Evaluation of three qPCR for the detection of pathogenic leptospires in domestic animals in Nicaragua
Abstract
Introduction: Molecular biology diagnostic methods such as real-time PCR should be used in Nicaragua to improve the diagnosis of leptospirosis in humans and animals.
Objective: To evaluate three qPCR methods for pathogenic Leptospira detection in domestic animals.
Materials and methods: Real-time PCR primers were designed for the amplification of specific regions from the Lip 32 gene of Leptospira in SYBER Green (SYBER Green-A) and TaqMan, as well in SYBER Green-B as previously published. The sequences of 12 strains obtained from the database of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) were aligned to select probes and primers. The analytical sensitivity was determined by calculating the detectable genomic equivalent while 18 pathogenic references strains and 28 negative controls were used to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of each one of the three sets in 129 urine samples of domestic animals.
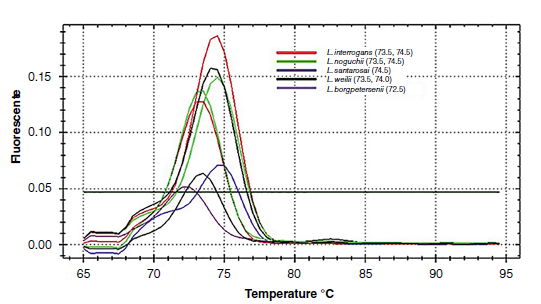
Results: The detection limit of four genomic equivalents per reaction was obtained from SYBR Green-A. The specificities were 94.4% (95% CI: 81.1-100.0) for TaqMan, 77.8% (95% CI: 55.8-99.8) for SYBR Green-A, while for SYBR Green-B it was 61.1% (95% CI: 35.8-86.4). In the three tests, we obtained a specificity of 100% (95% CI: 98.2-100.0). In the field samples, 26.4% were positive with SYBR Green-A and 6.1% with SYBR Green-B.
Conclusion: SYBR Green-A presented the lowest detection limit while the three techniques under evaluation showed high specificity while TaqMan was the most sensitive.
Downloads
References
Boonsilp S, Thaipadungpanit J, Amornchai P, Wuthiekanun V, Chierakul W, Limmathurotsakul D, et al. Molecular detection and speciation of pathogenic Leptospira spp. in blood from patients with culture-negative leptospirosis. BMC Infect Dis. 2011;11:338. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-11-338
Ko AI, Goarant C, Picardeau M. Leptospira: The dawn of the molecular genetics era for an emerging zoonotic pathogen. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009;7:736-47. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2208
Picardeau M, Bertherat E, Jancloes M, Skouloudis AN, Durski K, Hartskeerl RA. Rapid tests for diagnosis of leptospirosis: Current tools and emerging technologies. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014;78:1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2013.09.012
Ashford DA, Kaiser RM, Spiegel RA, Perkins BA, Weyant RS, Bragg SL, et al. Asymptomatic infection and risk factors for leptospirosis in Nicaragua. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000;63:249-54. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.2000.63.249
Agampodi SB, Matthias MA, Moreno AC, Vinetz JM. Utility of quantitative polymerase chain reaction in leptospirosis diagnosis: Association of level of leptospiremia and clinical manifestations in Sri Lanka. Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am. 2012;54:1249-55. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cis035
Levett PN, Morey RE, Galloway RL, Turner DE, Steigerwalt AG, Mayer LW. Detection of pathogenic leptospires by real-time quantitative PCR. J Med Microbiol. 2005;54:45-9. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.45860-0
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:2725-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
IDT. PrimerQuest Tool. Fecha de consulta: 29 de junio de 2018. Disponible en: http://www.idtdna.com/Primerquest/Home/Index
Nucleotide BLAST. Search nucleotide databases using a nucleotide query. Fecha de consulta: 29 de junio de 2018. Disponible en: http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi
Nascimento ALTO, Ko AI, Martins EAL, Monteiro-Vitorello CB, Ho PL, Haake DA, et al. Comparative genomics of two Leptospira interrogans serovars reveals novel insights into physiology and pathogenesis. J Bacteriol. 2004;186:2164-72. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.186.7.2164-2172.2004
Flores BJ, Pérez-Sánchez T, Fuertes H, Sheleby-Elías J, Múzquiz JL, Jirón W, et al. A crosssectional epidemiological study of domestic animals related to human leptospirosis cases in Nicaragua. Acta Trop. 2017;170:79-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2017.02.031
Xunta de Galicia. Dirección Xeral de Innovación e Xestión da Saúde Pública/Organización Panamericana de la Salud. Epidat 3.1. Fecha de consulta: 29 de junio de 2018. Disponible en: https://www.sergas.es/Saude-publica/EPIDAT?idioma=es
Cao H, Shockey JM. Comparison of TaqMan and SYBR Green qPCR methods for quantitative gene expression in tung tree tissues. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60:12296-303. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf304690e
Merien F, Portnoi D, Bourhy P, Charavay F, Berlioz-Arthaud A, Baranton G. A rapid and quantitative method for the detection of Leptospira species in human leptospirosis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005;249:139-47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2005.06.011
Haake DA, Chao G, Zuerner RL, Barnett JK, Barnett D, Mazel M, et al. The leptospiral major outer membrane protein LipL32 is a lipoprotein expressed during mammalian infection. Infect Immun. 2000;68:2276-85. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.68.4.2276-2285.2000
Pionzio AM, McCord BR. The effect of internal control sequence and length on the response to PCR inhibition in real-time PCR quantitation. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2014;9:55-60. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.fsigen.2013.10.010
Opel KL, Chung D, McCord BR. A study of PCR inhibition mechanisms using real time PCR. J Forensic Sci. 2010;55:25-33. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-4029.2009.01245.x
Hamond C, Martins G, Loureiro AP, Pestana C, Lawson-Ferreira R, Medeiros MA, et al. Urinary PCR as an increasingly useful tool for an accurate diagnosis of leptospirosis in livestock. Vet Res Commun. 2014;38:81-5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-013-9582-x
Pérez J, Goarant C. Rapid Leptospira identification by direct sequencing of the diagnostic PCR products in New Caledonia. BMC Microbiol. 2010;10:325. ttps://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-10-325
Some similar items:
- Piedad Agudelo-Flórez, Marcos Restrepo, Natalí Moreno, Diagnosis of leptospirosis by dark-field microscopy of blood samples and culture , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 1 (2008)
- Jorge Cedano, Sarita Rodríguez, Winy Kujundzic, Juan Sebastián Arana, Robinson Pacheco, Fernando Rosso, Clinical characterization of patients with severe leptospirosis in a tertiary hospital in Cali, Colombia, 2010-2016 , Biomedica: Vol. 39 No. Sp. 1 (2019): Suplemento 1, Microbiología médica, mayo
- Mercedes Salcedo-Cifuentes, Jesús Cabrera, Yesid Cuesta-Astroz, Edwin Carrascal, Yoshito Eizuru, Martha C. Domínguez, Adalberto Sánchez, Felipe García-Vallejo, Clonal expansion and genomic characterization of the human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I during the integration process in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 2 (2009)
- Martine Bonnaure-Mallet, Paula Juliana Pérez-Chaparro, Patrice Gracieux, Vincent Meuric, Zohreh Tamanai-Shacoori, Jaime Eduardo Castellanos, Distribution of Porphyromonas gingivalis fimA genotypes in isolates from subgingival plaque and blood sample during bacteremia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 2 (2009)
- Diego Fernando Zea, Martín Prager, Roger Adrian Figueroa, María Consuelo Miranda, Mucosal complication of cutaneous leishmaniasis , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 1 (2009)
- Ana Margarita Montalvo, Lianet Monzote, Jorge Fraga, Ivón Montano, Carlos Muskus, Marcel Marín, Simonne De Donck, Iván Darío Vélez, Jean Claude Dujardin, PCR-RFLP and RAPD for typing neotropical Leishmania , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 4 (2008)
- Concepción Judith Puerta, Johana María Guevara, Paula Ximena Pavía, Marleny Montilla, Rubén Santiago Nicholls, Edgar Parra, Yuli Katherine Barrera, Evaluation of TcH2AF-R and S35-S36 primers in PCR tests for the detection of Trypanosoma cruzi in mouse cardiac tissue , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 4 (2008)
- Marcel Marín, Yudy Alexandra Aguilar, José Robinson Ramírez, Omar Triana, Carlos Enrique Muskus, Molecular and immunological analyses suggest the absence of hydrophilic surface proteins in Leishmania (Viannia) panamensis , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 3 (2008)
- Astrid Elena Montoya, José Menco, Natalia Osorio, Maria Alejandra Zuluaga, Juliana Duque, Giovanny Torres, Marcos Restrepo, Concordance between thick blood smear, immunochromatography and polymerase chain reaction for malaria diagnosis , Biomedica: Vol. 28 No. 2 (2008)
- Concepción Judith Puerta, Paula Ximena Pavia, Marleny Montilla, Carolina Flórez, Giomar Herrera, Juan Manuel Ospina, Fred Manrique, Rubén Santiago Nicholls, The first case of congenital Chagas’ disease analyzed by AP-PCR in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 4 (2009)
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























