X-linked epileptic syndrome by protocadherin 19 mutation associated with leukoencephalopathy and posterior reversible tractopathy
Abstract
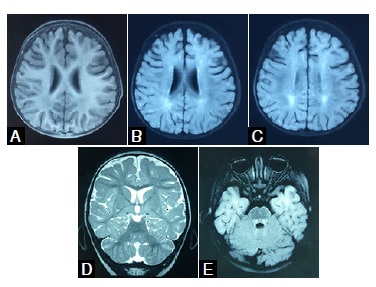
Epilepsy and mental retardation produced by mutations in gene PCDH19 (protocadherin 19) is an X-linked syndrome restricted to females. It starts with global and speech developmental delay and epilepsy; intellectual disability may continue in adults. At least in 20% of cases, there are no seizures or intellectual retardation. We report the case of a girl with epilepsy, developmental delay, and autistic conversion associated with posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy and tractopathy produced by PCDH19 mutation (c.142G>T/ p.Glu48X).
Downloads
References
Hirabayashi T, Yagi T. Protocadherins in neurological diseases. Adv Neurobiol. 2014;8:293-314.
Angst BD, Marcozzi C MA. The cadherin superfamily: Diversity in form and function. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:629-41.
Biswas S, Emond MR, Jontes JD. Protocadherin-19 and N-cadherin interact to control cell movements during anterior neurulation. J Cell Biol. 2010;191:1029-41. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201007008
Dibbens LM, Tarpey PS, Hynes K, Bayly MA, Scheffer IE, Smith R, et al. X-linked protocadherin 19 mutations cause female-limited epilepsy and cognitive impairment. Nat Genet. 2008;40:776-81. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.149
Liu Q, Sunil Bhattarai, Wang N, Sochacka-Marlowe A. Differential expression of protocadherin-19, protocadherin-17 and cadherin-6 in adult zebrafish brain. J Comp Neurol. 2016;8:583-92. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne. 23746
Emond MR, Biswas S, Jontes JD. Protocadherin-19 is essential for early steps in brain morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 2009;334:72-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.07.008
Cooper SR, Jontes JD, Sotomayor M. Structural determinants of adhesion by protocadherin-19 and implications for its role in epilepsy. Elife. 2016;5:1-22. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18529
Depienne C, LeGuern E. PCDH19-related infantile epileptic encephalopathy: An unusual X-linked inheritance disorder. Hum Mutat. 2012;33:627-34. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.22029
Fejerman N. Etiologías genéticas asociadas con epilepsias graves del lactante. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2012;110:421-9. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0325-00752012000500010
van Harssel JJ, Weckhuysen S, van Kempen MJ, Hardies K, Verbeek NE, De Kovel CG, et al. Clinical and genetic aspects of PCDH19-related epilepsy syndromes and the possible role of PCDH19 mutations in males with autism spectrum disorders. Neurogenetics. 2013;14:23-34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-013-0353-1
Kwong AK, Fung CW, Chan SY, Wong VC. Identification of SCN1A and PCDH19 mutations in Chinese children with Dravet syndrome. PLoS One. 2012;7:e41802. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041802
Baulac S, Gourfinkel-An I, Nabbout R, Huberfeld G, Serratosa J, Leguern E, et al. Fever, genes, and epilepsy. Lancet Neurol. 2004;3:421-39. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(04)00808-7
Specchio N, Fusco L, Vigevano F. Acute-onset epilepsy triggered by fever mimicking FIRES (febrile infectionrelated epilepsy syndrome): The role of protocadherin 19 (PCDH19) gene mutation. Epilepsia. 2011;52:172-5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03193.x
Sharma S, Prasad AN. Genetic testing of epileptic encephalopathies of infancy: An approach. Can J Neurol Sci. 2013;40:10-6. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0317167100012889
Liu A, Xu X, Yang X, Jiang Y, Yang Z, Liu X, et al. The clinical spectrum of female epilepsy patients with PCDH19 mutations in a Chinese population. Clin Genet. 2017;91:54-62. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.12846
Marini C, Mei D, Parmeggiani L, Norci V, Calado E, Ferrari A, et al. Protocadherin 19 mutations in girls with infantile-onset epilepsy. Neurology. 2010;75:646-53. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181ed9e67
Marini C, Darra F, Specchio N, Mei D, Terracciano A, Parmeggiani L, et al. Focal seizures with affective symptoms are a major feature of PCDH19 gene-related
epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2012;53:2111-9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03649.x
Antelmi E, Mastrangelo M, Bisulli F, Spaccini L, Stipa C, Mostacci B, et al. Semiological study of ictal affective behaviour in epilepsy and mental retardation limited to females (EFMR). Epileptic Disord. 2012;14:204-309. https://doi.org/10.1684/epd.2012.0526
Higurashi N, Nakamura M, Sugai M, Ohfu M, Sakauchi M, Sugawara Y, et al. PCDH19-related female-limited epilepsy: Further details regarding early clinical features and therapeutic efficacy. Epilepsy Res. 2013;106:191-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2013.04.005
Gagliardi M, Annesi G, Sesta M, Tarantino P, Conti P, Labate A, et al. PCDH19 mutations in female patients from Southern Italy. Seizure. 2015;24:118-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2014.08.010
Some similar items:
- Yolanda Cifuentes, Isabel De la Hoz, Martha Bermúdez, Clara Arteaga, Neonatal onset of organic acidemia (propionic) diagnosed by tandem mass spectrometry , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 1 (2008)
- Sara Emilia Giraldo, Javier Rincón, Pilar Puebla, Mariel Marder, Cristina Wasowski, Nadezdha Vergel, Mario Francisco Guerrero, Isovaleramide, an anticonvulsant molecule isolated from Valeriana pavonii , Biomedica: Vol. 30 No. 2 (2010)
- Diego Alberto Herrera, Sergio Alberto Vargas, Claudia Montoya, Neuroimaging findings in cerebroretinal microangiopathy with calcifications and cysts , Biomedica: Vol. 34 No. 2 (2014)
- Nancy Gélvez, Johana Acosta, Greizy López, Derly Castro, Juan Carlos Prieto, Martha Bermúdez, Marta L. Tamayo, Phenotypic and molecular characterization of a Colombian family with phenylketonuria , Biomedica: Vol. 36 No. 3 (2016)
- Luz Yaqueline Ladino, Johanna Galvis, Diana Yasnó, Adriana Ramírez, Orietta Ivonne Beltrán, A pathogenic homozygous variant of the BBS10 gene in a patient with Bardet Biedl syndrome , Biomedica: Vol. 38 No. 3 (2018)
- Blair Ortiz, Carolina Hernández, Norma Carolina Barajas, A radiological and clinical description of metastatic angiosarcoma simulating a hydatid cyst , Biomedica: Vol. 39 No. 3 (2019)
- José Bustos, Ledmar Vargas , Ricardo Quintero , Acute intermittent porphyria: A case report , Biomedica: Vol. 40 No. 1 (2020)
- Yully Andrea Rangel, Eugenia Espinosa, Early-onset generalized dystonia caused by a new mutation in the KMT2B gene: Case report , Biomedica: Vol. 42 No. 3 (2022)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























