Alpha sinuclein expression in blood and its relationship with chronic constipation in a population from Bogotá, D.C., with problems of alcohol consumption
Abstract
Introduction: Excessive alcohol consumption results in neuroadaptation, neurodegeneration, and differential expression of numerous genes.
Objective: To determine the relationship between the expression of the alpha synuclein gene (SNCA) in blood, single nucleotide variant (SNV) in its promoter region, and chronic constipation in people with problems of alcohol consumption.
Materials and methods: The sample consisted of 35 controls and 27 cases selected according to the score obtained with the AUDIT tool. For the diagnosis of constipation, the Rome IV criteria were applied. Nucleic acid extraction was performed from peripheral blood and the expression of the gene was evaluated by qPCR, protein quantification by ELISA, and the presence of SNV in the promoter region of the gene by Sanger sequencing.
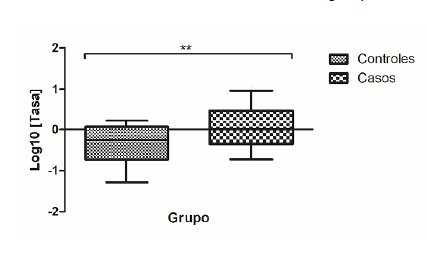
Results: We observed a relative gene overexpression of SNCA mRNA in the case group, which was not related to the diagnosis of chronic constipation. There was 4.8 times greater risk of presenting constipation in the group of cases. Besides, nine single nucleotide variants were found in a segment of the promoter region of the gene rich in CpG regulatory sequences with similar frequency between the groups while a variant was identified in position -2171, which is not reported in GenBank for variants and whose genotype A/T was associated with increased expression of SNCA mRNA.
Conclusion: We evidenced an overexpression of alpha synuclein mRNA in people with problems of alcohol consumption that was not related to the diagnosis of chronic constipation.
Downloads
References
Organización Mundial de la Salud. Estrategia mundial para reducir el uso nocivo del alcohol. Ginebra: Organización Mundial de la Salud; 2010. p. 1-46. Fecha de consulta: 5 de enero de 2018. Disponible en: https://www.who.int/substance_abuse/activities/msbalcstrategyes.pdf
Observatorio de Drogas de Colombia. Estudio de consumo de sustancias psicoactivas en Colombia, 2013. p. 1-182. Fecha de consulta: 5 de enero de 2018. Disponible en: https://www.unodc.org/documents/colombia/2014/Julio/Estudio_de_Consumo_UNODC.pdf
Serecigni J. Neurobiología del alcoholismo. Psicología desde el Caribe. 2013;30:21-35.
Janeczek P, Lewohl J. The role of a-synuclein in the pathophysiology of alcoholism. Neurochem Int. 2013;63:154-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2013.06.007
Swant J, Goodwin J, North A, Ali A, Gamble J, Chirwa S, et al. α-synuclein stimulates a dopamine transporter-dependent chloride current and modulates the activity of the transporter. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:43933-43. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.241232
Liang T, Carr LG. Regulation of alpha-synuclein expression in alcohol-preferring and -non preferring rats. J Neurochem. 2006;99:470-82. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04111.x
Butler B, Saha K, Rana T, Becker JP, Sambo D, Davari P, et al. Dopamine transporter activity is modulated by a-synuclein. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:29542-54. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.691592
Sui Y, Bullock K, Erickson M, Zhang J, Banks W. Alpha synuclein is transported into and out of the brain by the blood-brain barrier. Peptides. 2014;62:197-202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2014.09.018
Lööv C, Scherzer CR, Hyman BT, Breakefield XO, Ingelsson M. α-synuclein in extracellular vesicles: Functional implications and diagnostic opportunities. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016;36:437-48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0317-0
Simonsen A, Kuiperij B, El-Agnaf A, Omar M, Engelborghs S, Herukka S-K, et al. The utility of α-synuclein as biofluid marker in neurodegenerative diseases: A systematic review of the literature. Biomark Med. 2016;10:19-34. https://doi.org/10.2217/BMM.14.105
Omar M, Agnaf E, Salem S, Paleologou K, Cooper L, Fullwood N, et al. Synuclein implicated in Parkinson’s disease is present in extracellular biological fluids including human plasma. FASEB J. 2003;17:1945-7. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.03-0098fje
Henchcliffe C. Blood and cerebrospinal fluid markers in Parkinson’s disease: Current biomarker findings. Curr Biomark Find. 2015;5:1-11. https://doi.org/10.2147/CBF.S50424
Nakai M, Fujita M, Waragai M, Sugama S, Wei J, Akatsu H, et al. Expression of a-synuclein, a presynaptic protein implicated in Parkinson’s disease, in erythropoietic lineage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;358:104-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.04.108
Abd-Elhadi S, Honig A, Simhi-Haham D, Schechter M, Linetsky E, Ben-Hur T, et al. Total and proteinase K-resistant α-synuclein levels in erythrocytes, determined by their ability to bind phospholipids, associate with Parkinson’s disease. Sci Rep. 2015;5:1-12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11120
Kang W, Chen W, Yang Q, Zhang L, Zhang L, Wang X, et al. Salivary total α-synuclein, oligomeric α-synuclein and SNCA variants in Parkinson’s disease patients. Sci Rep. 2016;6:1-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28143
Wang X, Yu S, Li F, Feng T. Detection of α-synuclein oligomers in red blood cells as a potential biomarker of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett. 2015;599:115-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2015.05.030
B̈nsch D, Reulbach U, Bayerlein K, Hillemacher T, Kornhuber J, Bleich S. Elevated alpha synuclein mRNA levels are associated with craving in patients with alcoholism. Biol sychiatry. 2004;56:984-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.09.016
Ziolkowska B, Gieryk A, Wawrzczak-Bargiela A, Krowka T, Kaminska D, Korkosz A, et al. α-Synuclein expression in the brain and blood during abstinence from chronic alcohol drinking in mice. Neuropharmacology. 2008;54:1239-46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.04.001
Walker S, Grant K. Peripheral blood α-synuclein mRNA levels are elevated in cynomolgus monkeys that chronically self-administer ethanol. Alcohol. 2006;38:1-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alcohol.2006.03.008
Bönsch D, Lederer T, Reulbach U, Hothorn T, Kornhuber J, Bleich S. Joint analysis of the NACP-REP1 marker within the alpha synuclein gene concludes association with alcohol dependence. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14:967-71. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddi090
Foroud T, Wetherill LF, Liang T, Dick DM, Hesselbrock V, Kramer J, et al. Association of alcohol craving with a-synuclein (SNCA). Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007;31:537-45. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00337.x
Braak H, Rüb U, Gai WP, Del Tredici K. Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: Possible routes by which vulnerable neuronal types may be subject to neuroinvasion by an unknown pathogen. J Neural Transm. 2003;110:517-36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-002-0808-2
Shannon KM, Keshavarzian A, Dodiya HB, Jakate S, Kordower JH. Is alpha-synuclein in the colon a biomarker for premotor Parkinson’s disease? Evidence from 3 cases. Mov Disord. 2012;27:716-9. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25020
Chesselet MF, Richter F, Zhu C, Magen I, Watson MB, Subramaniam SR. A progressive mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: The Thy1-aSyn (“Line 61”) mice. Neurotherapeutics. 2012;9:297-314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-012-0104-2
Rockenstein E, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Song D, Shults CW, Lang I, et al. Differential neuropathological alterations in transgenic mice expressing a-synuclein from the plateletderived growth factor and Thy-1 promoters. J Neurosci Res. 2002;68:568-78. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.10231
Verbaan D, Marinus J, Visser M, Van Rooden SM, Stiggelbout AM, van Hilten JJ. Patient reported autonomic symptoms in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2007;69:333-41. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000266593.50534.e8
Wang L, Magen I, Yuan PQ, Subramaniam SR, Richter F, Chesselet MF, et al. Mice verexpressing wild-type human alpha-synuclein display alterations in colonic myenteric ganglia and defecation. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012;24:1-12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2982.2012.01974.x
Sampson TR, Debelius JW, Thron T, Janssen S, Shastri GG, Ilhan ZE, et al. Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell. 2016;167:1469-80.e12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.018
Engen P, Green S, Voigt R, Forsyth C, Keshavarzian A. The gastrointestinal microbiome: Alcohol effects on the composition of intestinal microbiota. Alcohol Res. 2015;37:223-36. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.4342.9285
Yan A, Fouts D, Brandl J, Starkel P, Torralba M, Schott E, et al. Enteric dysbiosis associated with a mouse model of alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 2011;53:96-105. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24018
Domingo J. The new Rome criteria (IV) of functional digestive disorders in clinical practice. Med Clin (Barc). 2017;148:464-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medcli.2016.12.020
Babor T, Higgins J, Saunders J, Monteiro M. Cuestionario de identificación de los transtornos debidos al consumo de alcohol. Ginebra: Organización Mundial de la Salud; 2001. p. 1-40.
Campo A, Villamil M, Herazo E. Confiabilidad y dimensionalidad del AUDIT en estudiantes de medicina. Psicología desde el Caribe. 2013;30:21-35.
Ospina J, Manrique F, Ariza N. Confiabilidad y dimensionalidad del cuestionario para identificación de trastornos debidos al consumo de alcohol (AUDIT) en estudiantes universitarios de Tunja (Colombia). Salud Uninorte. 2012;28:276-82.
Anderson P, Gual L, Colón J. Alcohol y atención primaria de la salud alcohol y atención primaria de la salud. Washington, D.C.: Organización Panamericana de la Salud; 2008.
Bönsch D, Greifenberg V, Bayerlein K, Biermann T, Reulbach U, Hillemacher T, et al. α-synuclein protein levels are increased in alcoholic patients and are linked to craving. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005;29:763-5. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ALC.0000164360.43907.24
Sheth U, Parker R. Decapping and decay of messenger RNA occur in cytoplasmic processing bodies. Science. 2003;300:805-8. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1082320
Parker R, Sheth U. P bodies and the control of mRNA translation and degradation. Mol Cell. 2007;25:635-46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2007.02.011
Doxakis E. Post-transcriptional regulation of a-synuclein expression by mir-7 and mir-153. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:12726-34. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.086827
McMillan K, Murray T, Bengoa N, Cordero O, Cooper J, Buckley A, et al. Loss of microRNA-7 regulation leads to α-synuclein accumulation and dopaminergic neuronal loss in vivo. Mol Ther. 2017;25:2404-14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.08.017
Wang L, Fleming S, Chesselet M, Taché Y. Abnormal colonic motility in mice overexpressing human wild-type α-synuclein. Neuroreport. 2008;19:873-6. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0b013e3282ffda5e
Kuo Y, Li Z, Jiao Y, Gaborit N, Pani A, Morrison B, et al. Extensive enteric nervous system abnormalities in mice transgenic for artificial chromosomes containing Parkinson disease associated alpha-synuclein gene mutations precede central nervous system changes. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19:1633-50. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0b013e3282ffda5e
Sharma A, Kurek J, Morgan JC, Wakade C, Rao SS. Constipation in Parkinson’s disease:
A nuisance or nuanced answer to the pathophysiological puzzle? Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2018;20:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-018-0609-x
Abbott R, Petrovitch H, White L, Masaki K, Tanner C, Curb J, et al. Frequency of bowel movements and the future risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neurology. 2001;57:456-62. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.58.5.838-a
Rodríguez O, Torres L, Meza K, López R, Ruiz H, Cosentino C. Estreñimiento como factor asociado a mayor severidad en pacientes con enfermedad de Parkinson del Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Neurológicas del Perú. Diagnóstico. 2019;57:180-3. https://doi.org/10.33734/diagnostico.v57i4.169
Leclercq S, De Timary P, Delzenne N, Stärkel P. The link between inflammation, bugs, the intestine and the brain in alcohol dependence. Transl Psychiatry. 2017;7:e1048. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2017.15
Some similar items:
- Ismael Reyes, Raj Tiwari, Jan Geliebter, Niradiz Reyes, DNA microarray analysis reveals metastasis-associated genes in rat prostate cancer cell lines , Biomedica: Vol. 27 No. 2 (2007)
- Vanihamín Domínguez, Itzen Aguiñiga, Leticia Moreno, Beatriz Torres, Edelmiro Santiago-Osorio, Sodium caseinate increases the number of B lymphocytes in mouse , Biomedica: Vol. 37 No. 4 (2017)
- Luis A. Franco, Germán E. Matiz, Jairo Calle, Roberto Pinzón, Luis F. Ospina, Antiinflammatory activity of extracts and fractions obtained from Physalis peruviana L. calyces , Biomedica: Vol. 27 No. 1 (2007)
- Ricardo A. Cifuentes, Emiliano Barreto, Supervised selection of single nucleotide polymorphisms in chronic fatigue syndrome , Biomedica: Vol. 31 No. 4 (2011)
- Luis Ángel Villar, Rosa Margarita Gélvez, Jairo Antonio Rodríguez, Doris Salgado, Beatriz Parra, Lyda Osorio, Irene Bosch, Biomarkers for the prognosis of severe dengue , Biomedica: Vol. 33 (2013): Suplemento 1, Fiebres hemorrágicas
- Tania M. Cortázar, John Walker, Genetic manipulation and the study of the protozoan parasite Leishmania. , Biomedica: Vol. 24 No. 4 (2004)
- Fabián Jaimes, Gisela de la Rosa, Anticoagulation and sepsis: the opportunity for a new use of heparin?. , Biomedica: Vol. 26 No. 1 (2006)
- Jesús Orlando Yepes, María Luz Gunturiz, Luis Felipe Henao, María Cristina Navas, Norman Balcázar, Luis Alberto Gómez, Differential display of messenger RNA and identification of selenocysteine lyase gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cells transiently expressing hepatitis C virus core protein. , Biomedica: Vol. 26 No. 2 (2006)
- Luis Alberto Gómez, María Luz Gunturiz, Identification and differential expression of the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor in heart and isolated cardiomyocytes from Guinea pigs: Possible role in hypertrophy and viability , Biomedica: Vol. 34 No. 3 (2014)
- Henry A. Vargas, Martín Rondón, Rodolfo Dennis, Pharmacological treatment and impairment of pulmonary function in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study , Biomedica: Vol. 36 No. 2 (2016)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























