national medication dispensing company between January, 2005 and September, 2013. Variables considered included: process involved (administration, dispensing, prescription and transcription), wrong drug, time delay for the report, error type, cause and severity. The analysis was conducted in the SPSS® software, version 22.0. Results: A total of 14,873 medication errors were reviewed, of which 67.2% in fact occurred, 15.5% reached the patient and 0.7% caused harm. Administration (OR=93.61, CI 95%: 48.510-180.655, p<0.001), dispensing (OR=21.58, CI 95%: 16.139-28.870, p<0.001), transcription errors (OR=5.64; CI 95%: 3.488-9.142, p<0.001), medicines for sensory organs (OR=2.04, CI 95%: 1.519-2.756, p<0.001), anti-infective drugs for systemic use (OR=1.99, CI 95%: 1.574-2.525, p0.001), confusion generated with the name of the drug (OR=1.28, CI 95%: 1.051-1.560, p=0.014), and trouble interpreting prescriptions (OR=1.32, CI 95%: 1.037-1.702, p=0.025) increased the risk for error reaching the patient. Conclusions: It is necessary to develop surveillance systems for medication errors in ambulatory care, focusing on the prescription, transcription and dispensation processes. Special strategies are needed for the prevention of medication errors related to anti-infective drugs.
Downloads
References
Santell JP, Hicks RW, McMeekin J, Cousins DD. Medication errors: Experience of the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) MEDMARX reporting system. J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;43:760-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0091270003254831
Benjamin DM. Reducing medication errors and increasing patient safety: Case studies in clinical pharmacology. J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;43:768-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0091270003254794
Bootman JL, Wolcott J, Aspden P, Cronenwett LR. Preventing medication errors: Quality Chasm Series. Danvers, USA: National Academies Press; 2006.
Keers RN, Williams SD, Cooke J, Ashcroft DM. Prevalence and nature of medication administration errors in health care settings: A systematic review of direct observational evidence. Ann Pharmacother. 2013;47:237-56. http://dx.doi.org/10.1345/aph.1R147
Díaz GE, Lázaro LA, Horta HA. Analysis of pharmaceutical intervention in outpatient pharmacy department. Farm Hosp. 2012;37:295-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.7399/FH.2013.37.4.588
Nicolas A, Eickhoff C, Griese N, Schulz M. Drug-related problems in prescribed medicines in Germany at the time of dispensing. Int J Clin Pharm. 2013;35:476-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11096-013-9769-9
The National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention. NCC MERP: The first ten years "defining the problem and developing solutions". Accessed on: January 2, 2014. Available at: http://www.nccmerp.org/pdf/reportFinal2005-11-29.pdf.
Gautam PL. Minimizing medication errors: Moving attention from individual to system. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2013;29:293-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/0970-9185.117037
Berman A. Reducing medication errors through naming, labeling, and packaging. J Med Syst. 2004;28:9-29. http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/B:JOMS.0000021518.60670.10
Knudsen P, Herborg H, Mortensen AR, Knudsen M, Hellebek A. Preventing medication errors in community pharmacy: Root-cause analysis of transcription errors. Qual Saf Health Care. 2007;16:285-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/qshc.2006.022053
Mansouri A, Ahmadvand A, Hadjibabaie M, Kargar M, Javadi M, Gholami K. Types and severity of medication errors in Iran; a review of the current literature. Daru. 2013;21:49. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/2008-2231-21-49
Merino P, Martín MC, Alonso A, Gutiérrez I, Álvarez J, Becerril F, et al . Medication errors in Spanish intensive care units. Med Intensiva. 2013;37:391-9. http://dx.doi.org/0.1016/j.medin.2012.11.002
Salmasi S, Khan TM, Hong YH, Ming LC, Wong TW. Medication errors in the Southeast Asian countries: A systematic review. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0136545. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136545
Carlton G, Blegen MA. Medication-related errors: A literature review of incidence and antecedents. Annu Rev Nurs Res. 2006;24:19-38.
Ambrosio L, Pumar-Méndez MJ. The role of occupational context factors in medication administration errors. An Sist Sanit Navar. 2013;36:77-85.
Oliven A, Michalake I, Zalman D, Dorman E, Yeshurun D, Odeh M. Prevention of prescription errors by computerized, on-line surveillance of drug order entry. Int J Med Inform. 2005;74:377-86. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2005.03.010
Aronson JK. 50 - Medication errors. Side Effects of Drugs Annual. 2010;32:903-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0378-6080(10)32050-2
Espinosa JC. Frecuencia y caracterización de los errores de medicación en un servicio de hospitalización de una clínica en Cali, Colombia. Rev Colomb Cienc Quím Farm. 2013;42:5-18.
Machado-Alba JE, Ossa-Ochoa L, Lotero-Jaramillo N, Valencia-Rojas A. Identification of medication errors in a first level hospital of Pereira, Colombia. Rev Fac Med 2013;61:267-73.
Gonzales K. Medication administration errors and the pediatric population: A systematic search of the literature. J Pediatr Nurs. 2010;25:555-65. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pedn.2010.04.002
Engum SA, Breckler FD. An evaluation of medication errors - The pediatric surgical service experience. J Pediatr Surg. 2008;43:348-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg. 2007.10.042
Jeetu G, Girish T. Prescription drug labeling medication errors: A big deal for pharmacists. J Young Pharm. 2010;2:107-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/0975-1483.62218
Some similar items:
- Luis Fernando Valladales-Restrepo , Camilo Alexander Constain-Mosquera , María Alejandra Hoyos-Guapacha , Karol Liceth Hoyos-Guapacha , Andrés Gaviria-Mendoza, Manuel Enrique Machado-Duque , Jorge Enrique Machado-Alba, Study of the indications for macrolide prescriptions in a Colombian population , Biomedica: Vol. 42 No. 2 (2022)
- Manuel Enrique Machado-Duque , Jorge Enrique Machado-Alba, Andrés Gaviria-Mendoza, Luis Fernando Valladales-Restrepo , Ilsa Yadira Parrado-Fajardo , Mauren Ospina-Castellanos , Luisa Fernanda Rojas-Chavarro , John Alexander López-Rincón , Identification of medication errors through a monitoring and minimization program in outpatients in Colombia, 2018-2019 , Biomedica: Vol. 41 No. 1 (2021)
- Jorge Enrique Machado-Alba, Manuel José Londoño-Builes, Luis Felipe Echeverri-Cataño, Sergio Andrés Ochoa-Orozco, Adverse drug reactions in Colombian patients, 2007-2013: Analysis of population databases , Biomedica: Vol. 36 No. 1 (2016)
- Jaime E. Bernal, Martha Lucía Tamayo , Ignacio Briceño , Escilda Benavides , Newborn screening in Colombia: The experience of a private program in Bogotá , Biomedica: Vol. 44 No. 1 (2024)
- Raúl Murillo, Ricardo Cendales, Carolina Wiesner, Marion Piñeros, Sandra Tovar, Effectiveness of cytology-based cervical cancer screening in the Colombian health system , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
- Sandra Lorena Girón, Julio César Mateus, Fabián Méndez, Impact of an open waste disposal site on the occurrence of respiratory symptoms and on health care costs of children , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
- José Joaquín Carvajal, Ligia Inés Moncada, Mauricio Humberto Rodríguez, Ligia del Pilar Pérez, Víctor Alberto Olano, Characterization of Aedes albopictus (Skuse, 1894) (Diptera:Culicidae) larval habitats near the Amazon River in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
- Andrés Páez, Gloria Rey, Carlos Agudelo, Alvaro Dulce, Edgar Parra, Hernando Díaz-Granados, Damaris Heredia, Luis Polo, Outbreak of urban rabies transmitted by dogs in Santa Marta, northern Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
- Patricia Escobar, Katherine Paola Luna, Indira Paola Hernández, César Mauricio Rueda, María Magdalena Zorro, Simon L. Croft, In vitro susceptibility of Trypanosoma cruzi strains from Santander, Colombia, to hexadecylphosphocholine (miltefosine), nifurtimox and benznidazole , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
- Mauricio Beltrán, María Cristina Navas, María Patricia Arbeláez, Jorge Donado, Sergio Jaramillo, Fernando De la Hoz, Cecilia Estrada, Lucía del Pilar Cortés, Amalia de Maldonado, Gloria Rey, Seroprevalence of hepatitis B virus and human immunodeficiency virus infection in a population of multiply-transfused patients in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 2 (2009)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























