Cost-effectiveness of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in Colombia
Abstract
Introduction: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy is expensive. There is evidence in the literature that it can be a cost-effective intervention in developed countries; however, in countries with low gross domestic product per capita, such as Colombia, there are still some doubts.
Objective: To determine the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in Colombia.
Materials and methods: Cost-effectiveness analysis in healthcare in relation to adult patients diagnosed with acute respiratory distress syndrome with mechanical ventilation with low volumes compared to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. The direct medical costs and the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio were determined at 6 months.
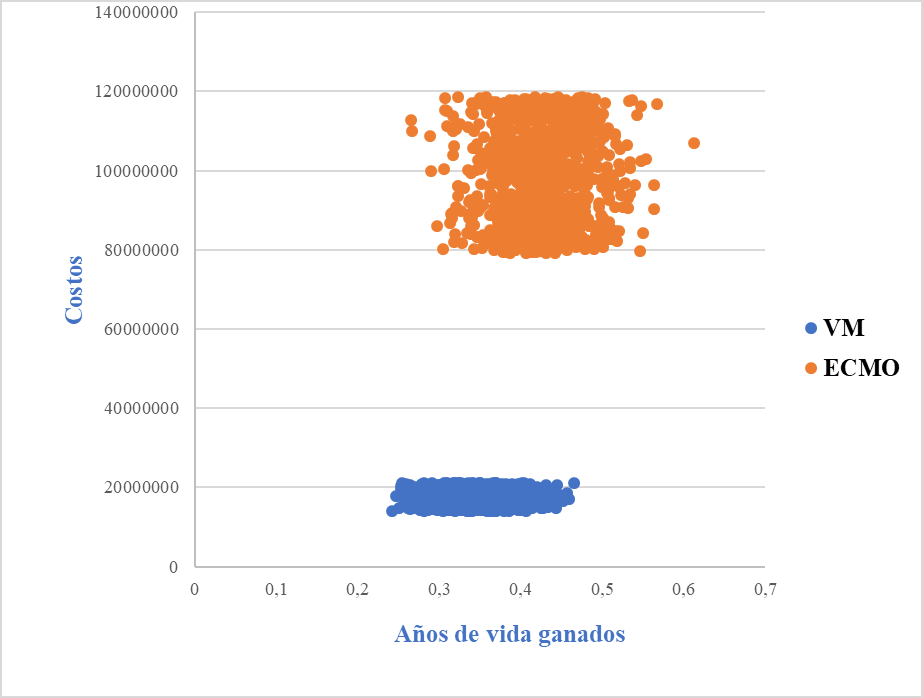
Results: The expected cost per patient on protective mechanical ventilation was COP$17,609,909. The cost of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy support in surviving patients was COP$ 98,784,116. The average cost-effectiveness ratio of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation was COP$ 141,662,435 for each life saved (USD$ 41,276).
Conclusions: Support with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy had an average cost of COP$ 141,662,435 for each life saved equivalent to USD$ 41,276. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio COP$ was 608,783,750 (USD$ 177,384); almost ten times higher than the decision rule of three gross domestic product per capita (COP$ 59,710,479).
Downloads
References
Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E, Weaver J, Martin DP, Neff M, et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1685-93. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa050333
Asbaugh D, Bigelow B, Petty T, Levine B. Acute respiratory distress in adults. Lancet. 1967;290:319-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90168-7
Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, Fan E, Brochard L, Esteban A, et al. Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries. JAMA. 2016;315:788-800. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.0291
Varón-Vega FA, Uribe Hernández AM, Palacios Rojas JO. Epidemiología, diferencias clínicas y desenlaces de pacientes con SDRA en unidades de cuidado intensivo de Colombia. Acta Colombiana de Cuidado Intensivo. 2019;19:74-80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acci.2019.01.005
Moss M, Huang DT, Brower RG, Ferguson ND, Ginde AA, Gong MN, et al. Early neuromuscular blockade in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1997-2008. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1901686
Lee JM, Bae W, Lee YJ, Cho YJ. The efficacy and safety of prone positional ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome: Updated study-level meta-analysis of 11 randomized controlled trials. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:1252-62. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000000122
Combes A, Hajage D, Capellier G, Demoule A, Lavoué S, Guervilly C, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1965-75. https://doi.org/10.1177/1054773816677808
Barrett KA, Hawkins N, Fan E. Economic evaluation of venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2019;47:186-93. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000003465
Combes A, Peek GJ, Hajage D, Hardy P, Abrams D, Schmidt M, et al. ECMO for severe ARDS: Systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46:2048-57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-020-06248-3
Fan E, Brodie D, Slutsky AS. Acute respiratory distress syndrome advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA. 2018;319:698-710. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.21907
Salazar LA, Uribe JD, Poveda Henao CM, Santacruz CM, Giraldo Bejarano E, Bautista DF, et al. Consenso ECMO colombiano para paciente con falla respiratoria grave asociada a COVID-19. Acta Colombiana de Cuidado Intensivo. 2021;21:272-82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acci.2020.09.001
Peek GJ, Mugford M, Tiruvoipati R, Wilson A, Allen E, Thalanany MM, et al. Efficacy and economic assessment of conventional ventilatory support versus extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe adult respiratory failure (CESAR): A multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;374:1351-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61069-2
Hamel MB, Phillips RS, Davis RB, Teno J, Connors AF, Desbiens N, et al. Outcomes and cost-effectiveness of ventilator support and aggressive care for patients with acute respiratory failure due to pneumonia or acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Med. 2000;109:614-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9343(00)00591-x
Bice T, Carson SS. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: Cost (early and long-term). Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;40:137-44. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1685463
Moreno M, Mejía A, Castro H. Manual para la elaboración de evaluaciones económicas en salud. Bogotá, D.C.: Instituto de Evaluación Tecnológica en Salud; 2014. p. 10-32.
Drummond MF, Sculpher MJ, Claxton K, Stoddart GL, Torrance GW. O’Brien BJ. Methods for the economic evaluation of health care programmes. Fourth edition. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2015. p. 1-445.
Zampieri FG, Mendes PV, Ranzani OT, Taniguchi LU, Pontes Azevedo LC, Vieira Costa EL, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe respiratory failure in adult patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of current evidence. J Crit Care. 2013;28:998-1005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.07.04
Herridge M, Tansay C, Matté A, Tomlinson G, Díaz-Granados N, Cooper A, et al. Functional disability 5 years after acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1293-304. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1011802
Skinner EH, Denehy L, Warrillow S, Hawthorne G. Comparison of the measurement properties of the AQoL and SF-6D in critical illness. Crit care Resusc. 2013;15:205-12.
Ramanathan K, Shekar K, Ling RR, Barbaro RP, Wong SN, Tan CS, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2021;25:1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-021-03634-1
Some similar items:
- Sara Atehortúa, Juan Manuel Senior, Paula Castro, Mateo Ceballos, Clara Saldarriaga, Nelson Giraldo, Guillermo Mora, Cost-utility analysis of an implantable cardioverterdefibrillator for the treatment of patients with ischemic or non-ischemic New York Heart Association class II or III heart failure in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 39 No. 3 (2019)
- Ana Helena Perea, Diego Rosselli, Immediate versus delayed breast reconstruction in breast cancer patients in Colombia: A costutility analysis , Biomedica: Vol. 38 No. 3 (2018)
- Roosevelt Fajardo, José Ignacio Valenzuela, Sandra Catalina Olaya, Gustavo Quintero, Gabriel Carrasquilla, Carlos Eduardo Pinzón, Catalina López, Juan Camilo Ramírez, Cost-effectiveness of laparoscopic versus open cholecystectomy , Biomedica: Vol. 31 No. 4 (2011)
- Óscar Gamboa, Sandra Díaz, Liliana Chicaíza, Mario García, Cost-benefit analysis of anastrazol and tamoxifen in adjuvant treatment of hormone receptor-positive, post-menopausal breast cancer , Biomedica: Vol. 30 No. 1 (2010)
- Raúl Murillo, Ricardo Cendales, Carolina Wiesner, Marion Piñeros, Sandra Tovar, Effectiveness of cytology-based cervical cancer screening in the Colombian health system , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
- Sandra Lorena Girón, Julio César Mateus, Fabián Méndez, Impact of an open waste disposal site on the occurrence of respiratory symptoms and on health care costs of children , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
- Jaime E. Bernal, Martha Lucía Tamayo , Ignacio Briceño , Escilda Benavides , Newborn screening in Colombia: The experience of a private program in Bogotá , Biomedica: Vol. 44 No. 1 (2024)
- Andrés Páez, Gloria Rey, Carlos Agudelo, Alvaro Dulce, Edgar Parra, Hernando Díaz-Granados, Damaris Heredia, Luis Polo, Outbreak of urban rabies transmitted by dogs in Santa Marta, northern Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
- Patricia Escobar, Katherine Paola Luna, Indira Paola Hernández, César Mauricio Rueda, María Magdalena Zorro, Simon L. Croft, In vitro susceptibility of Trypanosoma cruzi strains from Santander, Colombia, to hexadecylphosphocholine (miltefosine), nifurtimox and benznidazole , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 3 (2009)
- Mauricio Beltrán, María Cristina Navas, María Patricia Arbeláez, Jorge Donado, Sergio Jaramillo, Fernando De la Hoz, Cecilia Estrada, Lucía del Pilar Cortés, Amalia de Maldonado, Gloria Rey, Seroprevalence of hepatitis B virus and human immunodeficiency virus infection in a population of multiply-transfused patients in Colombia , Biomedica: Vol. 29 No. 2 (2009)
Copyright (c) 2022 Biomedica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

























